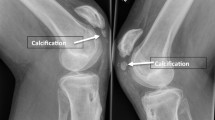
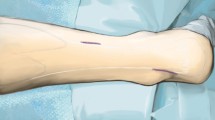
Summary
Objectives
Correction of recurrent dislocation of the patella in children using a semitendinosus tenodesis and a double breasting of the medial retinaculum.
Indications
Recurrent lateral patellar sub- or dislocation in skeletally immature patient.
Patella alta with recurrent subluxation of the patella.
Patella dislocation in the presence of generalized ligamentous laxity.
Contraindications
Degenerative changes of the patellofemoral joint.
Congenital dislocation of the patella.
Surgical Technique
First incision at the posterior aspect of the thigh: division of the semitendinosus at its musculotendinous junction. Its muscle belly is sutured to the semimembranosus. Second incision over the pes anserinus: the tendon is delivered through this wound. Third incision over middle of the patella: division of the lateral patellar retinaculum. Passing of the semitendinosus tendon through a drill hole in the patella from mediodistal to proximolateral and fixation at the proximal pole of the patella. Double breasting of the medial patellar retinaculum.
Results
Between 1990 and 1997, 29 children (5 boys, 24 girls) were operated for a recurrent patellar dislocation. Average age at surgery: 14 years and 3 months (7 years and 8 months to 17 years and 10 months). Preoperatively, pain was present in 19 out of 34 knees, ligamentous laxity in 13, a positive apprehension sign in 12, and a patellar hypermobility in 11. Average length of follow-up: 3 years and 2 months (1 year to 7 years and 2 months). 27 out of 34 knees were asymptomatic and the children returned to normal activities. Patellofemoral pain persisted in 7 children. A medial patellar subluxation occurred in one child. A medial release led to a good result.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baker RH, Caroll N, Dewar FP, Hall JE. The semitendinosus tenodesis for recurrent dislocation of the patella. J Bone Joint Surg [Br] 1972;54:103–9.
Blauth W, Schwarz I. Surgical management of habitual dislocation of the patella in childhood. Orthop Traumatol 1992;1:45–50.
Dewar FP, Hall JE. Recurrent dislocation of the patella. J Bone Joint Surg [Br] 1957:39:798.
Fiume M. La rotulopessi secondo galeazzi nella lussazione recidivante di rotula. Minerva Ortopedica 1954; 5:171.
Galeazzi R, Nouve applicazioni del trapianto muscolare e tendineo. Arch Ortop 1921;38:1922.
Hall JE, Micheli LJ, McManama GB. Semitendinosus tenodesis for recurrent subluxation or dislocation of the patella. Clin Orthop 1979;144:31–5.
Harrison MHM. The results of a realignment operation for recurrent dislocation of the patella. J Bone Joint Surg [Br] 1955;37:559–67.
MacNab I. Recurrent dislocation of the patella. J Bone Joint Surg [Am] 1952;34:957–67.
Marziani R. Sulla lussazione della rotula e sul suo trattamento operativo. Arch Ortop 1930;46:797.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Letts, M., Davidson, D. & Beaule, P. The semitendinosus tenodesis for recurrent dislocation of the patella in adolescents. Orthop Traumatol 7, 221–229 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03180941
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03180941