Abstract
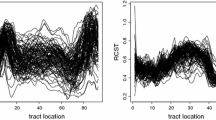
A general framework for smooth regression of a functional response on one or multiple functional predictors is proposed. Using the mixed model representation of penalized regression expands the scope of function-on-function regression to many realistic scenarios. In particular, the approach can accommodate a densely or sparsely sampled functional response as well as multiple functional predictors that are observed on the same or different domains than the functional response, on a dense or sparse grid, and with or without noise. It also allows for seamless integration of continuous or categorical covariates and provides approximate confidence intervals as a by-product of the mixed model inference. The proposed methods are accompanied by easy to use and robust software implemented in the pffr function of the R package refund. Methodological developments are general, but were inspired by and applied to a diffusion tensor imaging brain tractography dataset.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aguilera A, Ocaña F, Valderrama M (1999) Forecasting with unequally spaced data by a functional principal component approach. Test 8(1):233–253
Aneiros-Pérez G, Vieu P (2008) Nonparametric time series prediction: a semi-functional partial linear modeling. J Multivar Anal 99:834–857
Basser P, Mattiello J, LeBihan D (1994) MR diffusion tensor spectroscopy and imaging. Biophys J 66:259–267
Basser P, Pajevic S, Pierpaoli C, Duda J (2000) In vivo fiber tractography using DT-MRI data. Magn Reson Med 44:625–632
Bunea F, Ivanescu AE, Wegkamp MH (2011) Adaptive inference for the mean of a Gaussian process in functional data. J R Stat Soc Ser B 73(4):531–558
Claeskens G, Krivobokova T, Opsomer JD (2009) Asymptotic properties of penalized splines estimators. Biometrika 96(3):529–544
Crainiceanu C, Reiss P, Goldsmith J, Huang L, Huo L, Scheipl F, Swihart B, Greven S, Harezlak J, Kundu M, G, Zhao Y, McLean M, Xiao L (2014) Refund: regression with functional data, Website: http://CRAN.R-project.org/package=refund
Crainiceanu CM, Ruppert D (2004) Likelihood ratio tests in linear mixed models with one variance component. J R Stat Soc Ser B 66(1):165–185
Crainiceanu CM, Staicu A-M, Di C (2009) Generalized multilevel functional regression. J Am Stat Assoc 104(488):177–194
Eilers P, Marx B (1996) Flexible smoothing with B-splines and penalties. Stat Sci 11(2):89–121
Evangelou N, Konz D, Esiri MM, Smith S, Palace J, Matthews PM (2000) Regional axonal loss in the corpus callosum correlates with cerebral white matter lesion volume and distribution in multiple sclerosis. Brain 123(9):1845–1849
Fan Y, Foutz N, James GM, Jank W (2014) Functional response additive model estimation with online virtual stock markets. Ann Appl Stat, To appear
Ferraty F, Laksaci A, Tadj A, Vieu P (2011) Kernel regression with functional response. Electron J Stat 5:159–171
Ferraty F, Van Keilegom I, Vieu P (2012) Regression when both response and predictor are functions. J Multivar Anal 109:10–28
Ferraty F, Vieu P (2006) Nonparametric functional data analysis. Springer, New York
Ferraty F, Vieu P (2009) Additive prediction and boosting for functional data. Comput Stat Data Anal 53:1400–1413
Goldsmith J, Bobb J, Crainiceanu CM, Caffo BS, Reich D (2011) Penalized functional regression. J Comput Graph Stat 20(4):830–851
Greven S, Crainiceanu CM, Caffo BS, Reich D (2010) Longitudinal functional principal component analysis. Electron J Stat 4:1022–1054
Greven S, Crainiceanu CM, Küchenhoff H, Peters A (2008) Restricted likelihood ratio testing for zero variance components in linear mixed models. J Comput Graph Stat 17(4):870–891
He G, Müller H-G, Wang J-L, Wang W (2010) Functional linear regression via canonical analysis. Bernoulli 16(3):705–729
Horváth L, Kokoszka P (2012) Inference for functional data with applications. Springer, New York
Huang L, Goldsmith J, Reiss PT, Reich DS, Crainiceanu CM (2013) Bayesian scalar-on-image regression with application to association between intracranial DTI and cognitive outcomes. NeuroImage 83:210–223
Kadri H, Preux P, Duflos E, Canu S (2011) Multiple functional regression with both discrete and continuous covariates. In: Ferraty F (ed) Recent advances in functional data analysis and related topics, contributions to statistics. Physica-Verlag, Heidelberg, pp 189–195
Krivobokova T, Kauermann G (2007) A note on penalized spline smoothing with correlated errors. JASA 102(480):1328–1337
Lindquist MA (2012) Functional causal mediation analysis with an application to brain connectivity. J Am Stat Assoc 107(500):1297–1309
Matsui H, Kawano S, Konishi S (2009) Regularized functional regression modeling for functional response and predictors. J Math Ind 1(3):17–25
McLean MW, Hooker G, Staicu A-M, Scheipl F, Ruppert D (2014) Functional generalized additive models. J Comput Graph Stat 23(1):249–269
Matlab, The MathWorks Inc. (2014) Natick. Massachusetts, United States
Nychka D (1988) Confidence intervals for smoothing splines. J Am Stat Assoc 83:1134–1143
Ozturk A, Smith SA, Gordon-Lipkin EM, Harrison DM, Shiee N, Pham DL, Caffo BS, Calabresi PA, Reich DS (2010) MRI of the corpus callosum in multiple sclerosis: association with disability. Mult Scler 16(2):166–177
R Development Core Team (2014) R: a language and environment for statistical computing, R Foundation for Statistical Computing, Vienna, Austria. www.R-project.org
Ramsay JO, Wickham H, Graves S, Hooker G (2014) FDA: functional data analysis. Website: http://CRAN.R-project.org/package=fda
Ramsay JO, Hooker G, Graves S (2009) Functional data analysis with R and Matlab. Springer, New York
Ramsay JO, Silverman BW (2005) Functional data analysis. Springer, New York
Reiss P, Ogden T (2009) Smoothing parameter selection for a class of semiparametric linear models. J R Stat Soc Ser B 71(2):505–523
Ruppert D, Wand MP, Caroll RJ (2003) Semiparametric regression. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Scheipl F, Greven S, Küchenhoff H (2008) Size and power of tests for a zero random effect variance or polynomial regression in additive and linear mixed models. Comput Stat Data Anal 52(7):3283–3299
Scheipl F, Staicu A-M, Greven S (2014) Functional additive mixed models. J Comput Graph Stat. doi:10.1080/10618600.2014.901914
Song SK, Sun SW, Ramsbottom MJ, Chang C, Russell J, Cross AH (2002) Dysmyelination revealed through MRI as increased radial (but unchanged axial) diffusion of water. Neuroimage 17(3):1429–1436
Staicu A-M, Crainiceanu CM, Reich DS, Ruppert D (2012) Modeling functional data with spatially heterogeneous shape characteristics. Biometrics 68(2):331–343
Tievsky AL, Ptak T, Farkas J (1999) Investigation of apparent diffusion coefficient and diffusion tensor anisotropy in acute and chronic multiple sclerosis lesions. Am J Neuroradiol 20(8):1491–1499
Valderrama MJ, Ocaña FA, Aguilera AM, Ocaña-Peinado FM (2010) Forecasting pollen concentration by a two-step functional model. Biometrics 66(2):578–585
Wahba G (1983) Bayesian ‘confidence intervals’ for the cross-validated smoothing spline. J R Stat Soc Ser B 45:133–150
Wood SN (2006) Generalized additive models: an introduction with R. Chapman & Hall/CRC, New York
Wood SN (2011) Fast stable restricted maximum likelihood and marginal likelihood estimation of semiparametric generalized linear models. J R Stat Soc Ser B 73(1):3–36
Wood SN (2014) MGCV: mixed GAM computation vehicle with GCV/AIC/REML smoothness estimation. Website: http://CRAN.R-project.org/package=mgcv
Wu Y, Fan J, Müller H-G (2010) Varying-coefficient functional linear regression. Bernoulli 16(3):730–758
Yao F, Müller H-G, Wang J-L (2005a) Functional data analysis for sparse longitudinal data. J Am Stat Assoc 100(740):577–590
Yao F, Müller H-G, Wang J-L (2005b) Functional linear regression analysis for longitudinal data. Ann Stat 33(6):2873–2903
Zhang JT, Chen J (2007) Statistical inferences for functional data. Ann Stat 35(3):1052–1079
Acknowledgments
Staicu’s research was supported by U.S. National Science Foundation Grant Number DMS 1007466 and by the NCSU Faculty Research and Professional Development Grant. Fabian Scheipl and Sonja Greven were funded by Emmy Noether Grant GR 3793/1-1 from the German Research Foundation. We thank Daniel Reich and Peter Calabresi for the DTI tractography data. We would like to thank Ciprian Crainiceanu for helpful discussions and comments on earlier versions of the paper.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
The refund package is available from CRAN at the following website: http://CRAN.R-project.org/package=refund.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ivanescu, A.E., Staicu, AM., Scheipl, F. et al. Penalized function-on-function regression. Comput Stat 30, 539–568 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00180-014-0548-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00180-014-0548-4