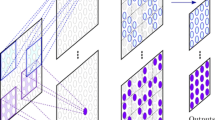
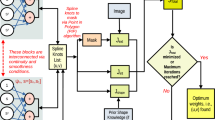
Abstract
Segmentation of a target object in the form of closed curves has many potential applications in medical imaging because it provides quantitative information related to its size and shape. Over the last few decades, many innovative methods of performing segmentation have been proposed, and these segmentation techniques are based on the basic recipes using thresholding and edge-based detection. Segmentation and classification in medical imaging are in fact experiencing a paradigm shift due to a marked and rapid advance in deep learning (DL) techniques. DL methods have nonlinear representability to extract and utilize global spatial features and local spatial features simultaneously, showing amazing overall performance in medical image segmentation. DL methods mostly lack transparency due to the black-box output, so clinicians cannot trace the output back to present the causal relationship of the output diagnosis. Therefore, in order to safely utilize DL algorithms in the medical field, it is desirable to design the models to transparently explain the reason for making the output diagnosis rather than a black-box. For explainable DL, a systematic study is needed to rigorously analyze which input characteristics affect the output of the network. Despite the lack of rigorous analysis in DL, recent rapid advances indicate that DL algorithms will improve their performance as training data and experience accumulate over time.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adams, R., Bischof, L.: Seeded region growing. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 16(6), 641–647 (1994)
Alexe, B., Thomas, D., Ferrari, V.: Measuring the objectness of image windows. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 34(11), 2189–2202 (2012)
Caselles, V., Catte, F., Francine, C., Tomeu, D., Dibos, F.: A geometric model for active contours in image processing. Numerische Mathematik 66(1), 1–31 (1993)
Caselles, V., Kimmel, R., Sapiro, G.: Geodesic active contours. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 22(1), 61–79 (1997)
Chan, T.F., Vese, L.A.: Active contours without edges. IEEE Trans. Image Proc. 10(2), 266–277 (2001)
Ching, T., Himmelstein, D.S., Beaulieu-Jones, B.K., Kalinin, A.A., Do, B.T., Way, G.P., Ferrero, Paul-Michael Agapow, E., Zietz, M., Hoffman, M.M. et al.: Opportunities and obstacles for deep learning in biology and medicine. J. R. Soc. Interf. 15(141), 20170387 (2018)
Cho, H.C., Sun, S., Hyun, C.M., Kwon, J.-Y., Kim, B., Park, Y., Seo, J.K.: Automated ultrasound assessment of amniotic fluid index using deep learning. Med. Image Anal. 101951
Everingham, M., Van Gool, L., Williams, C.K., Winn, J., Zisserman, A.: The pascal visual object classes (VOC) challenge. Int. J. Comput. Visi. 88(2), 303–338 (2010)
Finlayson, S.G., Bowers, J.D., Ito, J., Zittrain, J.L., Beam, A.L., Kohane, I.S.: Adversarial attacks on medical machine learning. Science 363(6433), 12871289 (2019)
Huazhu, F., Cheng, J., Yanwu, X., Wong, D.W.K., Liu, J., Cao, X.: Joint optic disc and cup segmentation based on multi-label deep network and polar transformation. IEEE Trans Med Imaging 37(7), 1597–1605 (2018)
Gao, Y., Liu, Y., Wang, Y., Shi, Z., Jinhua, Y.: A universal intensity standardization method based on a many-to-one weak-paired cycle generative adversarial network for magnetic resonance images. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 38(9), 20592069 (2019)
Girshick, R., Donahue, J., Darrell, T., Malik, J.: Rich feature hierarchies for accurate object detection and semantic segmentation. In: Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, pp 580–587 (2014)
Goldenberg, R., Kimmel, R., Rivlin, E., Rudzsky, M.: Fast geodesic active contours. IEEE Trans. Image Proc. 10(10), 1467–1475 (2001)
Goodfellow, I.J., Shlens, J., Szegedy, C.: Explaining and Harnessing Adversarial Examples (2014). arXiv:1412.6572
He, K., Gkioxari, G., Dollar, P., Girshick, R.: Mask r-CNN. In: Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 2961–2969 (2017)
Ibtehaz, N., Rahman, M.S.: Multiresunet: rethinking the u-net architecture for multimodal biomedical image segmentation. Neural Netw. 121, 74–87 (2020)
Jang, J., Park, Y., Kim, B., Lee, S.M., Kwon, J.-Y., Seo, J.K.: Automatic estimation of fetal abdominal circumference from ultrasound images. IEEE J. Biomed. Health Inf. 22(5), 1512–1520 (2017)
Jang, T.J., Kim, K.C., Cho, H.C., Seo, J.K.: A fully automated method for 3d individual tooth identification and segmentation in dental CBCT. Submitted to IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence (2021)
Kass, M., Witkin, A., Terzopoulos, D.: Snakes: active contour models. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 1(4), 321–331 (1988)
Kim, B., Kim, K.C., Park, Y., Kwon, J.-Y., Jang, J., Seo, J.K.: Machine-learning-based automatic identification of fetal abdominal circumference from ultrasound images. Physiol. Measurem 39(10), 105007 (2018)
Kim, H.P. Lee, S.M., Kwon, J.-Y., Park, Y., Kim, K.C., Seo, J.K.: Automatic evaluation of fetal head biometry from ultrasound images using machine learning. Physiol. Measur. 40(6), 065009 (2019)
Kim, K.C., Cho, H.C., Jang, T.J., Choi, J.M., Seo, J.K.: Automatic detection and segmentation of lumbar vertebrae from x-ray images for compression fracture evaluation. Computer Methods and Programs in Biomedicine, p. 105833 (2020)
Kim, K.C., Yun, H.S., Kim, S., Seo, J.K.: Automation of spine curve assessment in frontal radiographs using deep learning of vertebral-tilt vector. IEEE Access 8, 84618–84630 (2020)
Lee, S.M., Kim, H.P., Jeon, K., Lee, S.-H., Seo, J.K.: Automatic 3d cephalometric annotation system using shadowed 2d image-based machine learning. Phys. Med. Biol. 64(5):055002 (2019)
Li, C., Xu, C., Gui, C., Fox, M.D.: Distance regularized level set evolution and its application to image segmentation. IEEE Trans. Image Proc. 19(12), 3243–3254 (2010)
Litjens, G., Kooi, T., Bejnordi, B.E., Setio, A.A.A., Ciompi, F., Ghafoorian, M., Van Der Laak, J.A., Van Ginneken, B., Sanchez, C.I.: A survey on deep learning in medical image analysis. Med. Image Anal. 42, 60–88 (2017)
Livne, M., Rieger, J., Aydin, O.U., Taha, A.A., Akay, E.M., Kossen, T., Sobesky, J., Kelleher, J.D., Hildebrand, K., Frey, D. et al.: A u-net deep learning framework for high performance vessel segmentation in patients with cerebrovascular disease. Front. Neurosci. 13, 97 (2019)
Malladi, R., Sethian, J.A., Vemuri, B.C.: Shape modeling with front propagation: a level set approach. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 17(2), 158–175 (1995)
Oktay, O., Schlemper, J., Folgoc, L.L., Lee, M., Heinrich, M., Misawa, K., Mori, K., McDonagh, S., Hammerla, N.Y., Kainz, B. et al.: Attention u-net: learning where to look for the pancreas (2018). arXiv:1804.03999
Osher, S., Fedkiw, R.P.: Level set methods: an overview and some recent results. J. Comput. Phys. 169(2), 463–502 (2001)
Otsu, N.: A threshold selection method from gray-level histograms. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. 9(1), 62–66 (1979)
Park, H.S., Baek, J., You, S.K., Choi, J.K., Seo, J.K.: Unpaired image denoising using a generative adversarial network in x-ray ct. IEEE Access 7, 110414110425 (2019)
Redmon, J., Divvala, S., Girshick, R., Farhadi, A.: You only look once: unified, real-time object detection. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 779–788 (2016)
Ren, S., He, K., Girshick, R., Sun, J.: Faster r-CNN: towards real-time object detection with region proposal networks. In: Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, pp. 91–99 (2015)
Ronneberger, O., Fischer, P., Brox, T.: U-net: convolutional networks for biomedical image segmentation. In: International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention, pp. 234–241. Springer (2015)
Vincent, P., Larochelle, H., Lajoie, I., Bengio, Y., Manzagol, P.-A., Bottou, L.: Stacked denoising autoencoders: learning useful representations in a deep network with a local denoising criterion. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 11(12) (2010)
Xie, C., Wu, Y., van der Maaten, L., Yuille, A.L., He, K.: Feature denoising for improving adversarial robustness. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 501–509 (2019)
Yuan, X., He, P., Zhu, Q., Li, X.: Adversarial examples: attacks and defenses for deep learning. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 30(9), 2805–2824 (2019)
Yun, H.S., Jang, T.J., Lee, S.M., Lee, S.-H., Seo, J.K.: Learning-based local-to-global landmark annotation for automatic 3d cephalometry. Phys. Med. Biol. 65(8), 085018 (2020)
Zhou, Z., Siddiquee, M., Rahman, M., Nima, T., Jianming, L.: Unet++: redesigning skip connections to exploit multiscale features in image segmentation. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 39(6), 1856–1867 (2019)
Zhu, J.-Y., Park, T., Isola, P., Efros, A.A.: Unpaired image-to-image translation using cycle-consistent adversarial networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 2223–2232 (2017)
Acknowledgements
This research was supported by Samsung Science & Technology Foundation (No. SRFC-IT1902-09). Jang and Seo were supported by a grant of the Korea Health Technology R &D Project through the Korea Health Industry Development Institute (KHIDI), funded by the Ministry of Health & Welfare, Republic of Korea (grant number : HI20C0127). We are deeply grateful to HDXWILL for their help and collaboration.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2023 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Singapore Pte Ltd.
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Kim, K.C., Jang, T.J., Seo, J.K. (2023). Deep Learning Techniques for Medical Image Segmentation and Object Recognition. In: Seo, J.K. (eds) Deep Learning and Medical Applications. Mathematics in Industry, vol 40. Springer, Singapore. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-99-1839-3_2
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-99-1839-3_2
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Singapore
Print ISBN: 978-981-99-1838-6
Online ISBN: 978-981-99-1839-3
eBook Packages: Mathematics and StatisticsMathematics and Statistics (R0)