Abstract
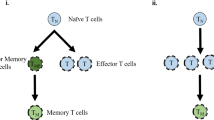
The correlation between properties of the T cell memory pool and the two regulatory mechanisms of cell death (apoptosis) and memory entry (differentiation) is investigated mathematically. Apoptosis of T cells occurs at the end of an immune response, removing unwanted activated T cells. T cells escaping apoptosis enter the memory pool composed of T cells specific for previously encountered antigens. We find that the relative efficiencies of these two pathways determine the clonal distribution and the long-term stability of the memory pool by regulating the number of new entries. The main result presented in this paper is that immunological memory of previously encountered pathogens cannot be erased by either severe or repeat infections with a particular pathogen (the diversity of the memory pool is ensured) only if apoptosis and/or memory differentiation are regulated by population dependent processes. Furthermore, vaccination properties are improved significantly by population dependent mechanisms and our mathematical analysis reveals that the T cell population must communicate with other parts of the immune system to ensure optimal performance of immunological memory.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abbas, A. K. (1996). Die and let live: eliminating dangerous lymphocytes. Cell 84, 655–657.
Ahmed, R. and D. Gray (1996). Immunological memory and protective immunity: understanding their relation. Science 272, 54–60.
Akbar, A. N., N. J. Brothwick, G. R. Wickremasinghe, P. Panayiotidis, D. Pilling, M. Bofill, S. Krajewski, J. C. Reed and M. Salmon (1996). Interleukin-2 receptor common γ-chain signalling cytokines regulate activated T cell apoptosis in response to growth factor withdrawal: selective induction of anti-apoptotic (bcl-2, bcl-x L ) but not pro-apoptotic (bax, bcl-x S ) gene expression. Eur. J. Immunol. 26, 294–299.
Akbar, A. N. and M. Salmon (1997). Cellular environments and apoptosis: tissue microenvironments control activated T cell death. Immunol. Today 18, 72–76.
Antia, R., S. S. Pilyugin and R. Ahmed (1998). Models of immune memory: on the role of cross-reactive stimulation, competition, and homeostasis in maintaining immune memory. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 95, 14926–14931.
Bell, E. B., S. M. Sparshott and C. Bunce (1998). CD4+ T cell memory, CD45R subsets and the persistence of antigen a unifying concept. Immunol. Today 19, 60–64.
Bradley, L. M. and S. R. Watson (1996). Lymphocyte migration into tissue: the paradigm derived from CD4 subsets. Curr. Opin. Immunol. 8, 312–320.
Broome, H. E., C. M. Dargan, E. F. Bessent, S. Krajewski and J. C. Reed (1995). Apoptosis and Bcl-2 expression in cultured murine splenic T cells. Immunology 84, 375–382.
DeBoer, R. J. and A. S. Perelson (1994). T cell repertoires and competitive exclusion. J. Theor. Biol. 169, 375–390.
Duke, R. C. and J. J. Cohen (1986). IL-2 addiction—withdrawal of growth-factor activates a suicide program in dependent T cells. Lymphokine Res. 5, 289–299.
Dutton, R. W., L. M. Bradley and S. L. Swain (1998). T cell memory. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 16, 201–223.
Freitas, A. A. and B. Rocha (2000). Population biology of lymphocytes: the flight for survival. Annu. Rev. Immunol 18, 83–111.
Gradstein, I. S. and I. M. Ryzhik Table of Integrals, Series and Products, 5th edn, San Diego: Academic Press.
Gray, D. and P. Matzinger (1991). T cell memory is short-lived in the absence of antigen. J. Exp. Med. 174, 969–974.
Greene, W. C. and W. J. Leonard (1986). The human interleukin-2 receptor. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 4, 69–95.
Hémar, A., A. Subtil, M. Lieb, E. Morelon, R. Hellio and A. Dautry-Varsat (1995). Endocytosis of interleukin-2 receptors in human T-lymphocytes—distinct intracellular localisation and fate of the receptor alpha-chain, beta-chain, and gamma-chain. J. Cell Biol. 129, 55–64.
Jacob, J. and D. Baltimore (1999). Modelling T cell memory by genetic marking of memory Tcells in vivo. Nature 399, 593–597.
Lau, L. L., B. D. Jamieson, T. Somasundaram and R. Ahmed (1994). Cytotoxic T cell memory without antigen. Nature 369, 648–652.
Lenardo, M., C. F. Ka-Ming, F. Hornung, H. McFarland, R. Siegel, J. Wang and L. Zheng (1999). Mature T lymphocyte apoptosis—immune regulation in a dynamic and unpredictable antigenic environment. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 17, 221–253.
Lynch, D. H., F. Ramsdell and M. R. Alderson (1995). Fas and FasL in the homeostatic regulation of immune responses. Immunol. Today 16, 569–574.
Mackay, C. R. (1993). Homing of naïve, memory and effector lymphocytes. Curr. Opin. Immunol. 5, 423–427.
Maple V release 5.1.
McHeyzer Williams, M. G. and M. M. Davis (1995). Antigen-specific development of primary and memory T cells in vivo. Science 268, 106–111.
McLean, A. R. (1994). Modelling T cell memory. J. Theor. Biol. 170, 63–74.
Michie, C. A., A. McLean, C. Alcock and P. C. L. Beverley (1992). Lifespan of human lymphocyte subsets defined by CD45 isoforms. Nature 360, 264–265.
Miyawaki, T., T. Uehara, R. Nibu, T. Tsuji, A. Yachie, S. Yonehara and N. Taniguchi (1992). Differential expression of apoptosis-related Fas antigen on lymphocyte subpopulations in human peripheral blood. J. Immunol. 149, 3753–3758.
Murali-Krishna, K. et al. (1998). Counting antigen-specific CD8 T cells: a reevaluation of bystander activation during viral infection. Immmunity 8, 177–187.
Murray, J. D. (1989). Mathematical Biology, Berlin: Springer.
Orteu, C. H., L. W. Poulter, M. H. A. Rustin, C. A. Sabin, M. Salmon and A. N. Akbar (1998). The role of apoptosis in the resolution of T-cell-mediated cutaneous inflammation. J. Immunol. 161, 1619–1629.
Pilling, D., A. N. Akbar, J. Girdlestone, C. H. Orteu, N. J. Borthwick, N. Amft, D. Schell-Toellner, C. D. Buckley and M. Salmon (1999). Interferon-β mediates stromal cell rescue of T cells from apoptosis. Eur. J. Immunol. 29, 1041–1050.
Schell-Toellner, D., D. Pilling, A. N. Akbar, D. Hardie, G. Lombardie, M. Salmon and J. M. Lord (1999). Inhibition of T cell apoptosis by IFN-β rapidly reverses nuclear translocation of protein kinases. Eur. J. Immunol. 29, 2603–2612.
Selin, L. K., K. Vergilis, R. M. Welsh and R. S. Nahill (1996). Reduction of otherwise remarkably stable virus-specific cytotoxic T lymphocyte memory by heterologous viral infections. J. Exp. Med. 183, 2489–2499.
Selin, L. K. and R. M. Welsh (1997). Cytolytikally active memory CTL present in lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus-immune mice after clearance of virus infection. J. Immunol. 158, 5366–5373.
Swain, S. L., H. Hu and G. Huston (1999). Class II-independent generation of CD4 memory T cells from effectors. Science 286, 1381–1383.
Takeda, S., H. R. Rodewald, H. Arakawa, H. Bluethmann and T. Shimizu (1996). MHC class II molecules are not required for survival of newly generated CD4+ T cells, but affect their long-term life span. Immunity 5, 217–228.
Tanchot, C., F. A. Lemonnier, B. Perarnau, A. A. Freitas and B. Rocha (1997). Differential requirements for survival and proliferation of CD8 naive or memory T cells. Science 276, 2075–2062.
Thomson, A. (1998). Cytokine Handbook, San Diego: Academic Press.
Tough, D. F., S. Siquan, Z. Xiaohong and J. Sprent (1999). Stimulation of naive and memory T cells by cytokines. Immunol. Rev. 170, 39–47.
Varga, S. M. and R. M. Welsh (1998). Stability of virus-specific CD4+ T cell frequencies from acute infection into long term memory. J. Immunol. 161, 367–374.
Waldmann, T. A. (1989). The multi-subunit interleukin-2 receptor. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 58, 875–911.
Webb, L. M. C., B. M. J. Focwell and M. Feldmann (1999). Putative role for interleukin-7 in the maintenance of the reciruclating naiveCD4+ T cell pool. Immunology 98, 400–405.
Zheng, L., C. L. Trageser, D. M. Willerford and M. J. Lenardo (1998). T cell growth cytokines cause the superinduction of molecules mediating antigen-induced T lymphocyte death. J. Immunol. 160, 763–769.
Zimmermann, C., A. Prévost-Blondel, C. Blaser and H. Pircher (1999). Kinetics of the reponse of naive and memory CD8 T cells to antigen: similarities and differences. Eur. J. Immunol. 29, 284–290.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Utzny, C., Burroughs, N.J. Stability of a diverse immunological memory is determined by T cell population dynamics. Bull. Math. Biol. 63, 685–713 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1006/bulm.2001.0242
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1006/bulm.2001.0242