Summary
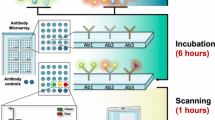
The sandwich ELISA microarray is a powerful screening tool in biomarker discovery and validation because of its ability to simultaneously probe for multiple proteins in a miniaturized assay. The technical challenges of generating and processing the arrays are numerous. However, careful attention to possible pitfalls in the development of one’s antibody microarray assay can overcome these challenges. In this chapter, we describe in detail the steps that are involved in generating a reliable and reproducible sandwich ELISA microarray assay.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Copland JA, Davies PJ, Shipley GL, Wood CG, Luxon BA, Urban RJ. The use of DNA microarrays to assess clinical samples: the transition from bedside to bench to bedside. Recent Prog Horm Res 2003;58:25–53.
Frolov AE, Godwin AK, Favorova OO. [Differential gene expression analysis by DNA microarrays technology and its application in molecular oncology.] Mol Biol (Mosk) 2003;37(4):573–584.
Sevenet N, Cussenot O. DNA microarrays in clinical practice: past, present, and future. Clin Exp Med 2003;3(1):1–3.
Finnskog D, Jaras K, Ressine A, et al. High-speed biomarker identification utilizing porous silicon nanovial arrays and MALDI-TOF mass spectrometry. Electrophoresis 2006;27(5–6):1093–1103.
Ho L, Sharma N, Blackman L, Festa E, Reddy G, Pasinetti GM. From proteomics to biomarker discovery in Alzheimer‘s disease. Brain Res Brain Res Rev 2005;48(2):360–369.
Hudelist G, Pacher-Zavisin M, Singer CF, et al. Use of high-throughput protein array for profiling of differentially expressed proteins in normal and malignant breast tissue. Breast Cancer Res Treat 2004;86(3):281–291.
Zangar RC, Varnum SM, Covington CY, Smith RD. A rational approach for discovering and validating cancer markers in very small samples using mass spectrometry and ELISA microarrays. Dis Markers 2004;20(3):135–148.
Angenendt P, Glokler J, Sobek J, Lehrach H, Cahill DJ. Next generation of protein microarray support materials: evaluation for protein and antibody microarray applications. J Chromatogr A 2003;1009(1–2):97–104.
Haab BB, Geierstanger BH, Michailidis G, et al. Immunoassay and antibody microarray analysis of the HUPO Plasma Proteome Project reference specimens: systematic variation between sample types and calibration of mass spectrometry data. Proteomics 2005;5(13):3278–3291.
Miller JC, Zhou H, Kwekel J, et al. Antibody microarray profiling of human prostate cancer sera: antibody screening and identification of potential biomarkers. Proteomics 2003;3(1):56–63.
Woodbury RL, Varnum SM, Zangar RC. Elevated HGF levels in sera from breast cancer patients detected using a protein microarray ELISA. J Proteome Res 2002;1(3):233–237.
Haab BB, Zhou H. Multiplexed protein analysis using spotted antibody microarrays. Methods Mol Biol 2004;264:33–45.
Wingren C, Borrebaeck CA. High-throughput proteomics using antibody microarrays. Expert Rev Proteomics 2004;1(3):355–364.
Rucker VC, Havenstrite KL, Herr AE. Antibody microarrays for native toxin detection. Anal Biochem 2005;339(2):262–270.
Gehring AG, Albin DM, Bhunia AK, Reed SA, Tu SI, Uknalis J. Antibody microarray detection of Escherichia coli O157:H7: quantification, assay limitations, and capture efficiency. Anal Chem 2006;78(18):6601–6607.
Hamelinck D, Zhou H, Li L, et al. Optimized normalization for antibody microarrays and application to serum-protein profiling. Mol Cell Proteomics 2005;4(6):773–784.
Poetz O, Ostendorp R, Brocks B, et al. Protein microarrays for antibody profiling: specificity and affinity determination on a chip. Proteomics 2005;5(9):2402–2411.
Varnum SM, Woodbury RL, Zangar RC. A protein microarray ELISA for screening biological fluids. Methods Mol Biol 2004;264:161–172.
Knecht BG, Strasser A, Dietrich R, Martlbauer E, Niessner R, Weller MG. Automated microarray system for the simultaneous detection of antibiotics in milk. Anal Chem 2004;76(3):646–654.
Pavlickova P, Schneider EM, Hug H. Advances in recombinant antibody microarrays. Clin Chim Acta 2004;343(1–2):17–35.
Kusnezow W, Hoheisel JD. Antibody microarrays: promises and problems. Biotechniques 2002;Suppl:14–23.
Steinhauer C, Wingren C, Khan F, He M, Taussig MJ, Borrebaeck CA. Improved affinity coupling for antibody microarrays: engineering of double-(His)6-tagged single framework recombinant antibody fragments. Proteomics 2006;6(15):4227–4234.
Brueggemeier SB, Kron SJ, Palecek SP. Use of protein-acrylamide copolymer hydrogels for measuring protein concentration and activity. Anal Biochem 2004;329(2):180–189.
Kusnezow W, Hoheisel JD. Solid supports for microarray immunoassays. J Mol Recognit 2003;16(4):165–176.
Stillman BA, Tonkinson JL. FAST slides: a novel surface for microarrays. Biotechniques 2000;29(3):630–635.
Frederix F, Bonroy K, Reekmans G, et al. Reduced nonspecific adsorption on covalently immobilized protein surfaces using poly(ethylene oxide) containing blocking agents. J Biochem Biophys Methods 2004;58(1):67–74.
Danczyk R, Krieder B, North A, Webster T, HogenEsch H, Rundell A. Comparison of antibody functionality using different immobilization methods. Biotechnol Bioeng 2003;84(2):215–223.
Lee Y, Lee EK, Cho YW, et al. ProteoChip: a highly sensitive protein microarray prepared by a novel method of protein immobilization for application of protein-protein interaction studies. Proteomics 2003;3(12):2289–2304.
Haab BB. Methods and applications of antibody microarrays in cancer research. Proteomics 2003;3(11):2116–2122.
Olle EW, Sreekumar A, Warner RL, et al. Development of an internally controlled antibody microarray. Mol Cell Proteomics 2005;4(11):1664–1672.
Nielsen UB, Geierstanger BH. Multiplexed sandwich assays in microarray format. J Immunol Methods 2004;290(1–2):107–120.
Geierstanger BH, Saviranta P, Brinker A. Antibody microarrays using resonance light-scattering particles for detection. Methods Mol Biol 2006;328:31–50.
Saviranta P, Okon R, Brinker A, Warashina M, Eppinger J, Geierstanger BH. Evaluating sandwich immunoassays in microarray format in terms of the ambient analyte regime. Clin Chem 2004;50(10):1907–1920.
White AM, Daly DS, Varnum SM, Anderson KK, Bollinger N, Zangar RC. ProMAT: protein microarray analysis tool. Bioinformatics 2006;22(10):1278–1279.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2008 Humana Press, a part of Springer Science+Business Media, LLC
About this protocol
Cite this protocol
Gonzalez, R.M., Varnum, S.M., Zangar, R.C. (2008). Sandwich ELISA Microarrays: Generating Reliable and Reproducible Assays for High-Throughput Screens . In: Wang, F. (eds) Biomarker Methods in Drug Discovery and Development. Methods in Pharmacology and Toxicology™. Humana Press. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-59745-463-6_13
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-59745-463-6_13
Publisher Name: Humana Press
Print ISBN: 978-1-934115-23-7
Online ISBN: 978-1-59745-463-6
eBook Packages: Springer Protocols