Summary
In diseases associated with thrombotic or thromboembolic complications, a reduction in the fibrinolytic potential may contribute to the risk to develop thrombosis.
To investigate whether iuvenile cerebral infarction is associated with a permanent defect of the fibrinolytic system we measured the main components of the fibrinolytic system, tissue plasminogen activator (t-PA) and its fast acting inhibitor (PAI) in plasma samples of 21 patients (aged 21–44 years) 3–24 months after the acute event. The data obtained were compared to those from thirteen healthy young volunteers (22–46 years). A direct effect of known risk factors on the fibrinolytic system could be excluded because patients avoided their risk factors immediately after the ischemic cerebral attack. Hypertension and the combination of oral contraceptives and smoking had been the most striking original risk factors.
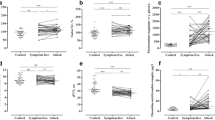
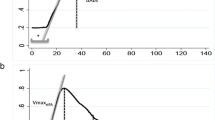
Levels of t-PA antigen and t-PA activity before and after venous occlusion, or PAI activity were not different between patients and controls suggesting that at least a permanent decrease in the activity of the fibrinolytic system does not exist in these patients. However, our findings do not exclude that a temporary defect in fibrinolysis might have contributed to the acute onset of the thrombotic cerebral event possibly induced by the risk factors originally present.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- t-PA:
-
tissue plasminogen activator
- PAI:
-
plasminogen activator inhibitor
- RIND:
-
reversibles ischämisches neurologisches Defizit
- KS:
-
kompletter Schlaganfall
- TIA:
-
transitorisch ischämische Attacke
Literatur
Algernam LO (1974) Abnormalities in clotting and thrombolysis as a risk factor for stroke. Thromb Haemost 31:245–264
Allen RA, Kluft C, Brommer EJP (1985) Effect of chronic smoking on fibrinolysis. Arteriosclerosis 5:443–450
Andersen LA, Gormsen J (1986) Platelet aggregation and fibrinolytic activity in transient cerebral ischemia. Acta neurol scand 55:76–82
Bachmann F (1987) Fibrinolysis. In: Verstraete M, Vermylen J, Lijnen R, Arnout J (Hrsg.) Thrombosis and Haemostasis 1987, University Press, Leuven, p 227
Bansal BC, Prakash C, Arya RK et al. (1978) Serum lipids, platelets and fibrinolytic activity in cerebrovascular disease. Stroke 9:137–139
Auff E, Zeiler K, Holzner F, Wimmer S, Deecke L (1986) Zum Stellenwert der oralen Kontrazeptiva als Risikofaktor zerebraler Gefäßerkrankungen. Wien Klin Wochenschr 98:304–310
Bogousslavsky J, Regli F (1987) Ischemic stroke in adults younger than 30 years of age. Arch Neurol 44:479–482
Boughner DR, Barnett HJM (1985) The enigma of the risk of stroke in mitral valve prolapse. Stroke 16:175–77
Candelise L, Bianchi F, Galligoni F et al. (1984) Italian multicenter study on reversible ischemic attacks: III — Influence of age and risk factors on cerebrovascular atherosclerosis. Stroke 15:379–382
Caronna JJ, Levy DE (1983) Clinical predictors of outcome in ischemic stroke. Neurol Clin 1:103–117
Cerebral Embolism Study Group (1984) Immediate anticoagulation of embolic stroke: brain hemorrhage and management options. Stroke 15:779–789
Dorfman LJ, Marshall WH, Enzmann DR (1979) Cerebral infarction and migraine: Clinical and radiological correlation. Neurol. 29:317–322
Faris AA, Hardin CA, Poser CM (1963) Pathogenesis of haemorrhagic infarction of the brain. Arch Neurol 9:468–476
Garcia JM (1985) Circulatory disorders and their effects on brain. In: Davis RL, Robertson DM. Textbook of Neuropathology. Williams & Wilkins, Baltimore, p 548
Goldstein M, Belis CL (1978) Part 1: Clinical stage. In: Cerebrovascular Disorders: Clinical and Research Classification WHO Health Classification) WHO Offset Publication No. 43, Geneva, p 10
Grans F, Rogers LR, Posner JB (1985) Cerebrovascular complications in patients with cancer. Medicine 64:16–35
Haglund O, Wibell L, Saldeen T (1985) Plasminogen activators and inhibitors of plasminogen activators in patients with deep venous thrombosis (DVT). Diurnal variation of the inhibitor. Thromb Haemostas 54:271–279
Hamsten A, Wiman B, DeFaire U, Blombäck M (1985) Increased plasma levels of a rapid inhibitor of tissue plasminogen activator in young survivors of myocardial infarction. N Engl J Med 313:1557–63
Hamsten A, Blombäck M, Wiman B et al. (1986) Haemostatic function in myocardial infarction. Br Heart J 55:58–66
Harenberg J, Staiger Ch, De Vries JX, Weber E, Zimmermann R, Schettler G (1985) The effects of a combination of cigarette smoking and oral contraception on coagulation and fibrinolysis in human females. Wien Klin Wochenschr 63:221–224
Hart RG, Miller VT (1983) Cerebral infarction in young adults: A practical approach. Stroke 14:110–114
Hindfelt B, Nilsson O (1977) Brain infarction in young adults. Acta Neurol Scand 55:145–157
Huber K, Resch I, Rosc D, Schuster E, Glogar DH, Binder BR (1987) Circadian variation of plasminogen activator inhibitor and the incidence of severe ischemic attacks in patients with coronary artery disease. Thromb Haemostas 58:66 (abstract 224)
Huber K, Rosc D, Resch I, Schuster E, Glogar DH, Binder BR (1988) Plasminogen activator inhibitor and tissue plasminogen activator levels in plasma of patients with unstable coronary artery disease. Thromb Haemost, in press
Jackson AC, Boughner DR, Barnett HJM (1984) Mitral valve prolapse and cerebral ischemic events in young patients. Neurology 34:784–787
Johnson SE, Skre H (1986) Transient cerebral ischemic attacks in the young and middle aged. Stroke 17:662–666
Juhan Vague I, Moerman B, DeCock F, Aillaud MF, Collen D (1984) Plasma levels of a specific inhibitor of tissue-type plasminogen activator (and urokinase) in normal and pathological conditions. Thromb Res 33:523–530
Juhan-Vague I, Valadier J, Alessi MC et al. (1987) Deficient t-PA release and elevated PA inhibito levels in patients with spontaneous or recurrent deep venous thrombosis. Thromb Haemostas 57:67–72
Kluft C, Verheijen JH, Rijken DC, Chang GTG, Jie AFH, Onkelinx C (1987) Diurnal fluctuations in the activity of the fast acting tPA inhibitor. In: Davidson JF, Donati MB, Coccheri S (eds) Progress in Fibrinolysis VII. Churchill Livingstone, Edinburgh London Melbourne New York, pp 117–119
Köhler M, Miyashita C (1988) Probleme bei der Messung von Parametern des fibrinolytischen Systems: Circadiane Rhythmik von Gewebe-Plasminogen Aktivator und Plasminogen Aktivator Inhibitor. Klin Wochenschr 66 (Suppl XII):62–67
Korninger C, Wagner O, Binder BR (1985) Tissue plasminogen activator inhibitor in human plasma: development of functional assay system and demonstration of a correlating Mr 50,000 antiactivator. J Lab Clin Med 105:718–24
Korninger C, Jäger R, Huber K, Lechner K (1988) Levels of plasminogen activator inhibitor in patients with angina pectoris. Klin Wochenschr 66 (Suppl XII):59–61
Lane DA, Wolff S, Ireland H, Gawel M, and Foadi M (1983) Activation of coagulation and fibrinolytic systems following stroke. Brit J Haematol 53:655–658
Lidegaard O, Soe M, Andersen MVN (1986) Cerebral thromboembolism among young women and men in denmark 1977–1982. Stroke 17:670–675
Longstreth WT, Swansson PD (1984) Oral contraceptives and stroke. Stroke 15:747–750
Lou HC, Nielsen JD, Bomholt A, Gormsen J (1977) Platelet hyperaggregability in young patients with completed stroke. Acta neurol Scand 56:326–334
Mettinger KL, Egbeng N (1982) A study of hemostasis in ischemic cerebrovascular disease: II. Abnormalities in vascular plasminogen activators, antiactivators, and alpha-2-antiplasmin. Thromb Res 26:203–210
Nilsson IM, Ljungner H, Tengborn L (1985) Two different mechanisms in patients with venous thrombosis and defective fibrinolysis: low concentration of plasminogen activator or increased concentration of plasminogen activator inhibitor. Br Med J 290:1453–55
Paramo JA, Colucci M, Collen D (1985) Plasminogen activator inhibitor in the blood of patients with coronary artery disease. Br Med J 291:574–575
Sloan MA (1987) Thrombolysis and stroke. Past and future. Arch Neurol 44:748–768
Snyder BD, Ramirez-Lassepas M (1980) Cerebral infarction in young adults. Stroke 11:149–153
Sörensen PS, Andersen LA, Gormsen J et al. (1983) Prognostic value of in vitro measurement of platelet aggregability and fibrinolytic activity in patients with reversible cerebral ischemic attacks. Europ Neurol 22:437–441
Spence JD, Delmaestro RF (1985) Hypertension in acute ischemic stroke: Treat. Arch Neurol 52:1000–1001
Tabaa MA, Snyder BD, Ramirez-Lassepas M, et al. (1986) Releasable tissue plasminogen activator in ischemic stroke. Ann Neurol 20:158
Tengborn L, Larsson SA, Hedner U, Nilsson IM (1981) Coagulation studies in children and young adults with cerebral ischemic episodes. Acta neurol scand 63:351–361
Vermylen JA, Chamone AF (1979) The role of the fibrinolytic system in thromboembolism. Progr Cardiovasc Diseases 21:255–66
Whisnant JP (1984) The decline of stroke. Stroke 15:160–168
Wojta J, Turcu L, Wagner OF, Korninger C, Binder BR (1987) Evaluation of fibrinolytic capacity by a combined assay system for t-PA antigen and t-PA function using monoclonal anti-t-PA antibodies. J Lab Clin Med 109:665–671
Yatsu FM, Zivin J (1985) Hypertension in acute ischemic stroke. Not to treat. Arch Neurol 52:999–1000
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Baumgartner, C., Huber, K., Holzner, F. et al. Untersuchung zur Frage von persistierenden Veränderungen der Fibrinolyseparameter t-PA und PAI bei Patienten nach juvenilem ischämischen cerebralem Insult. Klin Wochenschr 66, 1110–1115 (1988). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01727845
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01727845