Abstract
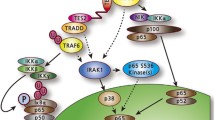
The Epstein-Barr virus latent membrane protein (LMP) 1 is a versatile protein that has profound effects on target cells through its effect on constitutive cellular proteins, e.g. TRAFs, TRADD, RIP, JAK3, BRAM1, and p85. LMP1 can stimulate or inhibit signaling pathways, resulting in transformation of rodent fibroblast cell lines, blockade of differentiation in epithelial cells, upregulation of antiapoptotic proteins, production of cytokines, upregulation of cell surface markers, upregulation of DNA methyltransferase activity, and downregulation of cell adhesion molecules and cyclin-dependent kinases. Overall, this results in greater transformation and survival in LMP1-expressing cells. Within nasopharyngeal carcinoma biopsy tissues, a naturally occurring LMP1 variant has been identified as having a 10-amino acid deletion in the C-terminus that seems to confer greater transformation potential than non-deleted LMP1. The role of LMP1 as a viral oncogene and its interaction with cellular factors are discussed.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ansieau S, Leutz A. The conserved Mynd domain of BS69 binds cellular and oncoviral proteins through a common PXLXP motif. J Biol Chem 277:4906–4910;2002.
Arch RH, Gedrich RW, Thompson CB. Tumor necrosis factor receptor-associated factors (TRAFs) — A family of adapter proteins that regulates life and death. Genes Dev 12:2821–2830;1998.
Arron JR, Vologodskaia M, Wong BR, Naramura M, Kim N, Gu H, Choi Y. A positive regulatory role for Cbl family proteins in tumor necrosis factor-related activation-induced cytokine (trance) and CD40L-mediated Akt activation. J Biol Chem 276:30011–30017;2001.
Arvanitakis L, Yaseen N, Sharma S. Latent membrane protein-1 induces cyclin D2 expression, pRb hyperphosphorylation, and loss of TGF-beta 1-mediated growth inhibition in EBV-positive B cells. J Immunol 155:1047–1056;1995.
Aviel S, Winberg G, Massucci M, Ciechanover A. Degradation of the Epstein-Barr virus latent membrane protein 1 (LMP1) by the ubiquitin-proteasome pathway. Targeting via ubiquitination of the N-terminal residue. J Biol Chem 275:23491–23499;2000.
Baker SJ, Reddy EP. Modulation of life and death by the TNF receptor superfamily. Oncogene 17:3261–3270;1998.
Bar-Sagi D, Hall A. Ras and Rho GTPases: A family reunion. Cell 103:227–238;2000.
Blake SM, Eliopoulos AG, Dawson CW, Young LS. The transmembrane domains of the EBV-encoded latent membrane protein 1 (LMP1) variant CAO regulate enhanced signalling activity. Virology 282:278–287;2001.
Brennan P, Floettmann JE, Mehl A, Jones M, Rowe M. Mechanism of action of a novel latent membrane protein-1 dominant negative. J Biol Chem 276:1195–1203;2001.
Cao Z, Xiong J, Takeuchi M, Kurama T, Goeddel DV. TRAF6 is a signal transducer for interleukin-1. Nature 383:443–446;1996.
Carpenter CL, Cantley LC. Phosphoinositide kinases. Curr Opin Cell Biol 8:153–158;1996.
Chang YS, Tyan YS, Liu ST, Tsai MS, Pao CC. Deletion of Epstein Barr virus DNA sequences in nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells by enzymatic DNA amplification. J Clin Microbiol 28:2398–2402;1990.
Chen ML, Tsai CN, Liang CL, Shu CH, Huang CR, Sulitzeanu D, Liu ST, Chang YS. Cloning and characterization of the latent membrane protein (LMP) of a specific Epstein-Barr virus variant derived from the nasopharyngeal carcinoma in the Taiwanese population. Oncogene 7:2131–2140;1992.
Chiang AK, Wong KY, Liang AC, Srivastava G. Comparative analysis of Epstein-Barr virus gene polymorphisms in nasal T/NK-cell lymphomas and normal nasal tissues: Implications on virus strain selection in malignancy. Int J Cancer 80:356–364;1999.
Chung PJ, Chang YS, Liang CL, Meng CL. Negative regulation of Epstein-Barr virus latent membrane protein 1-mediated functions by the bone morphogenetic protein receptor IA-binding protein, BRAM1. J Biol Chem 277:39850–39857;2002.
Coffin WF 3rd, Erickson KD, Hoedt-Miller M, Martin JM. The cytoplasmic amino-terminus of the Latent Membrane Protein-1 of Epstein-Barr Virus: Relationship between transmembrane orientation and effector functions of the carboxy-terminus and transmembrane domain. Oncogene 20:5313–5330;2001.
Coffin WF 3rd, Geiger TR, Martin JM. Transmembrane domains 1 and 2 of the latent membrane protein 1 of Epstein-Barr virus contain a lipid raft targeting signal and play a critical role in cytostasis. J Virol 77:3749–3758;2003.
Datta SR, Dudek H, Tao X, Masters S, Fu H, Gotoh Y, Greenberg ME. Akt phosphorylation of BAD couples survival signals to the cell-intrinsic death machinery. Cell 91:231–241;1997.
Dawson CW, Tramountains G, Eliopoulos AG, Young LS. Epstein-Barr virus latent membrane protein 1 (LMP1) activates the PI3-K/Akt pathway to promote cell survival and induce actin filament remodelling. J Biol Chem 278:3694–3704;2003.
Devergne O, Cahir McFarland ED, Mosialos G, Izumi KM, Ware CF, Kieff E. Role of the TRAF binding site and NF-kappaB activation in Epstein-Barr virus latent membrane protein 1-induced cell gene expression. J Virol 72:7900–7908;1998.
Devergne O, Hatzivassiliou E, Izumi KM, Kaye KM, Kleijnen MF, Kieff E, Mosialos G. Association of TRAF1, TRAF2, and TRAF3 with an Epstein-Barr virus LMP1 domain important for B-lymphocyte transformation: Role in NF-kappaB activation. Mol Cell Biol 16:7098–7108;1996.
Dolcetti R, Zancai P, De Re V, Gloghini A, Bigoni B, Pivetta B, De Vita S, Carbone A, Boiocchi M. Epstein-Barr virus strains with latent membrane protein-1 deletions: Prevalence in the Italian population and high association with human immunodeficiency virus-related Hodgkin's disease. Blood 89:1723–1731;1997.
D'Souza B, Rowe M, Walls D. The bfl-1 gene is transcriptionally upregulated by the Epstein-Barr virus LMP1, and its expression promotes the survival of a Burkitt's lymphoma cell line. J Virol 74:6652–6658;2000.
Eliopoulos AG, Blake SM, Floettmann JE, Rowe M, Young LS. Epstein-Barr virus-encoded latent membrane protein 1 activates the JNK pathway through its extreme C terminus via a mechanism involving TRADD and TRAF2. J Virol 73:1023–1035;1999.
Eliopoulos AG, Davies C, Blake SS, Murray P, Najafipour S, Tsichlis PN, Young LS. The oncogenic protein kinase Tp1–2/Cot contributes to Epstein-Barr virus-encoded latent infection membrane protein 1-induced NF-κB signaling downstream of TRAF2. J Virol 76:4567–4579;2002.
Eliopoulos AG, Gallagher NJ, Blake SM, Dawson CW, Young LS. Activation of the p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway by Epstein-Barr virus-encoded latent membrane protein 1 coregulates interleukin-6 and interleukin-8 production. J Biol Chem 274:16085–16096;1999.
Eliopoulos AG, Stack M, Dawson CW, Kaye KM, Hodgkin L, Sihota S, Rowe M, Young LS. Epstein-Barr virus-encoded LMP1 and CD40 mediate IL-6 production in epithelial cells via an NF-κB pathway involving TNF receptor-associated factors. Oncogene 14:2899–2916;1997.
Eliopoulos AG, Waites ER, Blake SM, Davies C, Murray P, Young LS. TRAF1 is a critical regulator of JNK signaling by the TRAF-binding domain of the Epstein-Barr virus-encoded latent infection membrane protein 1 but not CD40. J Virol 77:1316–1328;2003.
Eliopoulos AG, Young LS. Activation of the cJun N-terminal kinase (JNK) pathway by the Epstein-Barr virus-encoded latent membrane protein 1 (LMP1). Oncogene 16:1731–1742;1998.
Eliopoulos AG, Young LS. LMP1 structure and signal transduction. Semin Cancer Biol 11:435–444;2001.
Fahraeus R, Fu HL, Ernberg I, Finke J, Rowe M, Klein G, Falk K, Nilsson E, Yadav M, Busson P, et al. Expression of Epstein-Barr virusencoded proteins in nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Int J Cancer 42:329–338;1988.
Gilligan K, Sato H, Rajadurai P, Busson P, Young L, Rickinson A, Tursz T, Raab-Traub N. Novel transcription from the Epstein-Barr virus terminal EcoRI fragment, DIJhet, in a nasopharyngeal carcinoma. J Virol 64:4948–4956;1990.
Gires O, Kohlhuber F, Kilger E, Baumann M, Kieser A, Kaiser C, Zeidler R, Scheffer B, Ueffing M, Hammerschmidt W. Latent membrane protein 1 of Epstein-Barr virus interacts with JAK3 and activates STAT proteins. EMBO J 18:3064–3073;1999.
Gires O, Zimber-Strobl U, Gonnella R, Ueffing M, Marschall G, Zeidler R, Pich D, Hammerschmidt W. Latent membrane protein 1 of Epstein-Barr virus mimics a constitutively active receptor molecule. EMBO J 16:6131–6140;1997.
Hammerschmidt W, Sugden B, Baichwal VR. The transforming domain alone of the latent membrane protein of Epstein-Barr virus is toxic to cells when expressed at high levels. J Virol 63:2469–2475;1989.
Hatzivassiliou E, Miller WE, Raab-Traub N, Kieff E, Mosialos G. A fusion of the EBV latent membrane protein-1 (LMP1) transmembrane domains to the CD40 cytoplasmic domain is similar to LMP1 in constitutive activation of epidermal growth factor receptor expression, nuclear factor-kappa B, and stress-activated protein kinase. J Immunol 160:1116–1121;1998.
Henderson S, Rowe M, Gregory C, Croom-Carter D, Wang F, Longnecker R, Kieff E, Rickinson A. Induction of bcl-2 expression by Epstein-Barr virus latent membrane protein 1 protects infected B cells from programmed cell death. Cell 65:1107–1115;1991.
Higuchi M, Kieff E, Izumi KM. The Epstein-Barr virus latent membrane protein 1 putative Janus kinase 3 (JAK3) binding domain does not mediate JAK3 association or activation in B-lymphoma or lymphoblastoid cell lines. J Virol 76:455–459;2002.
Ho JH. Nasopharyngeal carcinoma (NPC). Adv Cancer Res 15:57–92;1972.
Hong SY, Yoon WH, Park JH, Kang SG, Ahn JH, Lee TH. Involvement of two NF-kappa B binding elements in tumor necrosis factor alpha-, CD40-, and Epstein-Barr virus latent membrane protein 1-mediated induction of the cellular inhibitor of apoptosis protein 2 gene. J Biol Chem 275:18022–18028;2000.
Horikawa T, Sheen TS, Takeshita H, Sato H, Furukawa M, Yoshizaki T. Induction of c-Met proto-oncogene by Epstein-Barr virus latent membrane protein-1 and the correlation with cervical lymph node metastasis of nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Am J Pathol 159:27–33;2001.
Hsu H, Shu HB, Pan MG, Goeddel DV. TRADD-TRAF2 and TRADD-FADD interactions define two distinct TNF receptor 1 signal transduction pathways. Cell 84:299–308;1996.
Hu LF, Zabarovsky ER, Chen F, Cao SL, Ernberg I, Klein G, Winberg G. Isolation and sequencing of the Epstein-Barr virus BNLF-1 gene (LMP1) from a Chinese nasopharyngeal carcinoma. J Gen Virol 72 (Pt 10):2399–2409;1991.
Huen DS, Henderson SA, Croom-Carter D, Rowe M. The Epstein-Barr virus latent membrane protein-1 (LMP1) mediates activation of NF-kappa B and cell surface phenotype via two effector regions in its carboxy-terminal cytoplasmic domain. Oncogene 10:549–560;1995.
Ihle JN, Kerr IM. Jaks and Stats in signaling by the cytokine receptor superfamily. Trends Genet 11:69–74;1995.
Izumi KM. Identification of EBV transforming genes by recombinant EBV technology. Semin Cancer Biol 11:407–414;2001.
Izumi KM, Cahir McFarland ED, Riley EA, Rizzo D, Chen Y, Kieff E. The residues between the two transformation effector sites of Epstein-Barr virus latent membrane protein 1 are not critical for B-lymphocyte growth transformation. J Virol 73:9908–9916;1999.
Izumi KM, Cahir McFarland ED, Ting AT, Riley EA, Seed B, Kieff ED. The Epstein-Barr virus oncoprotein latent membrane protein 1 engages the tumor necrosis factor receptor-associated proteins TRADD and receptor-interacting protein (RIP) but does not induce apoptosis or require RIP for NF-κB activation. Mol Cell Biol 19:5759–5767;1999.
Izumi KM, Kaye KM, Kieff ED. Epstein-Barr virus recombinant molecular genetic analysis of the LMP1 amino-terminal cytoplasmic domain reveals a probable structural role, with no component essential for primary B-lymphocyte growth transformation. J Virol 68:4369–4376;1994.
Izumi KM, Kaye KM, Kieff ED. The Epstein-Barr virus LMP1 amino acid sequence that engages tumor necrosis factor receptor associated factors is critical for primary B lymphocyte growth transformation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 94:1447–1452;1997.
Izumi KM, Kieff ED. The Epstein-Barr virus oncogene product latent membrane protein 1 engages the tumor necrosis factor receptor-associated death domain protein to mediate B lymphocyte growth transformation and activate NF-κB. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 94:12592–12597;1997.
Jones PA. DNA methylation and cancer. Oncogene 21:5358–5360;2002.
Kaye KM, Devergne O, Harada JN, Izumi KM, Yalamanchili R, Kieff E, Mosialos G. Tumor necrosis factor receptor associated factor 2 is a mediator of NF-kappa B activation by latent infection membrane protein 1, the Epstein-Barr virus transforming protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 93:11085–11090;1996.
Kaye KM, Izumi KM, Kieff E. Epstein-Barr virus latent membrane protein 1 is essential for B-lymphocyte growth transformation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 90:9150–9154;1993.
Kaye KM, Izumi KM, Mosialos G, Kieff E. The Epstein-Barr virus LMP1 cytoplasmic carboxy terminus is essential for B-lymphocyte transformation; fibroblast cocultivation complements a critical function within the terminal 155 residues. J Virol 69:675–683;1995.
Kaykas A, Sugden B. The amino-terminus and membrane-spanning domains of LMP-1 inhibit cell proliferation. Oncogene 19:1400–1410;2000.
Kaykas A, Worringer K, Sugden B. LMP-1's transmembrane domains encode multiple functions required for LMP-1's efficient signaling. J Virol 76:11551–11560;2002.
Kershaw GR, Berger C, McQuain C, al-Homsi AS, Pihan G, Quesenberry PJ, Woda BA, Knecht H. Selective outgrowth of a posttrans-plant B-immunoblastic lymphoma expressing a latent membrane protein-1 deletion variant. Transplantation 64:1079–1081;1997.
Kieser A, Kilger E, Gires O, Ueffing M, Kolch W, Hammerschmidt W. Epstein-Barr virus latent membrane protein-1 triggers AP-1 activity via the c-Jun N-terminal kinase cascade. EMBO J 16:6478–6485;1997.
Kilger E, Kieser A, Baumann M, Hammerschmidt W. Epstein-Barr virus-mediated B-cell proliferation is dependent upon latent membrane protein 1, which simulates an activated CD40 receptor. EMBO J 17:1700–1709;1998.
Kim KR, Yoshizaki T, Miyamori H, Hasegawa K, Horikawa T, Furukawa M, Harada S, Seiki M, Sato H. Transformation of Madin-Darby canine kidney (MDCK) epithelial cells by Epstein-Barr virus latent membrane protein 1 (LMP1) induces expression of Ets1 and invasive growth. Oncogene 19:1764–1771;2000.
Kim SH, Shin YK, Lee IS, Bae YM, Sohn HW, Suh YH, Ree HJ, Rowe M, Park SH. Viral latent membrane protein 1 (LMP-1)-induced CD99 down-regulation in B cells leads to the generation of cells with Hodgkin's and Reed-Sternberg phenotype. Blood 95:294–300;2000.
Kjoller L, Hall A. Signaling to Rho GTPases. Exp Cell Res 253:166–179;1999.
Knecht H, Bachmann E, Brousset P, Rothenberger S, Einsele H, Lestou VS, Delsol G, Bachmann F, Ambros PF, Odermatt BF. Mutational hot spots within the carboxy terminal region of the LMP1 oncogene of Epstein-Barr virus are frequent in lymphoproliferative disorders. Oncogene 10:523–528;1995.
Kurozumi K, Nishita M, Yamaguchi K, Fujita T, Ueno N, Shibuya H. BRAM1, a BMP receptor-associated molecule involved in BMP signalling. Genes Cells 3:257–264;1998.
Ladendorff NE, Wu S, Lipsick JS. BS69, an adenovirus E1A-associated protein, inhibits the transcriptional activity of c-Myb. Oncogene 20:125–132;2001.
Laherty CD, Hu HM, Opipari AW, Wang F, Dixit VM. The Epstein-Barr virus LMP1 gene product induces A20 zinc finger protein expression by activating nuclear factor kappa B. J Biol Chem 267:24157–24160;1992.
Li SN, Chang YS, Liu ST. Effect of a 10-amino acid deletion on the oncogenic activity of latent membrane protein 1 of Epstein-Barr virus. Oncogene 12:2129–2135;1996.
Lu J, Chua HH, Chen SY, Chen JY, Tsai CH. Regulation of matrix metalloproteinase-1 by Epstein-Barr virus proteins. Cancer Res 63:256–262;2003.
Malinin NL, Boldin MP, Kovalenko AV, Wallach D. MAP3K-related kinase involved in NF-κB induction by TNF, CD95 and IL-1. Nature 385:540–544;1997.
Masselink H, Bernards R. The adenovirus E1A binding protein BS69 is a corepressor of transcription through recruitment of N-CoR. Oncogene 19:1538–1546;2000.
Mehl AM, Floettmann JE, Jones M, Brennan P, Rowe M. Characterization of intercellular adhesion molecule-1 regulation by Epstein-Barr virus-encoded latent membrane protein-1 identifies pathways that cooperate with nuclear factor kappa B to activate transcription. J Biol Chem 276:984–992;2001.
Midgley RS, Blake NW, Yao QY, Croom-Carter D, Cheung ST, Leung SF, Chan AT, Johnson PJ, Huang D, Rickinson AB, Lee SP. Novel intertypic recombinants of Epstein-Barr virus in the Chinese population. J Virol 74:1544–1548;2000.
Miller WE, Mosialos G, Kieff E, Raab-Traub N. Epstein-Barr virus LMP1 induction of the epidermal growth factor receptor is mediated through a TRAF signaling pathway distinct from NF-κB activation. J Virol 71:586–594;1997.
Mitchell T, Sugden B. Stimulation of NF-kappa B-mediated transcription by mutant derivatives of the latent membrane protein of Epstein-Barr virus. J Virol 69:2968–2976;1995.
Mosialos G, Birkenbach M, Yalamanchili R, VanArsdale T, Ware C, Kieff E. The Epstein-Barr virus transforming protein LMP1 engages signaling proteins for the tumor necrosis factor receptor family. Cell 80:389–399;1995.
Murono S, Inoue H, Tanabe T, Joab I, Yoshizaki T, Furukawa M, Pagano JS. Induction of cyclooxygenase-2 by Epstein-Barr virus latent membrane protein 1 is involved in vascular endothelial growth factor production in nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 98:6905–6910;2001.
Okkenhaug K, Vanhaesebroeck B. New responsibilities for the PI3K regulatory subunit p85 alpha. Sci STKE 2001:PE1;2001.
Old LJ, Boyse EA, Oettgen HF, Haven ED, Geering G, Willin B, Clifford P. Precipitating antibody in human serum to antigen present in cultured Burkitt's lymphoma cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 66:1699–1704;1966.
O'Shea JJ, Gadina M, Schreiber RD. Cytokine signaling in 2002: New surprises in the Jak/Stat pathway. Cell 109(suppl):S121-S131;2002.
Pokrovskaja K, Trivedi P, Klein G, Szekely L. Epstein-Barr virus-encoded LMP-1 protein upregulates the pNDCF group of nucleoskeleton-cytoskeleton-associated proteins. J Gen Virol 78(Pt 8):2031–2040;1997.
Puls A, Eliopoulos AG, Nobes CD, Bridges T, Young LS, Hall A. Activation of the small GTPase Cdc42 by the inflammatory cytokines TNF(α) and IL-1, and by the Epstein-Barr virus transforming protein LMP1. J Cell Sci 112(Pt 17):2983–2992;1999.
Raab-Traub N, Flynn K, Pearson G, Huang A, Levine P, Lanier A, Pagano J. The differentiated form of nasopharyngeal carcinoma contains Epstein-Barr virus DNA. Int J Cancer 39:25–29;1987.
Rickinson AB, Kieff E. Esptein-Barr virus; in Fields BN, Knipe DM, Howley PM (eds): Fields Virology. Philadelphia, Lippinott-Raven, 1996, pp 2397–2446.
Rountree MR, Bachman KE, Herman JG, Baylin SB. DNA methylation, chromatin inheritance, and cancer. Oncogene 20:3156–3165;2001.
Rowe M, Peng-Pilon M, Huen DS, Hardy R, Croom-Carter D, Lundgren E, Rickinson AB. Upregulation of bcl-2 by the Epstein-Barr virus latent membrane protein LMP1: A B-cell-specific response that is delayed relative to NF-kappa B activation and to induction of cell surface markers. J Virol 68:5602–5612;1994.
Sandberg ML, Kaykas A, Sugden B. Latent membrane protein 1 of Epstein-Barr virus inhibits as well as stimulates gene expression. J Virol 74:9755–9761;2000.
Sandvej K, Gratama JW, Munch M, Zhou XG, Bolhuis RL, Andresen BS, Gregersen N, Hamilton-Dutoit S. Sequence analysis of the Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) latent membrane protein-1 gene and promoter region: Identification of four variants among wild-type EBV isolates. Blood 90:323–330;1997.
Schultheiss U, Puschner S, Kremmer E, Mak TW, Engelmann H, Hammerschmidt W, Kieser A. TRAF6 is a critical mediator of signal transduction by the viral oncogene latent membrane protein 1. EMBO J 20:5678–5691;2001.
Shanmugaratnam K. Histological Typing of Tumors of the Upper Respiratory Tract and Ear, ed 2. International Histological Classification of Tumors. Berlin, Springer, 1991.
Sylla BS, Hung SC, Davidson DM, Hatzivassiliou E, Malinin NL, Wallach D, Gilmore TD, Kieff E, Mosialos G. Epstein-Barr virus-transforming protein latent infection membrane protein 1 activates transcription factor NF-κB through a pathway that includes the NF-κB-inducing kinase and the IκB kinases IKKα and IKKβ. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 95:10106–10111;1998.
Takanashi M, Li J, Shirakata M, Mori S, Hirai K. Tumorigenicity of mouse BALB/c 3T3 fibroblast cells which express Epstein-Barr virusencoded LMP1 and show normal growth phenotypes in vitro is correlated with loss of transforming growth factor-beta 1-mediated growth inhibition. Arch Virol 144:241–257;1999.
Takeshita H, Yoshizaki T, Miller WE, Sato H, Furukawa M, Pagano JS, Raab-Traub N. Matrix metalloproteinase 9 expression is induced by Epstein-Barr virus latent membrane protein 1 C-terminal activation regions 1 and 2. J Virol 73:5548–5555;1999.
Takeuchi M, Rothe M, Goeddel DV. Anatomy of TRAF2. Distinct domains for nuclear factor-κB activation and association with tumor necrosis factor signaling proteins. J Biol Chem 271:19935–19942;1996.
Tsai CN, Tsai CL, Tse KP, Chang HY, Chang YS. The Epstein-Barr virus oncogene product, latent membrane protein 1, induces the down-regulation of E-cadherin gene expression via activation of DNA methyltransferases. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 99:10084–10089;2002.
Uchida J, Yasui T, Takaoka-Shichijo Y, Muraoka M, Kulwichit W, Raab-Traub N, Kikutani H. Mimicry of CD40 signals by Epstein-Barr virus LMP1 in B lymphocyte responses. Science 286:300–303;1999.
Wang D, Liebowitz D, Kieff E. An EBV membrane protein expressed in immortalized lymphocytes transforms established rodent cells. Cell 43:831–840;1985.
Wang D, Liebowitz D, Wang F, Gregory C, Rickinson A, Larson R, Springer T, Kieff E. Epstein-Barr virus latent infection membrane protein alters the human B-lymphocyte phenotype: Deletion of the amino terminus abolishes activity. J Virol 62:4173–4184;1988.
Wang F, Gregory C, Sample C, Rowe M, Liebowitz D, Murray R, Rickinson A, Kieff E. Epstein-Barr virus latent membrane protein (LMP1) and nuclear proteins 2 and 3C are effectors of phenotypic changes in B lymphocytes: EBNA-2 and LMP1 cooperatively induce CD23. J Virol 64:2309–2318;1990.
Wang S, Rowe M, Lundgren E. Expression of the Epstein-Barr virus transforming protein LMP1 causes a rapid and transient stimulation of the Bcl-2 homologue Mcl-1 levels in B-cell lines. Cancer Res 56:4610–4613;1996.
Wilson JB, Weinberg W, Johnson R, Yuspa S, Levine AJ. Expression of the BNLF-1 oncogene of Epstein-Barr virus in the skin of transgenic mice induces hyperplasia and aberrant expression of keratin 6. Cell 61:1315–1327;1990.
Wong BR, Besser D, Kim N, Arron JR, Vologodskaia M, Hanafusa H, Choi Y. TRANCE, a TNF family member, activates Akt/PKB through a signaling complex involving TRAF6 and c-Src. Mol Cell 4:1041–1049;1999.
Xin B, He Z, Yang X, Chan CP, Ng MH, Cao L. TRADD domain of Epstein-Barr virus transforming protein LMP1 is essential for inducing immortalization and suppressing senescence of primary rodent fibroblasts. J Virol 75:3010–3015;2001.
Yang X, Sham JS, Ng MH, Tsao SW, Zhang D, Lowe SW, Cao L. LMP1 of Epstein-Barr virus induces proliferation of primary mouse embryonic fibroblasts and cooperatively transforms the cells with a p16-insensitive CDK4 oncogene. J Virol 74:883–891;2000.
Yao L, Setsuda J, Sgadari C, Cherney B, Tosato G. Interleukin-18 expression induced by Epstein-Barr virus-infected cells. J Leukoc Biol 69:779–784;2001.
Yoshizaki T, Horikawa T, Qing-Chun R, Wakisaka N, Takeshita H, Sheen TS, Lee SY, Sato H, Furukawa M. Induction of interleukin-8 by Epstein-Barr virus latent membrane protein-1 and its correlation to angiogenesis in nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Clin Cancer Res 7:1946–1951;2001.
Young LS, Dawson CW, Clark D, Rupani H, Busson P, Tursz T, Johnson A, Rickinson AB. Epstein-Barr virus gene expression in nasopharyngeal carcinoma. J Gen Virol 69(Pt 5):1051–1065;1988.
Yu JS, Tsai HC, Wu CC, Weng LP, Li HP, Chung PJ, Chang YS. Induction of inducible nitric oxide synthase by Epstein-Barr virus B95-8-derived LMP1 in Balb/3T3 cells promotes stress-induced cell death and impairs LMP1-mediated transformation. Oncogene 21:8047–8061;2002.
Zhang L, Wu L, Hong K, Pagano JS. Intracellular signaling molecules activated by Epstein-Barr virus for induction of interferon regulatory factor 7. J Virol 75:12393–12401;2001.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, HP., Chang, YS. Epstein-barr virus latent membrane protein 1: Structure and functions. J Biomed Sci 10, 490–504 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02256110
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02256110