Abstract
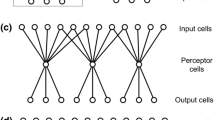
We propose a function-oriented model of the visual cortex. The model addresses an essential task of the visual system: to detect and represent objects. These are defined as sets, which reappear in the input with invariant inner relations. A network, incorporating an idealized description of anatomical and physiological data, is presented with a movie showing various moving objects. In the course of time, as a result of Hebbian plasticity, a connection scheme develops which embodies in its forward and lateral connections the information necessary to perform the operations involved in object recognition. We demonstrate that coherent neural activity can exploit this information. Two types of coherence have to be distinguished in this respect. Rate coherence performs invariance operations and association, while event coherence accomplishes segmentation tasks. The model reproduces and explains experimental findings made both in physiological recordings from the visual cortex and in psychophysical studies.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abeles M (1982) Local cortical circuits. An electrophysiological study. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York
Abeles M (1991) Corticonics. Neural circuits in the cerebral cortex. University Press, Cambridge
Abeles M, Gerstein GL (1988) Detecting spatiotemporal firing palterns among simultaneously recorded single neurons. J Neurophys 60:909–924
Aertsen A, Bonhoeffer T, Krüger J (1987) Coherent activity in neuronal populations: analysis and interpretation. In: Caianiello ER (ed) Physics of cognitive processes. World Scientific, Singapore, pp 1–34
Aertsen AMHJ, Gerstein GL (1991) Dynamic aspects of neuronal cooperativity: fast stimulus-locked modulations of ‘effective connectivity’. In: Krüger J (ed) Neuronal cooperativity. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York, pp 52–67
Aertsen A, Preissl H (1991) Dynamics of activity and connectivity in physiological neuronal networks. In: Schuster H (ed) Nonlinear dynamics and neuronal networks. Verlag Chemie, Weinheim pp 281–301
Aertsen A, Vaadia E, Abeles M, Ahissar E, Bergman H, Karmon B, Lavner Y, Margalit E, Nelken I, Rotter S (1992) Neural interactions in the frontal cortex of a behaving monkey: signs of dependence on stimulus context and behavioral state. J f Hirnforschung 32:735–743
Amit DJ (1989) Modeling brain function. The world of attractor neural networks. University Press, Cambridge
Barnard E, Casasent D (1990) Shift invariance and the neocognitron. Neural Networks 3:403–410
Bauer M, Martienssen (1991) Coupled circle maps as a tool to model synchronisation in neural networks. Network 2:345–351
Bonhoeffer T, Grinvald A (1991) Iso-orientation domains in cat visual cortex are arranged in pinwheel-like patterns. Nature 353:429–431
Boven K-H, Aertsen A (1990) Dynamics of activity give rise to fast modulations of functional connectivity. In: Eckmiller R et al. (eds) Parallel processing in neural systems and computers. Elsevier, New York Amsterdam, Oxford, pp 53–56
Braitenberg V (1978) Cell assemblies in the cerebral cortex. In: Heim R, Palm G (eds) Theoretical approaches to complex systems. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York, pp 171–188
Braitenberg V (1985) Charting the visual cortex. In: Peters A, Jones EG (eds) Cerebral cortex, Vol. 3. Plenum Press, New York London, pp 379–414
Braintenberg B (1986) Two views of the cerebral cortex. In: Palm G, Aertsen A (eds) Brain theory. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York, pp 81–96
Braitenberg V, Schüz A (1991) Anatomy of the cortex. Statistics and geometry. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York
Eckhorn R, Bauer R, Jordan W, Kruse W, Munk M, Reitboeck HJ (1988) Coherent oscillations: a mechanism of feature linking in the visual cortex? Multiple electrode and correlation analysis in the cat. Biol Cybern 60:121–130
Eckhorn R, Reitboeck HJ, Arndt M, Dicke P (1990) Feature linking via synchronization among distributed assemblies: simulations of results from cat visual cortex. Neural Comp 2:293–307
Eckhorn R (1991) Stimulus-specific synchronisations in visual cortex: linking features into global figures? In: Krüger J (ed) Neural cooperativity. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York, pp 184–219
Erb M, Aertsen A (1992) Dynamics of activity in biology-oriented neural network models: stability at low firing rates. In: Aertsen A, Braitenberg V (eds) Information processing in the cortex: experiments and theory. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York, pp 201–223
Frégnac Y, Imbert M (1984) Development of neural selectivity in primary visual cortex of cat. Physiol Rev 64:325–434
Fukushima K (1988) Neocognitron: A hierarchical neural network capable of visual pattern recognition. Neural Networks 1:119–130
Gerstein GL (1970) Functional association of neurons: detection and interpretation. In: Schmitt FO (ed) The neurosciences: second study program. Rockefeller University Press, New York, pp 648–661
Gerstein GL, Bloom MJ, Espinosa IE, Evanczuk S, Turner MR (1988) Design of a laboratory for multi-neuron studies. IEEE Trans Systems Man Cyb SMC-13:668–676
Gerstein GL (1988) Information flow and state in cortical neural networks: Interpreting multi-neuron experiments. In: von Seelen W, Shaw G, Leinhos UM (eds) Organization of neural networks, Verlag Chemie, Weinheim, pp 53–75
Gerstein GL, Bedenbaugh P, Aertsen AMHJ (1989) Neuronal assemblies. IEEE Trans Biomed Engin BME-36:4–14
Gilbert CD, Wiesel TN (1990) The influence of contextual stimuli on the orientation selectivity of cells in primary visual cortex of the cat. Vision Res. 30:1689–1701
Gilbert CD, Wiesel TN (1991) Short and long term changes in receptive field size and position following focal retinal lesions. Neurosci Abstr 17:1090
Gray CM, Singer W (1989) Stimulus-specific neuronal oscillations in orientation columns of cat visual cortex. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 86:1698–1702
Gray CM, König P, Engel AK, Singer W (1989) Oscillatory responses in cat visual cortex exhibit inter-columnar synchronisation which reflects global stimulus properties. Nature 388:334–337
Hebb DO (1949) The organisation of behavior Wiley, New York
Hubel DH, Wiesel TN (1965) Receptive fields and functional architecture in two nonstriate visual areas (18 and 19) of the cat. J Neurophysiol 28:229–289
Hubel DH, Wiesel TN (1977) Functional architecture of macaque monkey visual cortex (Ferrier Lecture). Proc Roy Soc London B 198:1–59
Johannesma P, Aertsen A, van den Boogaard H, Eggermont J, Epping W (1986) From synchrony to harmony: Ideas on the function of neural assemblies and on the interpretation of neural synchrony. In: Palm G, Aertsen A (eds) Brain theory. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York, pp 25–47
Kandel ER, Schwartz JH (1985) Principles in neural science. Elsevier, New York Amsterdam Oxford
Kaneko K (1990) Clustering, coding, switching, hierarchical ordering and control in a network of chaotic elements. Physica D41:137–172
Kanizsa G (1979) Organization in vision. Essays on Gestalt perception. Praeger, New York
Klein F (1921) Zum Erlanger Programm (1872). In: Fricke and Ostrowski (eds) Gesammele mathematische Abbhandlungen, vol. 1. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York
Koenderink JJ (1984a) The concept of local sign. In: van Doorn AJ, van der Grind WA, Koenderink JJ (eds) Limits in perception. VNU Science Press, Ultrecht, pp 495–547
Koenderink JJ (1984b) Simultaneous order in nervous nets from a functional standpoint. Biol Cybern 50:35–41
Koenderink JJ (1984c) Geometrical structures determined by the functional order in nervous nets. Biol Cybern 50:43–50
König P, Schillen TB (1991) Stimulus-dependent assembly formation of oscillatory responses. 1: Synchronisation. Neural Comp 3:155–167
Kohonen T (1982) Self-organized formation of topologically correct feature maps. Biol Cybern 43:59–69
Krüger J (1983) Simultaneous individual recordings from many cerebral neurons: techniques and results. Rev Physiol Biochem Pharmacol 98:177–233
Krüger J, Mayer M (1991) Two types of neural synchrony in monkey striate cortex. Biol Cybern 64:135–140
Kuramoto Y (1984) Cooperative dynamics of oscillator community. Progress of theoretical physics, [Suppl 79], 223–240
Lamport L (1978) Time, clocks and the ordering of events in a distributed system. Comm ACM 21:558–565
Mattern F (1989) Virtual time and global states of distributed systems. In: Cosnard M, Robert I, Quinton P, Raynal H (eds) Parallel and distributed algorithms. Elsevier, New York Amsterdam Oxford, pp 215–226
Marr D (1982) Vision. Freeman, San Francisco
Marr D, Ullmann S (1981) Directional selectivity and its use in early visual processing. Proc R Soc London B 211:151–180
Menon MM, Heinemann KG (1988) Classification of patterns using a self-organising neural network. Neural Networks 1:201–215
Minsky M, Papert S (1988) Perceptrons (expanded edition). MIT Press, Cambridge
Oja E (1989) Neural networks: principal components and subspaces. Int J Neural Systems 1:61–68
Orban GA (1984) Neural operations in the visual cortex. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York
Palm G (1980) On associative memory. Biol Cybern 36:19–31
Pettet MW, Gilbert CD (1991) Contextual stimuli influence receptive field size of single neurons in cat primary visual cortex. Neurosci Abstr 17:1090
Rumelhart DE, Zipser D (1986) Feature discovery by competitive learning. In: Rumelhart D, McClelland J (eds) and the PDP research group. Parallel distributed processing. MIT Press, Cambridge, pp 151–193
Sagi D, Julesz B (1985) ‘Where’ and ‘what’ in vision. Science 228:1217–1219
Schillen TB, König P (1991) Stimulus-dependent assembly formation of oscillatory responses. 2: Desynchronisation. Neural Comp 3:167–178
Schuster HG (1991) Nonlinear dynamics and neural oscillations. In: Schuster HG (ed) Nonlinear dynamics and neural networks. Verlag Chemie, Weinheim, pp 131–151
Schwartz EL (1977) Spatial mapping in primate visual sensory projection and relevance to perception. Biol Cybern 25:181–195
Schwarz C, Bolz J (1991) Functional specificity of the long-range horizontal connections in cat visual cortex: a cross-correlation study. J Neurosci 11:2995–3007
Sompolinsky H, Golomb D, Kleinfeld D (1990) Global processing of visual stimuli in a network of coupled oscillators. Proc Natl Acad Sci. USA 87:7200–7204
Sompolinsky H, Golomb D, Kleinfeld D (1991) Cooperative dynamics in visual processing. Physical Rev A 43:6990–7011
Spelke ES (1990) Origins of visual knowledge. In: Osherson DN, Kosslyn SM, Hollerbach JM (eds) Visual cognition and action. An invitation to cognitive science, vol. 2. MIT Press, Cambridge, pp 99–127
Sporns O, Gally JA, Reeke GN Jr, Edelman GM (1989) Reentrant signaling among simulated neuronal groups leads to coherency in their oscillatory activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 86:7265–7269
Treisman A (1986) Features and objects in visual processing. Sci Am 225:106–115
Ts'o DY, Gilbert CD, Wiesel TN (1986) Relationships between horizontal interactions and functional architecture in cat striate cortex as revealed by cross-correlation analysis. J Neurosci 6:1160–1170
Ts'o DY (1991) Connectivity and functional organisation in the mammalian visual cortex. In: Krüger J (ed) Neural cooperativity. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York, pp 133–164
Tusa RJ, Palmer LA, Rosenquist AC (1981) Multiple cortical visual areas: visual field topography in the cat. In: Woolsey CN (ed) Cortical sensory organisation vol. 2. Humana Press, Clifton, pp 1–29
Vaadia E, Ahissar E, Bergman H, Lavner Y (1991) Correlated activity of neurons: a neural code for higher brain functions? In: Krüger J (ed) Neuronal cooperativity. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York, pp 249–279
Vaadia E, Aertsen A (1992) Coding and computation in the cortex: single neuron activity and cooperative phenomena. In: Aertsen A, Braitenberg V (eds) Information processing in the cortex: experiments and theory. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York, pp 81–121
van Essen DC (1985) Functional organisation in primate visual cortex. In: Peters A, Jones EG (eds) Cerebral cortex vol. 3, Plenum Press, New York, pp 259–320
von der Heydt R, Peterhans E, Baumgartner G (1984) Illusory contours and cortical neuron responses. Science 224:1260–1262
von der Malsburg C (1981) The correlation theory of brain function. Internal report 81-2. MPI for Biophys Chem, Göttingen
von der Malsburg C (1986) Am I thinking assemblies? In: Palm G, Aertsen A (eds) Brain theory. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York, pp 161–176
von der Malsburg C, Schneider W (1986) A neural cocktail-party processor. Biol Cybern 54:29–40
von der Malsburg C, Singer W (1988) Principles of cortical network organization. In: von Seelen W, Shaw G, Leinhos UM (eds) Organization of neural networks. Verlag Chemie, Weinheim, pp 109–126
Wertheimer M (1923) Principles of perceptual organization. Psychologische Forschungen 4:301–350 (Edited and translated by Wertheimer M) in: Beardslee DC and Wertheimer M (eds) Readings in perception. Van Nostrand, Princeton
Wiesel TN (1982) Postnatal development of the visual cortex and the influence of environment. (Nobel lecture) Nature 299:583–591
Willshaw DJ, Buneman OP, Longuet-Higgins HC (1969) Non-holographic associative memory. Nature 222:960–962
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Neven, H., Aertsen, A. Rate coherence and event coherence in the visual cortex: a neuronal model of object recognition. Biol. Cybern. 67, 309–322 (1992). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02414887
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02414887