Abstract
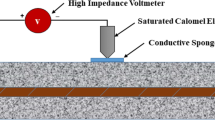
Most of the civil engineering laboratory experiment induces the rate of corrosion process based on current value Am/cm2 to represent the effect of corrosion, however this method has lack of quantifying the actual mass loss rate of steel in the natural environment. This paper presents the Linear Polarization Resistant (LPR) experimental test technique as supplementary method for supporting the impressed current method validation and result for square tubes with 3 mm thickness. The most important parameter of the current impressed method is the length of time required to run the test, size of the sample, and amount of current applied to achieve laboratory corrosion rate close to the natural rate. On the other hand, the linear polarization resistance (LPR) needed only 24 h to complete, and the result in this paper found correlation between the impressed current corrosion, to the LPR system in term of mass loss. Based on result of the tests, the mass loss of the impressed current can be validated by LPR mass loss yearly, which reveal the equivalent number of years needed to have natural corrosion as the same sample used in laboratory with accelerated impressed current method.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Austin SA, Lyons R, Ing M (2004) Electrochemical behavior of steel-reinforced concrete during accelerated corrosion testing. Corrosion 60(2):203–212
Scully JR (2000) Polarization resistance method for determination of instantaneous corrosion rates. Corrosion 56(2):199–218
G59-97, A. Standard test method for conducting potentiodynamic polarization resistance measurements. In: American society for testing and materials (2014)
Lankard DR et al (1993) Grouts for bonded post-tensioned concrete construction: protecting prestressing steel from corrosion. Mater J 90(5):406–414
Pacheco AR et al (2011) Linear polarization resistance tests on corrosion protection degree of post-tensioning grouts. ACI Mater J 108(4)
Ahmad S (2009) Techniques for inducing accelerated corrosion of steel in concrete. Arabian J Sci Eng 34(2):95
Cairns J, Du Y, Law D (2008) Structural performance of corrosion-damaged concrete beams. Mag Concr Res 60(5):359–370
Mangat PS, Elgarf MS (1999) Flexural strength of concrete beams with corroding reinforcement. Struct J 96(1):149–158
Ha T-H et al (2007) Accelerated short-term techniques to evaluate the corrosion performance of steel in fly ash blended concrete. Build Environ 42(1):78–85
Azad AK, Ahmad S, Azher SA (2007) Residual strength of corrosion-damaged reinforced concrete beams. ACI Mater J 104(1):40
El Maaddawy TA, Soudki KA (2003) Effectiveness of impressed current technique to simulate corrosion of steel reinforcement in concrete. J Mater Civ Eng 15(1):41–47
American society for testing and materials. ASTM G1-03: standard practice for preparing, cleaning, and evaluating corrosion test specimens. 2004. ASTM
Acknowledgements
The author wishes to acknowledge the financial support received from fundamental Research Grant Scheme of Malaysia [grant number FRGS/1/2018/TK01/UTP/02/9], and Universiti Teknologi PETRONAS (UTP).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2021 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Singapore Pte Ltd.
About this paper
Cite this paper
Alraeeini, A.S., Nikbakht, E., Ismail, M.C. (2021). Square Steel Tube Impressed Current Corrosion Rate in Term of Linear Polarization Resistance (LPR) Method. In: Bin Meor Razali, A.M.M.F., Awang, M., Emamian, S.S. (eds) Advances in Civil Engineering Materials. Lecture Notes in Civil Engineering, vol 139. Springer, Singapore. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-33-6560-5_14
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-33-6560-5_14
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Singapore
Print ISBN: 978-981-33-6559-9
Online ISBN: 978-981-33-6560-5
eBook Packages: EngineeringEngineering (R0)