Abstract
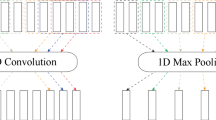
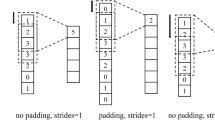
Numerical reservoir simulation is an important technology in reservoir production development, but the computational consumption of numerical simulation is a key factor affecting reservoir history matching, production prediction, and optimization. By constructing a computationally fast machine learning model to learn the mapping relationship between reservoir model parameters and production data, a maximum alternative to the numerical simulation process can be achieved to improve the efficiency of reservoir management and decision making. The current surrogate models of reservoir numerical simulation for large spatial variables, including permeability and porosity fields, often extract spatial features by convolutional neural networks and later use recurrent neural networks to learn the time-series relationships of production data. In this work, we study the method using convolutional neural networks to extract spatial parameters of reservoir models and propose a new module to convert the temporal and spatial features of surrogate models. By converting the spatial features extracted by convolution and adapting the input features and dimensions of the recurrent neural network, maximum extraction of spatial feature parameters is achieved. The proposed method was verified on a 3D reservoir model, and the results indicate that the method can enhance the accuracy of the surrogate model.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Peaceman, D.W.: Fundamentals of numerical reservoir simulation. Elsevier (2000)
Oliver, D.S., Chen, Y.: Recent progress on reservoir history matching: a review. Comput. Geosci.. Geosci. 15(1), 185–221 (2010)
Ertekin, T., Abou-Kassem, J.H., King, G.R.: Basic applied reservoir simulation (2001)
Gilman, J.R., Ozgen, C.: Reservoir simulation: history matching and forecasting. Society of Petroleum Engineers Richardson (2013)
Gu, Y., Oliver, D.S.: History matching of the PUNQ-S3 reservoir model using the ensemble Kalman filter. SPE J. 10(02), 217–224 (2005)
Zhang, K., Zhang, J.D., Ma, X.P., et al.: History matching of naturally fractured reservoirs using a deep sparse autoencoder. SPE J. 26(4), 1700–1721 (2021)
Zhong, C., Zhang, K., Xue, X., et al.: Historical window-enhanced transfer gaussian process for production optimization. SPE J. 27(05), 2895–2912 (2022)
Sun, W.Y., Hui, M.H., Durlofsky, L.J.: Production forecasting and uncertainty quantification for naturally fractured reservoirs using a new data-space inversion procedure. Comput. Geosci.. Geosci. 21(5–6), 1443–1458 (2017)
van Leeuwen, P.J., Evensen, G.: Data assimilation and inverse methods in terms of a probabilistic formulation. Mon. Weather Rev. 124(12), 2898–2913 (1996)
Oliver, D.S., Reynolds, A.C., Liu, N.: Inverse Theory for Petroleum Reservoir Characterization and History Matching. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge (2018)
Mohaghegh, S.D.: Reservoir simulation and modeling based on artificial intelligence and data mining (AI&DM). J. Natural Gas Sci. Eng. 3(6), 697–705 (2011)
Oladyshkin, S., Class, H., Nowak, W.: Bayesian updating via bootstrap filtering combined with data-driven polynomial chaos expansions: methodology and application to history matching for carbon dioxide storage in geological formations. Comput. Geosci.. Geosci. 17(4), 671–687 (2013)
de Lira, J.D., Willmersdorf, R.B., Afonso, S.M.B., et al.: Automatic history matching considering surrogate-based optimization and Karhunen-Loève expansions. J. Braz. Soc. Mech. Sci. Eng. 36(4), 919–928 (2014)
Ma, X.P., Zhang, K., Wang, J., et al.: An efficient spatial-temporal convolution recurrent neural network surrogate model for history matching. SPE J. 27(2), 1160–1175 (2022)
Ma, X., Zhang, K., Zhao, H., et al.: A vector-to-sequence based multilayer recurrent network surrogate model for history matching of large-scale reservoir. J. Petroleum Sci. Eng., 110548 (2022)
Ma, X., Zhang, K., Zhang, J., et al.: A novel hybrid recurrent convolutional network for surrogate modeling of history matching and uncertainty quantification. J. Petrol. Sci. Eng. 210, 110109 (2022)
Xiao, C., Lin, H.-X., Leeuwenburgh, O., et al.: Surrogate-assisted inversion for large-scale history matching: Comparative study between projection-based reduced-order modeling and deep neural network. J. Petroleum Sci. Eng., 208 (2022)
Jiang, S., Durlofsky, L.J.: Use of multifidelity training data and transfer learning for efficient construction of subsurface flow surrogate models. arXiv preprint arXiv:220411138 (2022)
Tang, M., Liu, Y.M., Durlofsky, L.J.: Deep-learning-based surrogate flow modeling and geological parameterization for data assimilation in 3D subsurface flow. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng., 376 (2021)
Gu, J., Wang, Z., Kuen, J., et al.: Recent advances in convolutional neural networks. Pattern Recogn.Recogn. 77, 354–377 (2018)
Medsker, L.R., Jain, L.: Recurrent neural networks. Des. Appl. 5, 64–67 (2001)
Hochreiter, S., Schmidhuber, J.: Long short-term memory. Neural Comput.Comput. 9(8), 1735–1780 (1997)
Cho, K., Van Merriënboer, B., Gulcehre, C., et al.: Learning phrase representations using RNN encoder-decoder for statistical machine translation. arXiv preprint arXiv:14061078 (2014)
Bjorck, N., Gomes, C.P., Selman, B., et al.: Understanding batch normalization. Advances in neural information processing systems, 31 (2018)
Nair, V., Hinton, G.E.: Rectified linear units improve restricted boltzmann machines. In: Proceedings of the Proceedings of the 27th International Conference on Machine Learning (ICML-10), F (2010)
He, K., Zhang, X., Ren, S., et al.: Deep residual learning for image recognition; proceedings of the Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (2016)
Peters, E., Chen, Y., Leeuwenburgh, O., et al.: Extended brugge benchmark case for history matching and water flooding optimization. Comput. Geosci.. Geosci. 50, 16–24 (2013)
Acknowledgments
This work is supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China under Grant 52274057, 52074340 and 51874335, the Major Scientific and Technological Projects of CNPC under Grant ZD2019-183-008, the Major Scientific and Technological Projects of CNOOC under Grant CCL2022RCPS0397RSN, the Science and Technology Support Plan for Youth Innovation of University in Shandong Province under Grant 2019KJH002, 111 Project under Grant B08028.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2024 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Singapore Pte Ltd.
About this paper
Cite this paper
Zhang, Jd. et al. (2024). Study of Spatial Feature Extraction Methods for Surrogate Models of Numerical Reservoir Simulation. In: Lin, J. (eds) Proceedings of the International Field Exploration and Development Conference 2023. IFEDC 2023. Springer Series in Geomechanics and Geoengineering. Springer, Singapore. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-97-0272-5_14
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-97-0272-5_14
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Singapore
Print ISBN: 978-981-97-0271-8
Online ISBN: 978-981-97-0272-5
eBook Packages: EngineeringEngineering (R0)