Rapid formation of carbon nanotubes–natural rubber films cured with glutaraldehyde for reducing percolation threshold concentration
Authors (first, second and last of 9)
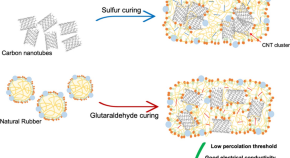
Collection
Ravindra Pratap Singh, Assistant Professor, Indira Gandhi National Tribal University, India. He has previously worked as a scientist at various esteemed laboratories globally, namely Sogang University, IGR Paris, etc. His work and research interests include biochemistry, biosensors, nanobiotechnology, electrochemistry, material sciences, and biosensors applications in biomedical, environmental, agricultural, and forensics.
Shyam S. Pandey, Professor, Kyushu Institute of Technology, Japan. His research interests deal with the Dye-Sensitized and Organic Solar Cells, Quantum Chemical Calculations, Organic Electronics & optoelectronics, Organic Conducting Polymers, Biosensors and Protein Biochips.
Jay Singh, Assistant Professor, Banaras Hindu University, India. He is actively engaged in the development of nanomaterials, based nanobiocomposite, conducting polymer and self-assembled monolayers based clinically important biosensors for estimation of bioanalyses such as cholesterol, xanthine, glucose, pathogens and pesticides/toxins using DNA and antibodies. He is also engaged in fabricating metal oxide-based biosensors for clinical diagnosis, food packaging applications, drug delivery, and tissue engineering applications.
