Abstract
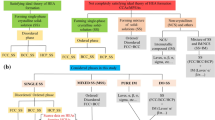
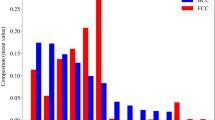
High-entropy alloys (HEAs) possess vast compositional space making them a suitable type of metallic alloy material that can be customized for a wide range of engineering applications ranging from structural, catalytic, functional, hydrogen storage and metamaterials. Predicting the phase of an HEA for a given composition in a certain molar ratio is a daunting task, and hitherto, trial-and-error approaches are employed. With the emergence of data-driven machine learning (ML) technique newer avenues have emerged to reduce the complexity in this task. In this work, we provide a canon of research in this area and used a testbed study by deploying random forest classifier (RFC) to predict distinct phases of HEAs, such as intermetallic (IM), BCC solid-solution (BCC_SS), FCC solid-solution (FCC_SS), and mixed (FCC + BCC) phase. With an average accuracy of 86%, a ROC_AUC score of 0.965, and tenfold cross-validation ROC_AUC score of 0.903, the random forest model showed great ability and prospects in future discovery of novel phases of HEAs. Based on this analysis, the input parameters such as the mixing enthalpy (ΔHmix) and valence electron concentration (VEC) were identified most influential in governing the stable phase of an HEA.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Katiyar N, Goel G, Goel S (2021) Emergence of machine learning in the development of high entropy alloy and their prospects in advanced engineering applications. Emergent Mater 4(6):1635–1648. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42247-021-00249-8
Senkova ON, Senkova SV, Woodward C, Miracle DB (2013) Low-density, refractory multi-principal element alloys of the Cr–Nb–Ti–V–Zr system: Microstructure and phase analysis. Acta Mater 61(5):1545–1557. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2012.11.032
Stepanov N, Shaysultanov D, Salishchev G, Tikhonovsky M (2015) Structure and mechanical properties of a light-weight AlNbTiV high entropy alloy. Mater Lett 142:153–155. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matlet.2014.11.162
Deng Y, Tasan C, Pradeep K, Springer H, Kostka A, Raabe D (2015) Design of a twinning-induced plasticity high entropy alloy. Acta Mater 94:124–133. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2015.04.014
Zhang Y, Li R (2020) New advances in high-entropy alloys. Entropy 22(10):1158. https://doi.org/10.3390/e22101158
Tsai M, Yeh J (2014) High-entropy alloys: a critical review. Mater Res Lett 2(3):107–123. https://doi.org/10.1080/21663831.2014.912690
Youssef K, Zaddach A, Niu C, Irving D, Koch C (2014) A novel low-density, high-hardness, high-entropy alloy with close-packed single-phase nanocrystalline structures. Mater Res Lett 3(2):95–99. https://doi.org/10.1080/21663831.2014.985855
Cantor B (2021) Multicomponent high-entropy Cantor alloys. Prog Mater Sci 120:100754. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pmatsci.2020.100754
Yeh J (2006) Recent progress in high-entropy alloys. Annales De Chimie Science Des Matériaux 31(6):633–648. https://doi.org/10.3166/acsm.31.633-648
Kremer K, Grest G (1990) Molecular dynamics (MD) simulations for polymers. J Phys Condens Matter 2(S):SA295-SA298. https://doi.org/10.1088/0953-8984/2/s/045
Neugebauer J, Hickel T (2013) Density functional theory in materials science. Wiley Interdiscip Rev: Comput Mol Sci 3(5):438–448. https://doi.org/10.1002/wcms.1125
Goel S, Knaggs M, Goel G, Zhou X, Upadhyaya H, Thakur V et al (2020) Horizons of modern molecular dynamics simulation in digitalized solid freeform fabrication with advanced materials. Mater Today Chem 18:100356. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mtchem.2020.100356
Osisanwo FY, Akinsola JE, Awodele O, Hinmikaiye JO, Olakanmi O, Akinjobi J (2017) Supervised machine learning algorithms: classification and comparison. Int J Comput Trends Technol 48(3):128–138. https://doi.org/10.14445/22312803/ijctt-v48p126
Nasteski V (2017) An overview of the supervised machine learning methods. HORIZONS B 4:51–62. https://doi.org/10.20544/horizons.b.04.1.17.p05
Islam N, Huang W, Zhuang H (2018) Machine learning for phase selection in multi-principal element alloys. Comput Mater Sci 150:230–235. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.commatsci.2018.04.003
Huang W, Martin P, Zhuang H (2019) Machine-learning phase prediction of high-entropy alloys. Acta Mater 169:225–236. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2019.03.012
Nassar A, Mullis A (2021) Rapid screening of high-entropy alloys using neural networks and constituent elements. Comput Mater Sci 199:110755. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.commatsci.2021.110755
Choudhury A, Konnur T, Chattopadhyay P, Pal S (2019) Structure prediction of multi-principal element alloys using ensemble learning. Eng Comput 37(3):1003–1022. https://doi.org/10.1108/ec-04-2019-0151
Risal S, Zhu W, Guillen P, Sun L (2021) Improving phase prediction accuracy for high entropy alloys with machine learning. Comput Mater Sci 192:110389. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.commatsci.2021.110389
Tancret F, Toda-Caraballo I, Menou E, Rivera Díaz-Del-Castillo P (2017) Designing high entropy alloys employing thermodynamics and Gaussian process statistical analysis. Mater Des 115:486–497. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matdes.2016.11.049
Li Y, Guo W (2019) Machine-learning model for predicting phase formations of high-entropy alloys. Phys Rev Mater 3(9). https://doi.org/10.1103/physrevmaterials.3.095005
Qi J, Cheung A, Poon S (2019) High entropy alloys mined from binary phase diagrams. Sci Rep 9(1). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-019-50015-4
Zhou X, Zhu J, Wu Y, Yang X, Lookman T, Wu H (2022) Machine learning assisted design of FeCoNiCrMn high-entropy alloys with ultra-low hydrogen diffusion coefficients. Acta Mater 224:117535. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2021.117535
Agrawal A, Choudhary A (2016) Perspective: materials informatics and big data: realization of the “fourth paradigm” of science in materials science. APL Mater 4(5):053208. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.4946894
Abdoon Al-Shibaany Z, Alkhafaji N, Al-Obaidi Y, Atiyah A (2020) Deep learning-based phase prediction of high-entropy alloys. IOP Conf Ser: Mater Sci Eng 987(1):012025. https://doi.org/10.1088/1757-899x/987/1/012025
Dai D, Xu T, Wei X, Ding G, Xu Y, Zhang J, Zhang H (2020) Using machine learning and feature engineering to characterize limited material datasets of high-entropy alloys. Comput Mater Sci 175:109618. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.commatsci.2020.109618
Kaufmann K, Vecchio K (2020) Searching for high entropy alloys: a machine learning approach. Acta Mater 198:178–222. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2020.07.065
Zhang L, Chen H, Tao X, Cai H, Liu J, Ouyang Y et al (2020) Machine learning reveals the importance of the formation enthalpy and atom-size difference in forming phases of high entropy alloys. Mater Des 193:108835. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matdes.2020.108835
Buranich V, Rogoz V, Postolnyi B, Pogrebnjak A (2020) Predicting the properties of the refractory high-entropy alloys for additive manufacturing based fabrication and mechatronic applications. In: IEEE international conference on “nanomaterials: applications & properties” (NAP-2020) symposium on additive manufacturing and applications (SAMA-2020) Sumy, Ukraine, 9–13 Nov 2020
Machaka R (2021) Machine learning-based prediction of phases in high-entropy alloys. Comput Mater Sci 188:110244. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.commatsci.2020.110244
Bhandari U, Rafi M, Zhang C, Yang S (2021) Yield strength prediction of high-entropy alloys using machine learning. Mater Today Commun 26:101871. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mtcomm.2020.101871
Lee S, Byeon S, Kim H, Jin H, Lee S (2021) Deep learning-based phase prediction of high-entropy alloys: optimization, generation, and explanation. Mater Des 197, 109260. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matdes.2020.109260
Zeng Y, Man M, Bai K, Zhang Y (2021) Revealing high-fidelity phase selection rules for high entropy alloys: a combined CALPHAD and machine learning study. Mater Des 202, 109532. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matdes.2021.109532
Krishna Y, Jaiswal U, Rahul R (2021) Machine learning approach to predict new multiphase high entropy alloys. Scripta Mater 197:113804. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2021.113804
Markoulidakis I, Rallis I, Georgoulas I, Kopsiaftis G, Doulamis A, Doulamis N (2021) Multiclass confusion matrix reduction method and its application on net promoter score classification problem. Technologies 9(4):81. https://doi.org/10.3390/technologies9040081
Lewis F, Butler A, Gilbert L (2010) A unified approach to model selection using the likelihood ratio test. Methods Ecol Evol 2(2):155–162. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.2041-210x.2010.00063
Acknowledgements
Swati Singh greatly acknowledge the scholarship provided by the Ministry of Education, Government of India. Saurav Goel greatly acknowledge the support provided by the Royal Academy of Engineering via Grants No. IAPP18-19\295 and TSP1332.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2023 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Singapore Pte Ltd.
About this paper
Cite this paper
Singh, S., Joshi, S.N., Goel, S. (2023). Summary of Efforts in Phase Prediction of High Entropy Alloys Using Machine Learning. In: Joshi, S.N., Dixit, U.S., Mittal, R.K., Bag, S. (eds) Low Cost Manufacturing Technologies. NERC 2022. Springer, Singapore. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-19-8452-5_4
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-19-8452-5_4
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Singapore
Print ISBN: 978-981-19-8451-8
Online ISBN: 978-981-19-8452-5
eBook Packages: EngineeringEngineering (R0)