Abstract
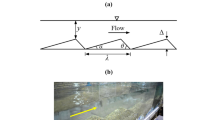
Due to disturbance in the equilibrium of an alluvial stream in such a manner that there is either a decrease in sediment load carrying capacity of the stream or increase in the rate of sediment loading over the sediment load carrying capacity of the alluvial stream, aggradation in such stream may occur. This paper presents a study dealing with problem of predicting aggradation due to sediment overloading for uniform sediment. The study is carried out to develop soft computing models using Artificial Neural Network (ANN) technique in Agile Neural Network software for predicting various aggradation elements, i.e. Aggradation length (L), maximum aggradation depth (z0) and depth of aggradation (z). The data collected from existing literature for the study were divided into two groups, and simultaneously, training and testing of the models were carried out. To select optimal network architecture, the approach of trial and error is used. After fixing, the number of iteration training of the networks for different activation functions is calculated. The statistical parameters like coefficient of correlation (R), determination coefficient (R2), mean square error (MSE), root mean square error (RMSE), mean absolute error (MAE), etc. are used to examine the performance of the models. The developed ANN models performed satisfactorily and the models were predicting data within ±30% error line.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Nagy HM, Watanabe KAND, Hirano M (2002) Prediction of sediment load concentration in rivers using artificial neural network model. J Hydraul Eng 128(6):588–595
Yitian LI, Gu RR (2003) Modeling flow and sediment transport in a river system using an artificial neural network. Environ Manag 31(1):0122–0134
Bhamidipathy S, Shen HW (1971) Laboratory study of degradation and aggradation. J Waterw Harb Coast Eng Div ASCE 97(WW4):615–630
Soni JP (1975) Aggradation of stream due to increase in sediment load. PhD thesis, University of Roorkee, Roorkee, India
Mehta PJ, Ranga Raju KG, Garde RJ (1979) Aggradation in alluvial stream due to withdrawal of water. In: Proceedings of the IAHR, 18th Congress
Sarda VK (1980) Prediction of transient bed profiles of a degrading stream. M.Tech thesis, Submitted to Punjab Agri. Univ., Ludhiana, India
Mehta PJ (1980) Study of aggradation in alluvial streams. PhD thesis, University of Roorkee, Roorkee, India
Yadav HS (1992) Bed level variations in alluvial streams. PhD thesis, University of Roorkee, India
Alves E, Cardoso AH (1999) Experimental study on aggradation. PhD thesis
Alves E, Cardoso AH (1999) Experimental study on aggradation. Int J Sediment Res 14(1)
Rahman A (2002) Hydraulic model study of bed level changes of alluvial river. MSc thesis, Department of Water Resources Engineering, BUET
Ataur RMd, Abdul MMd (2009) Numerical modeling of bed level changes of alluvial river. J Civil Eng (IEB) 3815364
Ansari Nadhir Ali IE, Moayad K, Sven K (2014) Experimental analysis of sediment deposition due to the effect of an upstream reservoir backwater. J Civil Eng Archit 8(9) (Serial No. 82):11851193. ISSN 19347359 USA
Andharia BR, Patel PL, Manekar VL (2018) Prediction of bed level variations in non-uniform sediment bed channel. Sadhana J (Springer Publication) 43:55
Andharia BR, Patel PL, Manekar VL, Porey PD (2018) Numerical and experimental studies in prediction of bed levels of aggrading channels. Current Sci J 114(8)
Culling WEH (1960) Analytical theory of erosion. J Geol 68(3)
De Vries M (1965) Considerations about non-steady bed-load transport in open channels. In: 11th congress, IAHR, vol 3, Paper No. 3.8
Tsuchiya A, Tshizaki K (1969) Estimation of rivers bed aggradation due to a dam. In: 13th congress, IAHR, vol 1, pp 297–304
Miloradov M, Muskatirovic D (1971) Calculation of river bed deformation in unsteady flow. In: 14 congress, IAHR, vol 3, pp 175–185
Swamee PK (1974) Analytical and experimental investigation of streambed variation upstream of a Dam. PhD thesis, Presented to University of Roorkee, India
De Vries M (1973) Dynamic model for channel bed degradation. In: International seminar on hydraulics of alluvial streams, IAHR, New Delhi
Bhallamudi SM, Chaudhary MH (1989) Numerical modeling of aggradation and degradation in alluvial channels. J Hydraul Eng 117(2):1145–1164
Chang CK, Azamathulla HM, Zakaria NA et al (2012) Appraisal of soft computing techniques in prediction of total bed material load in tropical rivers. J Earth Syst Sci 121:125–133
Boger Z, Guterman H (1997) Knowledge extraction from artificial neural network models. IEEE Int Conf Comput Cybern Simul 4(1997):3030–3035
Kurkova V (1992) Kolmogorov’s theorem and multilayer neural networks. Neural Netw 5:501–506
Ito Y (1994) Approximation capabilities of layered neural networks with sigmoid units on two layers. Neural Comput 6:1233–1243
Sarle W (1995) Stopped training and other remedies for overfitting. In: 27th symposium on the interface computing science and statistics, Pittsburgh
Witt SF, Witt CA (1995) Forecasting tourism demand: a review of empirical research. Int J Forecast 2(3):447–490
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2023 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Singapore Pte Ltd.
About this paper
Cite this paper
Das, A., Kumar, V., Maji, S. (2023). Prediction of Transient Bed Profiles in an Aggrading Stream Using ANN. In: Bhattacharjee, R., Neog, D.R., Mopuri, K.R., Vipparthi, S.K. (eds) Artificial Intelligence and Data Science Based R&D Interventions. NERC 2022. Springer, Singapore. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-99-2609-1_9
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-99-2609-1_9
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Singapore
Print ISBN: 978-981-99-2608-4
Online ISBN: 978-981-99-2609-1
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)