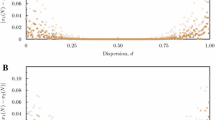
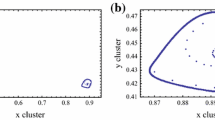
Abstract
We consider a spatially explicit metapopulation model with interaction among the two nearest neighbors to relate, with a simple mathematical expression, chaos in the local, uncoupled, populations, the degree of interaction among patches, size of the metapopulation, and the stability of the synchronized attractor. Since synchronism is strongly correlated with extinction, our results can provide useful information on factors leading to population extinction.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allen, J. C., W. M. Schaffer and D. Rosko (1993). Chaos reduces species extinction by amplifying local population noise. Nature 364, 229–232.
Commins, H. N., M. P. Hassel and R. M. May (1992). The spatial dynamics of host parasitoid systems. J. Anim. Ecol. 61, 735–748.
Doebeli, M. (1995). Dispersal and dynamics. Theor. Pop. Biol. 47, 82–106.
Gilpin, M. E. and I. Hanski (1991). Metapopulation Dynamics: Empirical and Theoretical Investigations, London: Academic Press.
Hanski, I. (1997). Metapopulation Dynamics: from Concepts and Observations to Predictive Models, London: Academic Press.
Hanski, I. and M. E. Gilpin (1997). Metapopulation Biology: Ecology Genetics and Evolution, London: Academic Press.
Hassel, M. P. (1975). Density dependence in single species populations. J. Anim. Ecol. 44, 283–295.
Hassel, M. P., H. N. Commins and R. M. May (1991). Spacial structure and chaos in insect population dynamics. Nature 353, 255–258.
Hassel, M. P., O. Miramontes, P. Rohani and R. M. May (1995). Appropriate formulations for dispersal in spatially structured models: comments on Bascompte & Solé. J. Anim. Ecol. 64, 662–664.
Hassel, M. P., J. N. Lawton and R. M. May (1976). Patterns of dynamical behavior in single-species populations. J. Anim. Ecol. 45, 471–486.
Hastings, A. (1992). Age dependent dispersal is not a simple process: density dependence, stability, and chaos. Theor. Pop. Biol. 41, 388–400.
Hastings, A. (1993). Complex interactions between dispersal and dynamics: lessons from coupled logistic equations. Ecology 74, 1262–1272.
Kaneko, K. (1989a). Pattern dynamics in spatiotemporal chaos. Physica D 34, 1–41.
Kaneko, K. (1989b). Spatiotemporal chaos in one-and two-dimensional coupled map lattices. Physica D 37, 60–82.
Kaneko, K. (1993). Theory and Applications of Coupled Map Lattices, New York: Wiley & Sons.
Lloyd, A. L. (1995). The coupled logistic map: a simple model for the effects of spatial heterogeneity on population dynamics. J. Theor. Biol. 173, 217–230.
May, R. M. (1974). Biological populations with nonoverlapping generations: stable points, stable cycles and chaos. Science 186, 645–647.
May, R. M. (1976). Simple mathematical models with very complicated dynamics. Nature 261, 459–469.
May, R. M. and G. F. Oster (1976). Bifurcations and dynamic complexity in simple ecological models. Am. Naturalist 110, 573–799.
Rohani, P., R. M. May and M. P. Hassel (1996). Metapopulation and equilibrium stability: the effects of spatial structure. J. Theor. Biol. 181, 97–109.
Ruxton, G. M. (1996a). Density-dependent migration and stability in a system of linked populations. Bull. Math. Biol. 58, 643–660.
Ruxton, G. M. (1996b). Synchronization between individuals and the dynamics of linked populations. J. Theor. Biol. 183, 47–54.
Solé, R. V. and J. P. G. Gamarra (1998). Chaos, dispersal and extinction in coupled ecosystems. J. Theor. Biol. 193, 539–541.
Solé, R. V. and J. Valls (1992a). Spiral waves, chaos and multiple attractors in lattice models of interaction populations. Phys. Lett. A 166, 123–128.
Solé, R. V. and J. Valls (1992b). On structural stability and chaos in biological systems. J. Theor. Biol. 155, 87–102.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Silva, J.A.L., De Castro, M.L. & Justo, D.A.R. Synchronism in a metapopulation model. Bull. Math. Biol. 62, 337–349 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1006/bulm.1999.0157
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1006/bulm.1999.0157