Abstract
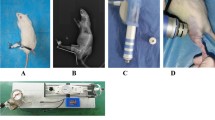
This study investigated the stimulative effect of extracorporeal shock wave therapy (ESWT) on the articular cartilage regeneration in the rabbit osteochondral defect model for the first time. An osteochondral defect, 3 mm in diameter and 3 mm in depth, was drilled in the patellar groove at the distal end of each femur in 24 mature New Zealand rabbits. The right patellar defects received 500 impulses of shock waves of \(1.2 \hbox { mJ}/\hbox {mm}^{2}\) (at 14 kV) at 1 week after surgery and were designated as the experimental samples; the left patellar defects served as control. At 4, 8, and 12 weeks after ESWT, cartilage repair was evaluated macroscopically and histologically using a semiquantitative grading scale. The total scores of the macroscopic evaluation at 4, 8, and 12 weeks in the experimental group were superior to those in the control group (statistical significance level \(P < 0.05\)). As to the total scores of the histologic evaluation, the experimental group showed a tendency toward a better recovery than the control group at 4 weeks (\(0.05 < P < 0.1\)). At 8 and 12 weeks the differences between the experimental and control groups became mild and had no significance on statistical analysis. These findings suggested that regeneration of articular cartilage defects might be promoted by ESWT, especially at the early stage. The easy and safe ESWT is potentially viable for clinical application.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Mainil-Varlet, P., Aigner, T., Brittberg, M., Bullough, P., Hollander, A., Hunziker, E., Kandel, R., Nehrer, S., Pritzker, K., Roberts, S., Stauffer, E.: Histological assessment of cartilage repair. J. Bone Jt. Surg. 85, 45–57 (2003)
Key, J.A.: Experimental arthritis: the changes in joints produced by creating defects in articular cartilage. J. Bone Jt. Surg. 13, 725–739 (1931)
Depalma, A., Mckeever, D., Sudin, D.: Process of repair of articular cartilage as demonstrated by histology and autoradiography with tritiated thymidine. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 48, 229–241 (1966)
Convey, F.R., Akeson, W.H., Keown, G.H.: The repair of large osteo-chondral defects: an experimental study in horses. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 82, 253–262 (1972)
Mankin, H.J.: The response of articular cartilage to mechanical injury. J. Bone Jt. Surg. 64A, 460–466 (1982)
Shapiro, F., Koide, S., Glimcher, M.J.: Cell origin and differentiation in the repair of full-thickness defects of articular cartilage. J. Bone Jt. Surg. Am. 75, 532–533 (1993)
Jackonson, D.W., Lalor, P.A., Aberman, H.M., Simonet, T.M.: Spontaneous repair of full-thickness defects of articular cartilage in a goat model. J. Bone Jt. Surg. Am. 83, 53–64 (2001)
Amiel, D., Coutts, R.D., Abel, M., Stewart, W., Harwood, F., Akeson, W.H.: Rib perichondrial grafts for the repair of full-thickness articular-cartilage defects. A morphological and biochemical study in rabbits. J. Bone Jt. Surg. Am. 67, 911–920 (1985)
Rothwell, A.G.: Synovium transplantation onto the cartilage denuded patellar groove of the sheep knee joint. Orthopedics 13, 433–442 (1990)
Wakitani, S., Goto, T., Pineda, S.J., Young, R., Mansour, J., Caplan, A., Goldberg, V.M.: Mesenchymal cell-based repair of large, full-thickness defects of articular cartilage. J. Bone Jt. Surg. Am. 76, 579–592 (1994)
Gillogly, S.D., Voight, M., Blackbum, T.: Treatment of articular cartilage defects of the knee with autologous chondrocyte implantation. J. Orthop. Sports Phys. Ther. 28(4), 241–251 (1998)
Peterson, L., Brittberg, M., Kiviranta, I., Akerlund, E.L., Lindahl, A.: Autologous chondrocyte transplantation. Biomechanics and long-term durability. Am. J. Sports Med. 30, 2–12 (2002)
Imhoff, A.B., Ottl, G.M., Burkart, A., Traub, S.: Autologous osteochondral transplantation on various joints. Orthopade 28(1), 33–44 (1999)
Kumagai, K., Saito, T., Koshino, T.: Articular cartilage repair of rabbit chondral defect: promoted by creation of periarticular bony defect. J. Orthop. Sci. 8, 700–706 (2003)
Steadman, J.R., Rodkey, W.G., Briggs, K.K., Rodrigo, J.J.: The microfracture technique in the management of complete cartilage defects in the knee joint. Orthopade 28, 26–32 (1999)
Hunziker, E.B.: Articular cartilage repair: basic science and clinical progress. A review of the current status and prospects. Osteoarthr. Cartil. 10, 432–463 (2002)
Siebert, W., Buch, M. (eds.): Extracorporeal Shock Waves in Orthopaedics. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg, New York (1997)
Wang, C.J., Wang, F.S., Yang, K.D., Weng, L.H., Hsu, C.C., Huang, C.S., Yang, L.C.: Shock wave therapy induces neovascularization at the tendon-bone junction, a study in rabbits. J. Orthop. Res. 21, 984–989 (2003)
Mcclure, S.R., Van Sickle, D., White, M.: Effects of extracorporeal shock wave therapy on bone. Vet. Surg. 33(1), 40–48 (2004)
Bischofberger, A.S., Ringer, S.K., Geyer, H., Imboden, I., Ueltschi, G., Lischer, C.: Histomorphologic evaluation of extracorporeal shock wave therapy of the fourth metatarsal bone and the origin of the suspensory ligament in horses without lameness. Am. J. Vet. Res. 67(4), 577–580 (2006)
Bulut, O., Eroglu, M., Ozturk, H., Tezeren, G., Bulut, S., Koptagel, E.J.: Extracorporeal shock wave treatment for defective nonunion of the radius: a rabbit model. J. Orthop. Surg. 14(2), 133–137 (2006)
Pineda, S., Pollack, A., Stevenson, S., Goldberg, V., Caplan, A.: A semiquantitative scale for histologic grading of articular cartilage repair. Acta Anat. 143, 335–340 (1992)
Wang, C.J., Huang, H.Y., Chen, H.H., Pai, C.H., Yang, K.D.: Effect of shock wave therapy on acute fractures of the tibia. A study in a dog model. Clin Orthop. 387, 112–118 (2001)
Wang, C.J., Huang, H.Y., Pai, C.H.: Shock wave therapy enhanced neovascularization at the tendon-bond junction: an experiment in dogs. J. Foot Ankle Surg. 41, 16–22 (2002)
Wang, F.S., Yang, K.D., Chen, R.F., Wang, C.J., Sheen-Chen, S.M.: Extracorporeal shock wave promotes bone marrow stromal cell growth and differentiation toward osteoprogenitors associated with TGF-\(\beta \) 1 induction. J. Bone Jt. Surg. 84B, 457–461 (2002)
Wang, C.J., Weng, L.H., Ko, J.Y., Sun, Y.C., Yang, Y.J., Wang, F.S.: Extracorporeal shockwave therapy shows chondroprotective effects in osteoarthritic Rat knee. Arch. Orthop. Trauma Surg. 131, 1153–1158 (2011)
Wang, C.J., Weng, L.H., Ko, J.Y., Wang, J.W., Chen, J.M., Sun, Y.C., Yang, Y.J.: Extracorporeal shockwave shows regression of osteoarthritis of the knee in rats. J. Surg. Res. 171, 601–608 (2011)
Wang, C.J., Hsu, S.L., Weng, L.H., Sun, Y.C., Wang, F.S.: Extracorporeal shockwave therapy shows a number of treatment related chondroprotective effect in osteoarthritis of the knee in rats. Musculoskelet. Disord. 14, 44–51 (2013)
Labek, G., Auersperg, V., Ziernhöld, M., Poulios, N., Böhler, N.: Influence of local anesthesia and energy level on the clinical outcome of extracorporeal shock wave-treatment of chronic plantar fasciitis. Z. Orthop. Ihre Grenzgeb. 143(2), 240–246 (2005). (German)
Gerdesmeyer, L., Weil, L.S.: Extracorporeal Shockwave Therapy: Clinical Results, Technologies, Basics, Chap. 25. Data Trace, Towson (2007)
Acknowledgments
The study was supported by a grant from Show-Chwan Memorial Research Fund RD96004. No benefits in any form have been received or will be received from a commercial party related to the subject of this article. Authors are appreciative of the support of Dr. Yu, C. D., Department of Orthopedics, Chang-Hwa Christian Hospital, Taiwan, in the animal experiments.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by H. Hosseini.
Each author certifies that his or her institution has approved the animal protocol for this investigation and that all investigations were conducted in conformity with ethical principles of research.
The extracorporeal shock wave therapy on rabbits was performed at Show-Chwan Memorial Hospital, Chang-Hwa, Taiwan and histologic examination of all resected specimens was performed at National Cheng-Kung University Hospital, Tainan, Taiwan.
Each author certifies that he or she has no commercial associations (e.g., consultancies, stock ownership, equity interest, patent/licensing arrangements, etc.) that might pose a conflict of interest in connection with the submitted article.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chu, CH., Yen, YS., Chen, PL. et al. Repair of articular cartilage in rabbit osteochondral defects promoted by extracorporeal shock wave therapy. Shock Waves 25, 205–214 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00193-014-0510-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00193-014-0510-y