Collection
3D printing manufacturing technologies for the advancement of analytical sciences
- Submission status
- Closed
During the last decade, the use of additive manufacturing technologies, also known as 3D printing, has become very popular in industry and research institutions. For analytical chemistry applications, 3D printing can be adopted to fabricate a wide range of tools, from common laboratory hardware, to fluidic systems, sample treatment platforms, sensing structures, and complete fully functional analytical devices. One of the most important advantages of 3D printing over conventional fabrication processes, is the ability of rapid prototyping. Analytical systems and devices can be quickly fabricated (within hours), tested and validated against theoretical predictions without the need of tedious, costly and time-consuming outsourced manufacturing services. The range of materials and affordable machines is constantly increasing, providing to the analytical chemistry community with unprecedented freedom to implement innovative designs and original analytical strategies.
Editors
-
Adriano Ambrosi
Adriano Ambrosi is currently a Senior Scientist at the Institute of Materials Research and Engineering, A*STAR (Singapore), and adjunct Professor at Qingdao University of Science and Technology (China). His research interests include the use of nanomaterials for sensing and energy related applications and the fabrication of electrochemical devices by 3D printing. He published over 120 peer-reviewed articles (h-index: 52) and has been recognized as Highly Cited Researcher in 2018 by Clarivate Analytics.
Articles (12 in this collection)
-
-
3D-printed electrochemical platform with multi-purpose carbon black sensing electrodes
Authors
- Habdias A. Silva-Neto
- Anderson A. Dias
- Wendell K. T. Coltro
- Content type: Original Paper
- Published: 28 May 2022
- Article: 235

-
3D printed spinning cup-shaped device for immunoaffinity solid-phase extraction of diclofenac in wastewaters
Authors (first, second and last of 5)
- Enrique Javier Carrasco-Correa
- José Manuel Herrero-Martínez
- Manuel Miró
- Content type: Original Paper
- Open Access
- Published: 02 April 2022
- Article: 173
-
3D-printed electrochemical pestle and mortar for identification of falsified pharmaceutical tablets
Authors (first, second and last of 4)
- Ricoveer S. Shergill
- Anna Farlow
- Bhavik A. Patel
- Content type: Original Paper
- Published: 12 February 2022
- Article: 100
-
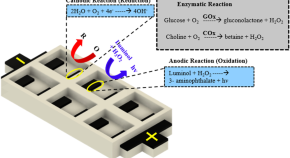
Multiplexed and simultaneous biosensing in a 3D-printed portable six-well smartphone operated electrochemiluminescence standalone point-of-care platform
Authors
- Manish Bhaiyya
- Prasant Kumar Pattnaik
- Sanket Goel
- Content type: Original Paper
- Published: 29 January 2022
- Article: 79
-
Influence of design and material characteristics on 3D printed flow-cells for heat transfer-based analytical devices
Authors (first, second and last of 12)
- Leonardo F. Figueiredo
- Felipe S. Vieira
- Marloes Peeters
- Content type: Original Paper
- Open Access
- Published: 24 January 2022
- Article: 73
-
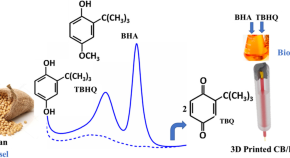
Electrochemical determination of several biofuel antioxidants in biodiesel and biokerosene using polylactic acid loaded with carbon black within 3D-printed devices
Authors (first, second and last of 4)
- Nélio I. G. Inoque
- Afonso F. João
- Rodrigo A. A. Muñoz
- Content type: Original Paper
- Published: 10 January 2022
- Article: 57
-
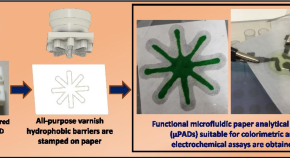
Simple, fast, and instrumentless fabrication of paper analytical devices by novel contact stamping method based on acrylic varnish and 3D printing
Authors (first, second and last of 5)
- Tatiane Alfonso de Araujo
- Natália Canhete de Moraes
- Bruno Gabriel Lucca
- Content type: Original Paper
- Published: 27 November 2021
- Article: 437
-
Lab-made 3D-printed accessories for spectroscopy and spectroelectrochemistry: a proof of concept to investigate dynamic interfacial and surface phenomena
Authors
- Joadir Humberto da Silva Junior
- Jailson Vieira de Melo
- Pollyana Souza Castro
- Content type: Short Communication
- Published: 27 October 2021
- Article: 394

-
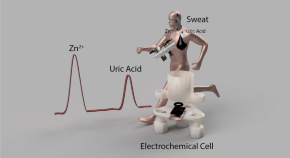
Additively manufactured carbon/black-integrated polylactic acid 3Dprintedsensor for simultaneous quantification of uric acid and zinc in sweat
Authors (first, second and last of 6)
- Vanessa N. Ataide
- Diego P. Rocha
- Lucio Angnes
- Content type: Original Paper
- Published: 19 October 2021
- Article: 388
-
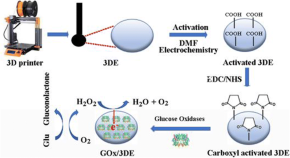
Covalently modified enzymatic 3D-printed bioelectrode
Authors
- Lujun Wang
- Martin Pumera
- Content type: Original Paper
- Published: 10 October 2021
- Article: 374
-
How 3D printing can boost advances in analytical and bioanalytical chemistry
Authors
- Adriano Ambrosi
- Alessandra Bonanni
- Content type: Review Article
- Published: 21 July 2021
- Article: 265



