Abstract
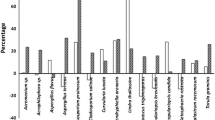
Bacteria and fungi associated with the marine wood-boring isopods Limnoria lignorum and Sphaeroma serratum, and with their wood burrows and seawater were investigated. Plate counts using nutrient agar and Czapex Dox agar media in natural and in artificial seawater were used. The diversity and number of bacteria associated with the two isopods were much higher than those associated with wood or seawater, whereas the opposite was true for fungi. The hydrolytic activity of the predominant genera on carboxymethylcellulose and on different types of wood was investigated. The magnitude of fungal cellulase activity exceeded that of bacteria. Activities of bacterial extracellulases exceeded those of intracellulases, while the opposite was observed for fungi. Cellulolytic activity of the predominant isolates biodegraded labkh, peach, white oak and mahogany in decreasing order of activity. Evidence provided by the cellulolytic activities, detected in woodcontaining cultures, suggests that the predominant micro-organisms isolated may play an important role in the woodboring process. Specimens used in the present study were collected from Port Fouad at Port Said Harbour, Egypt.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ball AS, McCarthy AJ (1988) Saccharification of straw by actinomysete enzymes. J gen Microbiol 134:2139–2147
Bernier R, Stutzenberger F (1989) B-glucosidase biosynthesis in Thermomonospora curvata. Mircen J 5:15–25
Bisaria VS, Ghose TK (1981) Biodegradation of cellulosic materials: substrates, microorganisms enzymes and products. Enzyme microb Technol 3:90–104
Boyle PJ, Mitchell R (1978) Absence of microorganisms in crustacean digestive tracts. Science, NY 200:1157–1159
Boyle PJ, Mitchell R (1981a) The function of microorganisms in marine wood boring process. Oceans 9:526–531
Boyle PJ, Mitchell R (1981b) External microflora of a marine woodboring isopod. Appl envirl Microbiol 42:720–729
Boyle PJ, Mitchell R (1982) Intestinal microflora in the deep-sea isopod Bathynomus giganteus. Curr Microbiol 7:311–314
Carlucci AF, Shimp SL (1974) Isolation and growth of a marine bacterium in low concentration of substrate. In: Colwell RR, Morita RY (eds) Effect of the ocean environment on microbial activity. Academic Press Inc, New York, pp 363–367
Clarke RTJ (1977) The gut and its microorganisms. In: Clarke RTJ, Bouchop T (eds) Microbial ecology of the gut. Academic Press Inc, New York, pp 35–72
Claus D, Berkeley RCW (1986) Genus Bacillus Cohn 1873, 174. In: Mair PHA, Sharpe NS, Holt ME (eds) Bergey's manual of systematic bacteriology. 2. Williams and Wilkins, Baltimore, pp 1105–1139
Eriksson EE (1979) Biosynthesis of polysaccharases. In: Berkeley RCW, Gooday GW, Ellwood DC (eds) Microbial polysaccharides and polysaccharases. Academic Press, London, pp 285–296
Gilman JC (1957) A manual of soil fungi. Iowa State University Press, Iowa, USA
Hartenstein R (1964) Feedings, digestion, glycogen and the environmental conditions of the digestive system in Oniscus asellus. J Ins Physiol 10:611–621
Hendrie MS, Shewan JM (1979) The identification of pseudomonads. In: Skiner FA, Lovelock DW (eds) Identification methods for microbiologists, 2nd edn. Academic Press, London, pp 1–14
Jones DA (1971) The systematic and ecology of some sand beach isopods (Crustacea: Eurydicidae) from the cost of Kenya. J Zool, London 165:201–227
Jones DA, Icelly JD (1981) Excirolana bowmani, a new mangrove boring isopod from Kenya (Isopoda, Cirolamidae). Curstaceana 40:266–271
Jones NS (1974) The ecology of the amphipoda of the south of the isle of Man. J mar Biol Ass UK 27:400–439
Juni E (1986) Genus Acinetobacter Brisou and Pevot 1954, 727. In: Krieg NR, Holt ME (eds) Bergey's manual of systematic bacteriology. 1. Williams and Wilkins Baltimore, pp 303–307
Kaneko T, Colwell RR (1975) Adsorption of Vibrio parahaemolyticus onto chitin and copepods. Appl Microbiol 29:269–274
Keddie RM, Shaw S (1986) Genus Kurthia Trevisan 1885. In: Mair PHA, Sharpe NS, Holt ME (eds) Bergey's manual of systematic bacteriology. 2. Williams and Wilkins, Baltimore, pp 1255–1258
Keddie RM, Collins MD, Jones D (1986) Genus Arthrobacter Conn and Dimmick 1947, 300. In: Mair PHA, Sharpe NS, Holt ME (eds) Bergey's manual of systematic bacteriology. 2. Williams and Wilkins, Baltimore, pp 1288–1300
Kocur M (1986) Genus III. Planococcus Migula 1894, 236. In: Mair PHA, Sharpe NS, Holt ME (eds) Bergey's manual of systematic bacteriology. 2. Williams and Wilkins. Baltimore, pp 1011–1013
Lang K (1949) Contribution to the systematics and synonymies of the Tanaidaceae. Ark Zool 420:1–14
McCarthy AJ (1987) Lignocellulose-degrading actinomycetes. Fedn eur microbiol Soc (FEMS) Microbiol. Rev 46:145–163
Miller GL (1959) Use of dinitrosalicylic acid reagent for determination of reducing sugar. Analyt Chem 31:238–244
Nair NB (1959) The marine timber-boring mollusces and crustaceans of Western Norway. Espergrend 25:1
Plleroni NT (1984) Genus Pseudomonas Migula 1894, 237. In: Krieg NA, Holt ME (eds) Bergey's manual of systematic bacteriology. 1. Williams and Wilkins, Baltimore, pp 144–199
Raper KB, Fennell DI (1965) The Genus Aspergillus. Williams and Wilkins, Baltimore
Ray DL, Julian JR (1952) Occurrence of cellulase in Limnoria. Nature, Lond 169:32
Rizk ST (1988) Surveillance and ecological studies on crustacea associated with fouling in Suez Canal. MSc thesis, Faculty of Science, Tanta University, Tanta, Egypt
Rodina AG (1972) Methods in aquatic microbiology. University Park Press, Baltimore
Samson RA (1979) A compilation of the Aspergilli described since 1965. Stud mycol 18:39
Sanyal A, Kundu AK, Dube SY, Dube DK (1988) Extracellular cellulolytic enzyme system of Aspergillus japonicus: 2. Purification and characterization of an inducible extracellular beta-glucosidase. Enzyme Microb Technol 10:91–99
Sletter TD, Boyle PJ, Cundell AM, Mitchell R (1978) Relationships between marine microorganisms and the wood-boring isopod Limnoria tripunctata. Mar Biol 45:329–336
Turner RD (1955) The family pholadidae in the Western Atlantic Eastern Pacific. Part II. Martesinae, Jouannetinae and Xylophagidae. Johnsonia 3:34
Unkles SE (1977) Bacterial flora of the sea urchin Echinus asculentus. Appl envirl Micribiol 34:347–350
Wakarchuk WW, Kilburn DG, Miller RC, Wassen RAJ (1984) The preliminary characterization of the beta-glucosidases of Cellulomonas firmi. J Gen Microbiol 130:1385–1389
Wilson DB (1988) Cellulases of Thermomonospora fusca. Meth Enzym 160:314–323
Zachary A, Colwell RR (1978) Gut-associated microflora of Limnoria tripunctata in marine creoste-treated wood. Pillings. Nature, Lond 282:716–717
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Communicated by T. M. Fenchel, Helsingør
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
El-Shanshoury, A.R., Mona, M.H., Shoukr, F.A. et al. The enumeration and characterization of bacteria and fungi associated with marine wood-boring isopods, and the ability of these microorganisms to digest cellulose and wood. Marine Bioliogy 119, 321–326 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00347528
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00347528