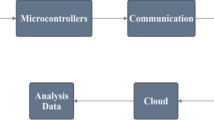
Abstract
Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) is a digital platform to perform machine-to-machine communication, acquire sensor data, analyse, and deliver comprehensive information and also facilitate the manufacturing system to implement smart decisions faster. This paper presents modelling and analysis of an IoT-enabled autonomous manufacturing system based on the performance metrics. Multi-agent interaction has been defined through a generalised control architecture, considering as an autonomous manufacturing system. The number of jobs entering and leaving the machines computes time-dependent performance metrics such as cycle time and work in process using Little’s law. The mean arrival rate of each machine is calculated by evaluating the amount of work and a utilisation factor. The squared coefficient of inter-arrival rates based on successive substitution of job flow from machine x to machine y has also been obtained. This is preliminary work in the process of designing an IoT-enabled autonomous manufacturing system capable of self-learning and executing accurate decision faster.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Vieira, G.E., Hermann, J.W., Lin, E.: Rescheduling manufacturing systems: a framework of strategies, policies, and methods. J. Sched. 39–62 (2003)
Park, H.S., Choi, H.W.: Development of a modular structure-based changeable manufacturing system with high adaptability. Int. J. Precis. Eng. Manuf. 7–12 (2008)
Wang, Y.F., et al.: An integrated approach to reactive scheduling subject to machine breakdown. In: Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Automation and Logistics, pp. 542–547 (2008)
Shea, K., et al.: Design-to-fabrication automation for the cognitive machine shop. Adv. Eng. Inform. 251–268 (2010)
Leitão, P., Restivo, F.: ADACOR: a holonic architecture for agile and adaptive manufacturing control. Comput. Ind. 121–130 (2006)
Park, H.S., et al.: Agent-based shop control system under holonic manufacturing concept. In: Proceedings of the 4th Korea-Russia International Symposium, pp. 116–121 (2000)
Zäh, et al.: The cognitive factory. In: Changeable and Reconfigurable Manufacturing Systems, pp. 355–371. Springer, London (2009)
Bannat, A., et al.: Artificial cognition in production systems. IEEE Trans. Autom. Sci. Eng. 148–174 (2011)
Monostori, L.: AI and machine learning techniques for managing complexity, changes and uncertainties in manufacturing. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 277–291 (2003)
Matsuda, M., Ishikawa, Y., Utsumi, S.: Configuration of machine tool agents for flexible manufacturing. In: 39th CIRP International Conference on Manufacturing Systems, pp. 351–357 (2006)
Wang, S., et al.: Towards smart factory for industry 4.0: a self-organized multi-agent system with big data based feedback and coordination. Comput. Netw. 158–168 (2016)
Wang, M., et al.: A MPN-based scheduling model for IoT-enabled hybrid flow shop manufacturing. Adv. Eng. Inform. 728–736 (2016)
Curry, G.L., Feldman, R.M.: Manufacturing Systems Modeling and Analytics. Springer Science & Business (2010)
Acknowledgements
Authors sincerely thank the Ministry of Electronics and Information Technology (MeitY), Government of India, for providing financial assistance under Visvesvaraya Ph.D. Scheme to carry out this research work at IIITDM Kancheepuram, Chennai, India.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2019 Springer Nature Singapore Pte Ltd.
About this paper
Cite this paper
Badri Narayanan, K.B., Sreekumar, M. (2019). Modelling and Analysis of Multi-agent Approach for an IoT-Enabled Autonomous Manufacturing System. In: Narayanan, R., Joshi, S., Dixit, U. (eds) Advances in Computational Methods in Manufacturing. Lecture Notes on Multidisciplinary Industrial Engineering. Springer, Singapore. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-32-9072-3_54
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-32-9072-3_54
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Singapore
Print ISBN: 978-981-32-9071-6
Online ISBN: 978-981-32-9072-3
eBook Packages: Chemistry and Materials ScienceChemistry and Material Science (R0)