Abstract
This paper launches concepts instrumental to environmental impact assessment (EIA) studies on hydropower schemes and lake regulations. Norwegian hydro-electric lakes (hydrolakes) and their environmental features are described, and evaluated against non-manipulated waters. A tentative classification of hydrolakes vs. natural waters is proposed. The need for a multiple approach to habitat classification is emphasized. Recommendations for future biological impact assessment approaches are suggested.
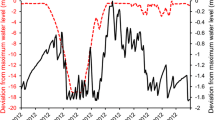
Hydrolakes differ broadly from natural lakes by combining physical features not ordinarily co-occurring in non-manipulated water bodies. Storage type hydrolakes (reservoirs) feature winter draw-downs and enhancement of yearly level fluctuations; whereas other types of hydro-electric lakes have elevated water levels throughout winter. Hydrochemistry and optics of the studied hydrolakes exhibited no clear differences to non-impacted Norwegian inland waters. All lakes had signs of sublacustrine erosional activity related to internal waves and thermocline movements.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aass, P., 1973. Some effects of lake impoundment on salmonids in Norwegian hydroelectric reservoirs. Abstr. Uppsala Diss. 234, 14 pp.
Aass, P., 1986. Utvidet senkning i regulerte innsjøef - effekt på fisket. [In Norwegian]. Fauna 39: 85–91.
Baxter, R. M., 1977. Environmental effects of dams and impoundments. Annu. Rev. Ecol. Syst. 8: 255–283.
Bodaly, R. A., D. M. Rosenberg, M. N. Gaboury, R. E. Hecky, R. W. Newbury & K. Patalas, 1984. Ecological effects of hydroelectric development in Northern Manitoba, Canada: The Churchill — Nelson River Diversion. In Sheehan, P. J., D. R. Miller, G. C. Butler & P. Bourdeau (eds), Effects of Pollutants at the Ecosystem level. Wiley, London: 274–309.
Brillinger, D. R., 1981. Time Series: Data Analysis and Theory. Holden-Day, San Francisco, 540 pp.
Canfield, D. E., K. A. Langeland, S. B. Linda & W. T. Hailer, 1985. Relations between water transparency and maximum depth of macrophyte colonization in lakes. J. Aquat. Plant Manage. 23: 25–28.
Canter, L. W., 1985. Environmental impact of water resources projects. Lewis Publishers, Chelsea, Michigan, 352 pp.
Chambers, P. A. & J. Kalff, 1985. Depth distribution and biomass of submersed aquatic macrophyte communities in relation to Secchi depth. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 42: 701–709.
Cyberski, J. 1973. Erosion of banks of storage reservoirs in Poland. Hydrol. Sci. Bull. 18: 317–320.
Duarte, C. M., J. Kalff & R. H. Peters, 1986. Patterns in biomass and cover of aquatic macrophytes in lakes. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 43: 1900–1908.
Gerritsen, J. & B. C. Patten, 1985. System theory formulation of ecological disturbance. Ecol. Modelling 29: 383–397.
Godshalk, G. L. & J. W. Barko, 1985. Vegetative succession and decomposition in reservoirs. In Gunnison, D. (ed.), Microbial Processes in Reservoirs. Junk, Dordrecht: 59–77.
Grahn, O., 1985. Macrophyte biomass and production in Lake Gårdsjön — an acidified clearwater lake in SW Sweden. Ecol. Bull. 37: 203–212.
Granju, J. P., J. Garrison & J. Price, 1973. Hydraulic transients in man-made lakes. In: Ackermann, W. C., G. F. White & E. B. Worthington (eds), Man-made Lakes: Their Problems and Environmental Effects. Geophysical Monograph Series 17, American Geophysical Union, Washington, D.C.: 320–326.
Grelsson, G., 1986. Vegetational changes on two eroding banks of a short-term regulated river reservoir in northern Sweden. Nord. J. Bot. 5: 581–614.
Grimås, U., 1962. The effect of increased water level fluctuation upon the bottom fauna in Lake Blåsjön, northern Sweden. Rept. Inst. Freshwater. Res. Drottningholm 44: 14–41.
Grime, J. P., 1979. Plant strategies and vegetation processes. Wiley, Chichester, 222 pp.
Håkanson, L., 1977. The influence of wind, fetch, and water depth on the distribution of sediments in Lake Vänern, Sweden. Can. J. Earth Sci. 14: 397–412.
Håkanson, L., 1981. On lake bottom dynamics — the energytopography factor. Can. J. Earth Sci. 18: 899–909.
Håkanson, L., 1982. Bottom dynamics of lakes. Hydrobiologia 91: 9–22.
Hecky, R. E., 1984. Thermal and optical characteristics of Southern Indian Lake before, during, and after impoundment and Churchill River diversion. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 41: 579–590.
Hecky, R. E. & G. K. McCullough, 1984. Effect of impoundment and diversion on the sediment budget and nearshore sedimentation of Southern Indian Lake. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 41: 567–578.
Hecky, R. E., R. W. Newbury, R. A. Bodaly, K. Patalas & D. M. Rosenberg, 1984. Environmental impact prediction and assessment: the Southern Indian Lake experience. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 41: 720–732.
Holtan, H., 1973. Temperature distribution and water circulation in Lake Mjøsa. Proc. Helsinki Symposium. IAHS Publ. 109: 42–48.
Howard-Williams, C. & W. F. Vincent, 1984. Optical properties of New Zealand lakes. I. Attenuation, scattering, and a comparison of downwelling and scalar irradiances. Arch. Hydrobiol. 99: 318–330.
Huston, M., 1979. A general hypothesis of species diversity. Am. Nat. 113: 81–101.
Hutchinson, G. E., 1957. A Treatise on Limnology. I:1. Geography, Physics, and Chemistry. Wiley, New York, 672 pp.
Hutchinson, G. E., 1975. A Reatise on Limnology. 3. Limnological Botany. Wiley, New York, 660 pp.
Jenkins, G. M. & D. G. Watts, 1968: Spectral analysis and its applications. Holden-Day, San Francisco, 525.
Johnson, T. C., 1980. Sediment redistribution by waves in lakes, reservoirs and embayments. Proc. Symposium Surface Water Impoundments, Minneapolis 1980, ASCE Publ.: 1307–1317.
Kachugin, E. G., 1966. The destructive action of waves on the water reservoir banks. Proc. Symposium de Garda, IAHS Publ. 70: 511–517.
Keddy, P. A., 1982. Quantifying within-lake gradients of wave energy: interrelationships of wave energy, substrate particle size and shoreline plants in Axe Lake, Ontario. Aquat. Bot. 14: 41–58.
Keddy, P. A., 1983. Shoreline vegetation in Axe lake, Ontario: effects of exposure on zonation patterns. Ecology 64: 331–344.
Kirk, J. T. O., 1983. Light and Photosynthesis in Aquatic Systems. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, 401 pp.
Kirk, R. M. & P. R. Henriques, 1986. Physical and biological aspects of shoreline change: Lake Ohau, South Island, New Zealand. J. Shoreline Manage. 2: 305–326.
Komar, P. D., 1976. Beach Processes and Sedimentation. Prentice-Hall, Englewood Cliffs, New Jersey, 429 pp.
Kondrachev, N. E., 1966. Bank formation of newly established reservoirs. Proc. Symposium de Garda, IAHS Publ. 70: 804–811.
Kuusisto, E. [E.], 1984. Filling in the gap between hydrology and hydrobiology — the viewpoint of a hydrologist. Aqua Fenn. 14: 155–169.
Kuusisto, E. E., 1985. Lakes: Their physical aspects. In J. C. Rodda (ed.), Facets of Hydrology, II. Wiley, Chichester: 153–181.
Lindström, T., 1973. Life in a lake reservoir: fewer options, decreased production. Ambio 2: 145–153.
Liu, P. C., 1985. Testing parametric correlations for wind waves in the Great Lakes. J. Great Lakes Res. 11: 478–491.
Lohammar, G., 1965. The vegetation of Swedish lakes. Acta Phytogeogr. Suec. 50: 28–48.
Newbury, R. W. & G. K. McCullough, 1984. Shoreline erosion and restabilization on the Southern Indian Lake reservoir. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 41: 558–565.
Nilsson, C., 1981. Dynamics of the shore vegetation of a North Swedish hydro-electric reservoir during a 5-year period. Acta Phytogeogr. Suec. 69: 1–94.
Nilsson, C., 1984. Effects of stream regulation on riparian vegetation. In Lillehammer, A. & S. J. Saltveit (eds), Regulated rivers. Universitetsforlaget, Oslo: 93–106.
Nisbet, R. M. & W. S. C. Gurney, 1982. Modelling Fluctuating Populations. Wiley, Chichester, 379 pp.
Magadza, C. H. D., 1979. Physical and chemical ecology of six hydroelectric lakes on the Waikato River, 1970–72. New Zeal. J. Mar. Freshwater. Res. 13: 561–572.
Matarzin, Y. M. & I. A. Pechorkin, 1973. The role of hydrological and geological processes in the formation of shores and beds of large storage reservoirs. Proc. Helsinki Symposium, IAHS Publ. 109: 423–427.
Mortimer, C. H., 1961. Motion in thermoclines. Verh. int. Ver. Limnol. 14: 79–82.
Mortimer, C. H., 1974. Lake hydrodynamics. Mitt. int. Ver. Limnol. 20: 124–197.
Patalas, K., 1984. Mid-summer mixing depths of lakes of different latitudes. Verh. int. Ver. Limnol. 22: 97–102.
Pimm, S. L., 1984. The complexity and stability of ecosystems. Nature (London) 307: 321–326.
Quennerstedt, N., 1958. Effects of water level fluctuations on lake vegetation. Verh. int. Ver. Limnol. 13: 901–906.
Ragotzkie, R. A., 1978. Heat budgets of lakes. In Lerman, A. (ed.), Lakes-chemistry, geology, physics. Springer-Verlag, New York: 1–19.
Rohde, W., 1964. Effects of impoundment on water chemistry and plankton in Lake Ransaren (Swedish Lappland). Verh. int. Ver. Limnol. 15: 437–443.
Rørslett, B., 1984. Environmental factors and aquatic macrophyte response in regulated lakes — a statistical approach. Aquat. Bot. 19: 199–220.
Rørslett, B., 1985a. Regulation impact on submerged macrophytes in the oligotrophic lakes of Setesdal, South Norway. Verh. int. Ver. Limnol. 22: 2927–2936.
Rørslett, B., 1985b. Death of submerged macrophytes — actual field observations and some implications. Aquat. Bot. 22: 7–19.
Rørslett, B., 1987a. Statistics of the underwater light field: an empirical model. Int. Revue ges. Hydrobiol. 72: 1–25.
Rørslett, B., 1987b. A generalized spatial niche model for aquatic macrophytes. Aquat. Bot. 29: 63–81.
Rørslett, B., 1987c. Niche statistics of submerged macrophytes in Tyrifjord, a large oligotrophic Norwegian lake. Arch. Hydrobiol. (in press).
Rørslett, B., 1987d. Niche extension of aquatic macrophytes in hydrolakes: predictive assessment of environmental impacts. Submitted to Int. Revue ges. Hydrobiol.
Rørslett, B. & M. Agami, 1987. Downslope limits of aquatic macrophytes: a test of the transient niche hypothesis. Aquat. Bot. 29: 83–95.
Rørslett, B., D. Berge & S. W. Johansen, 1986. Lake enrichment by submersed macrophytes: a Norwegian whole-lake experience with Elodea canadensis. Aquat. Bot. 26: 325–340.
Rørslett, B., N. W. Green & K. Kvalvågnæs, 1978. Stereophotography as a tool in aquatic biology. Aquat. Bot. 4: 73–81.
Rott, E., 1986. The light climate of a small deep lake (Piburger See, Austria) and its influence on phytoplankton production. Arch. Hydrobiol. 107: 89–117.
Rustamov, S. G. & S. B. Kchalilov, 1973. The shore dynamics of a mountain plain reservoir of the Azerbaijan SSR. Proc. Helsinki Symposium, IAHS Publ. 109: 417–422.
Ryder, R. A., 1978. Ecological heterogeneity between north-temperate reservoirs and glacial lake systems due to differing succession rates and cultural uses. Verh. int. Ver. Limnol. 20: 1568–1574.
Rykiel, E. J., 1985. Towards a definition of ecological disturbance. Austr. J. Ecol. 10: 361–365.
Sand-Jensen, K. & M. Søndergaard, 1981. Phytoplankton and epiphyte development and their shading effect on submerged macrophytes in lakes of different nutrient status. Int. Revue ges. Hydrobiol. 66: 529–552.
Sly, P. G., 1978. Sedimentary processes in lakes. In Lerman, A. (ed.), Lakes — chemistry, geology, physics. Springer-Verlag, New York: 65–89.
Smith, I. R. & I. J. Sinclair, 1972. Deep water waves in lakes. Freshwat. Biol. 2: 387–399.
Spence, D. H. N., 1982. The zonation of plants in freshwater lakes. Adv. Ecol. Res. 12: 37–125.
Statistisk Sentralbyrå, 1983. Naturressurser 1982. (Norwegian Nature Resources 1982. In Norwegian). Central Bureau of Statistics of Norway, Report 83/1: 1–62.
Thunmark, S., 1931. Der See Fiolen und seine Vegetation. Acta Phytogeogr. Suec. 2: 1–198.
Vogt, H., 1978. An ecological and environmental survey of the humic man-made lakes in Finland. Aqua Fenn. 8: 12–24.
Wassén, G., 1966. Gardiken. Vegetation und Flora eines lapplän-dischen Seeufers. K. Sv. Vetenskapsakad. Avh. Naturskyddsärend 22: 1–142.
Welch, P. D., 1967. The use of fast Fourier transform for the estimation of power spectra: a method based on time averaging over short, modified periodograms. IEEE Transactions on Audio and Electro-acoustics, Vol. AU-15, no.2, June 1967.
Wright, R. F., 1984. Water chemistry: Interaction of stream regulation and acid precipitation. In Lillehammer, A. & S. J. Saltveit (eds), Regulated Rivers. Universitetsforlaget, Oslo: 71–80.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rørslett, B. An integrated approach to hydropower impact assessment. I. Environmental features of some Norwegian hydro-electric lakes. Hydrobiologia 164, 39–66 (1988). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00014349
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00014349