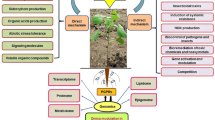
Abstract
Millets are worldwide used crops, and more than thousands of varieties of millet crops are cultivated globally because of their beneficial supplement to the human diet. Also, it is rich in micronutrients and protein. Shoot fly, stem borer, and pink borer are the major millets’ pests that cause agricultural and economic losses and increase the demand for chemical or synthetic pesticides for millet crop protection. These pesticides affect the environment by manipulating ecosystems. The focus on microbial bioremediation procedures has been increased to maintain sustainable growth and reduce the economic, environmental, and health effects due to the overuse of pesticides. It has been observed that the rhizosphere microbes are the most potent natural bioremediation agent. For example, bacterial genera like Rhizobium (strain RF12 and RZ11), Flavobacterium, Actinobacter, Pseudomonas, Bacillus, Agrobacterium sp., etc., are identified as pesticide-degrading strains. Many microbial and fungal species also degrade major harmful chemicals like acetochlor, carfentrazone, and clothianidin. These chemicals are converted into nontoxic chemical compounds by the enzymatic action of the microorganisms of the Rhizobiaceae group. The researchers are currently focusing on isolating these novel microbial strains. These strains’ detailed genetic and molecular studies will help to manipulate their genetic makeup. Thus, the pesticide-degrading effect could be increased and further applied to large-scale use and producing genetically engineered crops as self-herbicide/insecticide/fungicide-resistant plants that eventually lead to reduced pesticide use. A whole microbial community and many novel strains like arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi (AMF) are found in the millet-cultivating soil. This chapter focuses on those novel microbial strains found in millets that can degrade pesticides. Several studies can be designed to isolate and characterize for further evaluation that could help to reduce the problems related to pesticide use soon.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abd-Alla MH (1994) Phosphodiesterase and phosphotriesterase in Rhizobium and Bradyrhizobium strains and their roles in the degradation of organophosphorus pesticides. Lett Appl Microbiol 19(4):240–243
Adegun AO, Akinnifesi TA, Ololade IA, Busquets R, Hooda PS, Cheung PC, Aseperi AK, Barker J (2020) Quantification of neonicotinoid pesticides in six cultivable fish species from the river Owena in Nigeria and a template for food safety assessment. Water 12(9):2422
Adeleye IA, Okorodudu E, Lawal O (2004) Effect of some herbicides used in Nigeria on Rhizobium phaseoli, Azotobacter vinelandii and Bacillus subtilis. J Environ Biol 25(2):151–156
Akbar S, Sultan S, Kertesz M (2015) Determination of cypermethrin degradation potential of soil bacteria along with plant growth-promoting characteristics. Curr Microbiol 70(1):75–84
Alsohaili SA, Bani-Hasan BM (2018) Morphological and molecular identification of fungi isolated from different environmental sources in the Northern Eastern desert of Jordan. Jordan J Biol Sci 11(3):329–337
Arya R, Kumar R, Mishra NK, Sharma AK (2017) Microbial flora and biodegradation of pesticides: trends, scope, and relevance. Adv Environ Biol 243–263
Asim N, Hassan M, Shafique F, Ali M, Nayab H, Shafi N, Khawaja S, Manzoor S (2021) Characterizations of novel pesticide-degrading bacterial strains from industrial wastes found in the industrial cities of Pakistan and their biodegradation potential. PeerJ 9:e12211
Bakker PA, Berendsen RL, Doornbos RF, Wintermans PC, Pieterse CM (2013) The rhizosphere revisited: root microbiomics. Front Plant Sci 4:165
Bass C, Field LM (2011) Gene amplification and insecticide resistance. Pest Manag Sci 67(8):886–890
Bhatt P, Huang Y, Zhan H, Chen S (2019) Insight into microbial applications for the biodegradation of pyrethroid insecticides. Front Microbiol 10:1778
Bordjiba O, Steiman R, Kadri M, Semadi A, Guiraud P (2001) Removal of herbicides from liquid media by fungi isolated from a contaminated soil. J Environ Qual 30(2):418–426
Christos AD (2009) Understanding benefits and risks of pesticide use. Sci Res Essays 4(10):945–949
Daly H, Doyen JT, Purcell AH (1998) Introduction to insect biology and diversity, 2nd edn. Oxford University Press, New York
Damalas CA (2009) Understanding benefits and risks of pesticide use. Sci Res Essays 4(10):945–949
Elhussein AA, Osman AG, Sherif AM (2011) Isolation, characterization, identification and potentiality of fungicide thiram (TMTD) degraders under laboratory conditions. Int J Appl Environ Sci 6(2):193–199
Fabra A, Angelini J, Donolo A, Permigiani M, Castro S (1998) Biochemical alterations in Bradyrhizobium sp USDA 3187 induced by the fungicide Mancozeb. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 73(3):223–228. https://doi.org/10.1023/a:1000987524112
FAO (2017) Statistics, statistical pocketbook. FAO, Rome
Gahukar RT, Reddy GV (2019) Management of economically important insect pests of millet. J Integr Pest Manag 10(1):28
Gaind S, Rathi MS, Kaushik BD, Nain L, Verma OP (2007) Survival of bio-inoculants on fungicides-treated seeds of wheat, pea and chickpea and subsequent effect on chickpea yield. J Environ Sci Health B 42(6):663–668. https://doi.org/10.1080/03601230701465759
Gilbert LI, Gill SS (eds) (2010) Insect control: biological and synthetic agents. Academic
Gill HK, Garg H (2014) Pesticide: environmental impacts and management strategies. Pesticides-toxic aspects, 8, p 187
Girgi M, O'Kennedy MM, Morgenstern A, Mayer G, Lörz H, Oldach KH (2002) Transgenic and herbicide resistant pearl millet (Pennisetum glaucum L.) R. Br. via microprojectile bombardment of scutellar tissue. Mol Breed 10:243–252
Gopalakrishnan S, Sathya A, Vijayabharathi R, Varshney RK, Gowda CL, Krishnamurthy L (2015) Plant growth promoting rhizobia: challenges and opportunities. 3 Biotech 5(4):355–377
Gupta M, Mathur S, Sharma TK, Rana M, Gairola A, Navani NK, Pathania R (2016) A study on metabolic prowess of Pseudomonas sp. RPT 52 to degrade imidacloprid, endosulfan and coragen. J Hazard Mater 301:250–258
Hameeda B, Rupela OP, Reddy G, Satyavani K (2006) Application of plant growth-promoting bacteria associated with composts and macrofauna for growth promotion of pearl millet (Pennisetum glaucum L.). Biol Fertil Soils 43(2):221–227
Hassan AA (2010) Characterization of bacterial isolates (Rhizobium leguminosarum and Bacillus thuringiensis) able to degrade of malathion and methomyl pesticides. J Agric Chem Biotechnol 1(11):575–588
Hussaini SZ, Shaker M, Iqbal MA (2013) Isolation of bacteria for degradation of selected pesticides. Adv Biores 4(3):82–85
Iqbal MA, Bartakke KV (2014) Isolation of pesticide degrading microorganisms from soil. Adv Biores 4:164–168
Jambagi SR, Kambrekar DN, Mallapur CP, Naik VR (2022) Novel insecticides for the management of shoot fly, Atherigona approximata Malloch (Diptera: Muscidae): an emerging insect pest of wheat in India. https://doi.org/10.21203/rs.3.rs-1120869/v1
Juwarkar AA, Jambhulkar HP (2008) Phytoremediation of coal mine spoil dump through integrated biotechnological approach. Bioresour Technol 99(11):4732–4741
Kafilzadeh F, Ebrahimnezhad M, Tahery Y (2015) Isolation and identification of endosulfan-degrading bacteria and evaluation of their bioremediation in Kor River, Iran. Osong Public Health Res Perspect 6(1):39–46
Kumar S, Chandra A, Pandey KC (2008) Bacillus thuringiensis (Bt) transgenic crop: an environment friendly insect-pest management strategy. J Environ Biol 29(5):641–653
Kunze M, Zerlin KF, Retzlaff A, Pohl JO, Schmidt E, Janssen DB, Vilchez-Vargas R, Pieper DH, Reineke W (2009) Degradation of chloroaromatics by Pseudomonas putida GJ31: assembled route for chlorobenzene degradation encoded by clusters on plasmid pKW1 and the chromosome. Microbiology 155(12):4069–4083
Liu CM, McLean PA, Sookdeo CC, Cannon FC (1991) Degradation of the herbicide glyphosate by members of the family Rhizobiaceae. Appl Environ Microbiol 57(6):1799–1804
Manickam N, Reddy MK, Saini HS, Shanker R (2008) Isolation of hexachlorocyclohexane-degrading Sphingomonas sp. by dehalogenase assay and characterization of genes involved in γ-HCH degradation. J Appl Microbiol 104(4):952–960
Mansfield J, Genin S, Magori S, Citovsky V, Sriariyanum M, Ronald P, Dow MA, Verdier V, Beer SV, Machado MA, Toth IA (2012) Top 10 plant pathogenic bacteria in molecular plant pathology. Mol Plant Pathol 13(6):614–629
Masotti F, Garavaglia BS, Piazza A, Burdisso P, Altabe S, Gottig N, Ottado J (2021) Bacterial isolates from argentine pampas and their ability to degrade glyphosate. Sci Total Environ 774:145761
Melo ALDA, Soccol VT, Soccol CR (2016) Bacillus thuringiensis: mechanism of action, resistance, and new applications: a review. Crit Rev Biotechnol 36(2):317–326
Mendes R, Garbeva P, Raaijmakers JM (2013) The rhizosphere microbiome: significance of plant beneficial, plant pathogenic, and human pathogenic microorganisms. FEMS Microbiol Rev 37(5):634–663
Mirza BS, Mirza MS, Bano A, Malik KA (2007) Coinoculation of chickpea with Rhizobium isolates from roots and nodules and phytohormone-producing Enterobacter strains. Aust J Exp Agric 47(8):1008–1015
Murali M, Amruthesh KN, Sudisha J, Niranjana SR, Shetty HS (2012) Screening for plant growth promoting fungi and their ability for growth promotion and induction of resistance in pearl millet against downy mildew disease. J Phytology 4(5):30–36
Mythili M, Ramalakshmi A (2022) Unravelling the distribution of AMF communities and their metabolites associated with soils of minor millets. Rhizosphere 21:100473
Nandini B, Puttaswamy H, Saini RK, Prakash HS, Geetha N (2021) Trichovariability in rhizosphere soil samples and their biocontrol potential against downy mildew pathogen in pearl millet. Sci Rep 11(1):1–15
Nwanze KF, Harris KM (1992) Insect pests of pearl millet in West Africa. Rev Agric Entomol 80(12):1132–1155
Oerke E (2006) Crop losses to pests. J Agric Sci 144(1):31–43. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0021859605005708
Ortiz-Hernández ML (2002) Biodegradación de plaguicidas organofosforados por nuevas bacterias aisladas del suelo. Thesis. Biotechnology PhD, pp 130
Ortiz-Hernández ML, Sánchez-Salinas E, Olvera-Velona A, Folch-Mallol JL (2011) Pesticides in the environment: impacts and their biodegradation as a strategy for residues treatment. In: Pesticides—formulations, effects, fate, pp 551–574
Ortiz-Hernández ML, Sánchez-Salinas E, Dantán-González E, Castrejón-Godínez ML (2013) Pesticide biodegradation: mechanisms, genetics, and strategies to enhance the process. Biodegrad Life Sci 10:251–287
Ouw HK, Simpson GR, Siyali DS (1976) Use and health effects of Aroclor 1242, a polychlorinated biphenyl, in an electrical industry. Arch Environ Health 31(4):189–194
Pang S, Lin Z, Li J, Zhang Y, Mishra S, Bhatt P, Chen S (2022) Microbial degradation of Aldrin and Dieldrin: mechanisms and biochemical pathways. Front Microbiol 13:713375
Philippot L, Raaijmakers JM, Lemanceau P, van der Putten WH (2013) Going back to the roots: the microbial ecology of the rhizosphere. Nat Rev Microbiol 11(11):789–799. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrmicro3109
Pizzul L, Castillo MDP, Stenström J (2009) Degradation of glyphosate and other pesticides by ligninolytic enzymes. Biodegradation 20(6):751–759
Ramakrishnan B, Megharaj M, Venkateswarlu K, Sethunathan N, Naidu R (2011) Mixtures of environmental pollutants: effects on microorganisms and their activities in soils. In: Whitacre D (ed) Reviews of environmental contamination and toxicology, vol 211. Springer, New York. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4419-8011-3_3
Rayu S, Nielsen UN, Nazaries L, Singh BK (2017) Isolation and molecular characterization of novel chlorpyrifos and 3, 5, 6-trichloro-2-pyridinol-degrading bacteria from sugarcane farm soils. Front Microbiol 8:518
Reddy BR, Sethunathan N (1983) Mineralization of parathion in the rhizosphere of rice and pearl millet. J Agric Food Chem 31(6):1379–1381
Robert Y, Woodford JT, Ducray-Bourdin DG (2000) Some epidemiological approaches to the control of aphid-borne virus diseases in seed potato crops in northern Europe. Virus Res 71(1–2):33–47
Roy T, Das N, Majumdar S (2020) Pesticide tolerant rhizobacteria: paradigm of disease management and plant growth promotion. In: Plant microbe Symbiosis. Springer, Cham, pp 221–239
Roy T, Bandopadhyay A, Paul C, Majumdar S, Das N (2022) Role of plasmid in pesticide degradation and metal tolerance in two plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria Bacillus cereus (NCIM 5557) and Bacillus safensis (NCIM 5558). Curr Microbiol 79(4):1–12
Sakamoto S (1987) Origin and dispersal of common millet and foxtail millet. JARQ 21(22):84–89
Sangwan P, Raj K, Wati L, Kumar A (2021) Isolation and evaluation of bacterial endophytes against Sclerospora graminicola (Sacc.) Schroet, the causal of pearl millet downy mildew. Egypt J Biol Pest Control 31(1):1–11
Sekar J, Raju K, Duraisamy P, Ramalingam Vaiyapuri P (2018) Potential of finger millet indigenous rhizobacterium Pseudomonas sp. MSSRFD41 in blast disease management—growth promotion and compatibility with the resident rhizomicrobiome. Front Microbiol 9:1029
Sharma A, Kalyani P, Trivedi VD, Kapley A, Phale PS (2019) Nitrogen-dependent induction of atrazine degradation pathway in Pseudomonas sp. strain AKN5. FEMS Microbiol Lett 366(1):277
Singh BK, Walker A (2006) Microbial degradation of organophosphorus compounds. FEMS Microbiol Rev 30(3):428–471
Sinha S, Mukherjee SK (2008) Cadmium-induced siderophore production by a high Cd-resistant bacterial strain relieved Cd toxicity in plants through root colonization. Curr Microbiol 56(1):55–60. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00284-007-9038-z
Smith FW (2002) The phosphate uptake mechanism. In: Food security in nutrient-stressed environments: exploiting plants’ genetic capabilities. Springer, Dordrecht, pp 235–244
Sogorb MA, Vilanova E (2002) Enzymes involved in the detoxification of organophosphorus, carbamate and pyrethroid insecticides through hydrolysis. Toxicol Lett 128(1–3):215–228. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0378-4274(01)00543-4
Sonchieu J, Benoit Ngassoum M, Bosco Tchatchueng J, Srivastava AK, Srivastava LP (2010) Survey of pesticide residues in maize, cowpea and millet from northern Cameroon: part I. Food Addit Contam 3(3):178–184
Sowunmi K, Shoga SM, Adewunmi OM, Oriyomi AF, Sowunmi L. (2021) Isolation and molecular characterization of pesticide degrading bacteria in polluted soil. bioRxiv, 2020–07
Srivastava AK, Kesavachandran C (2019) Health effects of pesticides, 1st edn. CRC Press, Boca Raton. https://doi.org/10.1201/9780429058219
Surekha Rani M, Vijaya Lakshmi K, Suvarnalatha Devi P, Jaya Madhuri R, Aruna S, Jyothi K, Narasimha G, Venkateswarlu K (2008) Isolation and characterization of a chlorpyrifos-degrading bacterium from agricultural soil and its growth response. Afr J Microbiol Res 2(2):26–31
Thomashow MF, Nutter R, Montoya AL, Gordon MP, Nester EW (1980) Integration and organization of Ti plasmid sequences in crown gall tumors. Cell 19(3):729–739
Usta C (2013) Microorganisms in biological pest control—a review (bacterial toxin application and effect of environmental factors). Curr Progress Biol Res 13:287–317
Vásquez M, Reyes W (2002) Degradación de Aroclor 1242 por Pseudomas sp. Biblioteca Nacional del Perú, Perú
Xu L, Yi M, Yi H, Guo E, Zhang A (2018) Manure and mineral fertilization change enzyme activity and bacterial community in millet rhizosphere soils. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 34(1):1–13
Yamamoto I, Casida JE (1999) Nicotinoid insecticides and the nicotinic acetylcholine receptor. Springer, Tokyo. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-4-431-67933-2
Zhongli C, Shunpeng L, Guoping F (2001) Isolation of methyl parathion-degrading strain M6 and cloning of the methyl parathion hydrolase gene. Appl Environ Microbiol 67(10):4922–4925
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2023 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Singapore Pte Ltd.
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Hazra, S., Dey, J., Mukherjee, S., Kalam, A., Mal, C. (2023). Identification of Novel Microbial Strains for Reduced Pesticide Use in Millets. In: Pudake, R.N., Kumari, M., Sapkal, D.R., Sharma, A.K. (eds) Millet Rhizosphere . Rhizosphere Biology. Springer, Singapore. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-99-2166-9_5
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-99-2166-9_5
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Singapore
Print ISBN: 978-981-99-2165-2
Online ISBN: 978-981-99-2166-9
eBook Packages: Biomedical and Life SciencesBiomedical and Life Sciences (R0)