Abstract
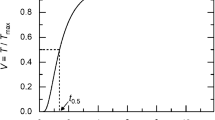
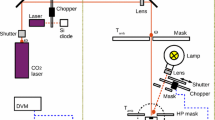
When using an infrared detector to measure temperature changes as in the case of the flash technique, the effects of detector nonlinearity can have drastic effects on the experimental data. In the flash technique, the detector nonlinearity tends to shift the calculated half-time to larger values, resulting in underpredicted values of thermal diffusivity especially in experiments performed at room temperature. In order to predict the error in the diffusivity calculation, the nonlinear relationship between the detector signal and the temperature change was developed into a Taylor series expansion used in the flash technique's mathematical model. The nonlinear detector model proves to yield accurate correction factors for the presently calculated values of diffusivity. In order to utilize the model, it is necessary to estimate the maximum temperature rise of the back surface and the degree of detector nonlinearity.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
W. J. Parker, R. J. Jenkins, C. P. Butler, and G. L. Abbott, J. Appl. Phys. 32:1679 (1961).
R. E. Taylor and K. D. Maglić, in Compendium of Thermophysical Property Measurement Methods, Vol. I, K. D. Maglić, A. Cezairliyan, and V. E. Peletsky, eds. (Plenum Press, New York, 1984), pp. 305–336.
L. M. Clark III and R. E. Taylor, J. Appl. Phys. 46:4584 (1975).
R. C. Heckman, J. Appl. Phys. 44:1455 (1973).
M. G. Dreyfus, Appl. Opt. 2(11):1113 (1963).
R. E. Taylor and L. M. Clark III, High Temp. High Press. 6:65 (1974).
R. E. Taylor, H. Groot, and R. L. Shoemaker, in 17 Biennial Conference on Carbon, University of Kentucky, Lexington (1985).
R. E. Taylor, in Thermal Conductivity, Vol. 19, D. W. Yarbrough, ed. (Plenum Press, New York, 1988), pp. 407–409.
D. P. H. Hasselman and K. Y. Donaldson, Int. J. Thermophys. (in press).
D. P. H. Hasselman and G. Mekel, J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 72:967 (1989).
R. Siegel and J. R. Howell, Thermal Radiation Heat Transfer (McGraw-Hill, New York, 1981), Chaps. 2 and 13.
J. J. Hoefler, M.S.M.E. thesis (Purdue University, West Lafayette, Ind., Dec. 1989), Chap. 2, App. B.
P. Cielo, J. Appl. Phys. 56:230 (1984).
H. Groot, in Thermal Conductivity, Vol. 20, D. P. H. Hasselman and J. R. Thomas, Jr., eds. (Plenum Press, New York, 1989), pp. 361–363.
G. C. Wei and J. M. Robbins, Bull. Am. Ceram. Soc. 64:691 (1985).
W. D. Lawson and J. W. Sabey, in Research Techniques in Nondestructive Testing, Vol. I, R. S. Sharpe, ed. (Academic Press, New York, 1970), pp. 443–454.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hoefler, J.J., Taylor, R.E. Effects of infrared detector nonlinearity on thermal diffusivity measurements using the flash method. Int J Thermophys 11, 1099–1110 (1990). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00500563
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00500563