Abstract
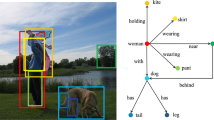
The current scene graph generation (SGG) task still follows the method of first detecting objects-pairs and then predicting relationships between objects-pairs. This paper introduces a parallel SGG thought that decouples relationship detection and object detection. In detail, we propose an independent visual relationship detection method, ‘Relationship You Only Look Once’ (RYOLO), which calculates relationships directly from the input image. For SGG, we present Similar Relationship Suppression and Object Matching Rules to match relationships and detected objects. In this way, the relationship detection and object detection can be calculated in parallel, and detected relationships can easily cooperate with detected objects to generate diversified scene graphs. Finally, our thought has verified the feasibility on the public Visual Genome dataset, and our method may be the first to attain real-time SGG.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Gu, J., Joty, S., Cai, J., Zhao, H., Yang, X., Wang, G.: Unpaired image captioning via scene graph alignments. In: CVPR (2019)
Hudson, D.A., Manning, C.D.: Learning by abstraction: the neural state machine. In: NIPS (2019)
Wan, H., Luo, Y., Peng, B., Zheng, W.: Representation learning for scene graph completion via jointly structural and visual embedding. In: IJCAI (2018)
Yang, J., Lu, J., Lee, S., Batra, D., Parikh, D.: Graph R-CNN for scene graph generation. In: Ferrari, V., Hebert, M., Sminchisescu, C., Weiss, Y. (eds.) ECCV 2018. LNCS, vol. 11205, pp. 690–706. Springer, Cham (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-01246-5_41
Zellers, R., Yatskar, M., Thomson, S., Choi, Y.: Neural motifs: scene graph parsing with global context. In: CVPR (2018)
Zareian, A., Karaman, S., Chang, S.-F.: Bridging knowledge graphs to generate scene graphs. In: Vedaldi, A., Bischof, H., Brox, T., Frahm, J.-M. (eds.) ECCV 2020. LNCS, vol. 12368, pp. 606–623. Springer, Cham (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-58592-1_36
Zhang, J., Kalantidis, Y., Rohrbach, M., Paluri, M., Elgammal, A., Elhoseiny, M.: Large-scale visual relationship understanding. In: AAAI (2019)
Lin, X., Li, Y., Liu, C., Ji, Y., Yang, J.: Scene graph generation based on node-relation context module. In: Cheng, L., Leung, A.C.S., Ozawa, S. (eds.) ICONIP 2018. LNCS, vol. 11302, pp. 134–145. Springer, Cham (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-04179-3_12
Ren, S., He, K., Girshick, R., Sun, J.: Faster R-CNN: towards real-time object detection with region proposal networks. In: NIPS (2015)
He, K., Gkioxari, G., Dollár, P., Girshick, R.: Mask R-CNN. In: ICCV (2017)
Gkanatsios, N., Pitsikalis, V., Koutras, P., Maragos, P.: Attention-translation-relation network for scalable scene graph generation. In: ICCV Workshops (2019)
Glenn-Jocher, et al.: yolov5 (2021). https://github.com/ultralytics/yolov5
Redmon, J., Divvala, S., Girshick, R., Farhadi, A.: You only look once: unified, real-time object detection. In: CVPR (2016)
Lin, X., Ding, C., Zeng, J., Tao, D.: GPS-Net: graph property sensing network for scene graph generation. In: CVPR (2020)
Hung, Z., Mallya, A., Lazebnik, S.: Contextual translation embedding for visual relationship detection and scene graph generation. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 43(11), 3820–3832 (2020)
Gu, J., Zhao, H., Lin, Z., Li, S., Cai, J., Ling, M.: Scene graph generation with external knowledge and image reconstruction. In: CVPR (2019)
Lu, C., Krishna, R., Bernstein, M., Fei-Fei, L.: Visual relationship detection with language priors. In: Leibe, B., Matas, J., Sebe, N., Welling, M. (eds.) ECCV 2016. LNCS, vol. 9905, pp. 852–869. Springer, Cham (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-46448-0_51
Tang, K., Zhang, H., Wu, B., Luo, W., Liu, W.: Learning to compose dynamic tree structures for visual contexts. In: CVPR (2019)
Chen, T., Yu, W., Chen, R., Lin, L.: Knowledge-embedded routing network for scene graph generation. In: CVPR (2019)
Xu, D., Zhu, Y., Choy, C.B., Fei-Fei, L.: Scene graph generation by iterative message passing. In: CVPR (2017)
Liu, H., Yan, N., Mortazavi, M., Bhanu, B.: Fully convolutional scene graph generation. In: CVPR (2021)
Yu, J., Chai, Y., Wang, Y., Hu, Y., Wu, Q.: CogTree: cognition tree loss for unbiased scene graph generation. In: IJCAI (2021)
Tang, K., Niu, Y., Huang, J., Shi, J., Zhang, H.: Unbiased scene graph generation from biased training. In: CVPR (2020)
Yang, G., Zhang, J., Zhang, Y., Wu, B., Yang, Y.: Probabilistic modeling of semantic ambiguity for scene graph generation. In: CVPR (2021)
Newell, A., Deng, J.: Pixels to graphs by associative embedding. In: NIPS (2017)
Krishna, R., et al.: Visual genome: connecting language and vision using crowdsourced dense image annotations. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 123(1), 32–73 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11263-016-0981-7
Joseph, K.J., Khan, S., Khan, F., Balasubramanian, V.: Towards open world object detection. In: CVPR (2021)
Everingham, M., Eslami, S.M.A., Van Gool, L., Williams, C.K.I., Winn, J., Zisserman, A.: The Pascal visual object classes challenge: a retrospective. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 111(1), 98–136 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11263-014-0733-5
Acknowledgement
The research was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. U21A20488) and the ‘10000 Talents Plan’ of Zhejiang Province (Grant, No. 2019R51010). The research was supported by Lab-initiated Research Project of Zhejiang Lab (No. G2021NB0AL03).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2023 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Singapore Pte Ltd.
About this paper
Cite this paper
Jin, T. et al. (2023). Independent Relationship Detection for Real-Time Scene Graph Generation. In: Tanveer, M., Agarwal, S., Ozawa, S., Ekbal, A., Jatowt, A. (eds) Neural Information Processing. ICONIP 2022. Communications in Computer and Information Science, vol 1791. Springer, Singapore. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-99-1639-9_9
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-99-1639-9_9
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Singapore
Print ISBN: 978-981-99-1638-2
Online ISBN: 978-981-99-1639-9
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)