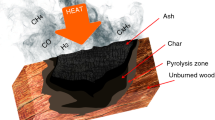
Abstract
Uncontrolled fires cause much loss of human life and property damage every year. Fire in simple terms is the consequence of complex chemical and physical reactions induced by heating materials to their respective ignition temperatures. The growth and development of a fire can be represented by a number of stages or states, i.e. ignition, fire growth, fully developed fire, decay and finally extinction. At each stage in the progress of a fire, many hazards usually in the form of heat energy and combustion products are generated which may pose a threat to life and property. Generally, the fire hazards associated with material are referred to as ignitability, flame spread, heat release, smoke production, toxicity and corrosivity. However, the fire hazard associated with a material is not only dependent on the nature of the materials but is also a function of the environment in which the fire occurs, i.e. ventilation rates and geometry of the enclosed space as well as the orientation of the material. Different end-use applications of the same material or component may create different fire hazards.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
The SFPE Handbook of Fire Protection Engineering, (1995) 2nd edn, National Fire Protection Association, Quincy, MA, USA.
Scudamore, M.J., Briggs, R.J. and Prager, F.H. (1991) Fire and Materials, 15, 65–84.
Zhang, J., Shields, T.J. and Silcock, G.W.H. (1996) Proceedings of Interflam’96, Interscience Communications, London, pp. 853–857.
Gad, S.C. and Anderson, R.C. (eds) (1990) Combustion Toxicology, CRC Press, Boca Raton, FL.
Kessel, S.L., Rogers, C.E. and Bennett Jr, J.G. (1994) J. Fire Sci., 12, 197–233.
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 1999 Springer Science+Business Media Dordrecht
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Shields, T.J., Zhang, J. (1999). Fire hazard with polypropylene. In: Karger-Kocsis, J. (eds) Polypropylene. Polymer Science and Technology Series, vol 2. Springer, Dordrecht. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-94-011-4421-6_34
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-94-011-4421-6_34
Publisher Name: Springer, Dordrecht
Print ISBN: 978-94-010-5899-5
Online ISBN: 978-94-011-4421-6
eBook Packages: Springer Book Archive