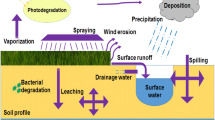
Abstract
Pests and insects are present in every nook and corner of the surrounding area which causes whooping economic losses. The substance or reagent that reduces the effective growth of these intruders like weeds, fungi, rodents and insects and other dreadful creatures are called pesticides. This chapter addresses the solutions to prohibit the toxic pollutants which spread in the pesticide form and it will become a priority for environmentalists and researchers working in this respective field.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Tarla DN, Erickson LE (2020) Phytoremediation and bioremediation of pesticide-contaminated soil. Appl Sci 2020(10):1217
Velazquez-Fernandez, Martinez-Rizo AB, Ramirez- Sandoval M (2012) Biodegradation and bioremediation of organic pesticides. Pesticides – Recent Trends Pestic Residue Assay 12:254–272
Divya M, Aanand S, Srinivasan A, Ahilan B (2015) Bioremediation – an eco- friendly tool for effluent treatment: a review. Int J Appl Res 1(12):530–537
Chawl N, Bhardwaj J, Singh L (2020) Bioremediation of organophosphate pesticides: current status and future prospective. Plant Arch 20:3405–3412
Nawaz K, Hussain K, Choudary N, Majeed A, Ilyas U, Ghani A, Lin F, Ali K, Afghan S, Raza G, Lashari MI (2011) Eco–friendly role of biodegradation against agricultural pesticides hazards. Afri J Microbiol Res 5(3):177–183
Huang X, He J, Yan X, Hong Q, Chen K, He Q et al (2017) Microbial catabolism of chemical herbicides: Microbial resources, metabolic pathways and catabolic genes. Pestic Biochem Physiol 143:272–297. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pestbp.2016.11.010
Ahmad M, Ahmad I (2014) Bioremediation of pesticides: biotechnology, vol 11: biodegradation and bioremediation
Katayama A, Matsumura F (2009) Degradation of organochlorine pesticides, particularly endosulfan, by Trichoderma harzianum. Environ Toxicol Chem 12(6):1059–1065
Sutherland TD, Horne I, Harcourt RL, Russell RJ, Oakeshott JG (2002) Isolation and characterization of a Mycobacterium strain that metabolizes the insectide endosulfan. J Appl Microbiol 93:380–389
Singh BK, Kuhad RC, Singh A, Lal R, Tripathi KK (1999) Biochemical and molecular basis of pesticide degradation by microorganisms. Crit Rev Biotechnol 19:197–225
Parekh NR, Hartmann A, Charnay MP, Fournier JC (1995) Diversity of carbofuran–degrading soil bacteria and detection of plasmid–encoded sequences homologous to the mcd gene. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 17:149–160
Sharma R, Peshin R, Shankar U, Kaul V, Sharma S (2015) Impact evaluation indicators of an Integrated Pest Management program in vegetable crops in the subtropical region of Jammu and Kashmir, India. Crop Prot 67:191–199. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cropro.2014.10.014
Sharma A, Shukla A, Attri K, Kumar M, Kumar P, Suttee A et al (2020) Global trends in pesticides: a looming threat and viable alternatives. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 201:110812. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2020.110812
Morya R, Salvachúa D, Thakur IS (2020) Burkholderia: an untapped but promising bacterial genus for the conversion of aromatic compounds. Trends Biotechnol 389:963–975. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tibtech.2020.02.008
Arora PK (2020) Bacilli-mediated degradation of xenobiotic compounds and heavy metals. Front Bioeng Biotechnol 8:570307. https://doi.org/10.3389/fbioe.2020.570307
Howard LO (1935) La menace des insectes. Flammarion, Paris, France
Hunt EG, Bischoff AI (1960) Inimical effects on wildlife of periodic DDD applications to Clear Lake. Calif Fish Game 46:91–106
Mouches C, Pasteur N, Berge JB, Hyrien O, Raymond M, Desaintvincent BR, Desilvestri M, Georghiou GP (1986) Amplification of an esterase gene is responsible for insecticide resistance in a California Culex mosquito. Science 233(4765):778–780. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.3755546
Regnault-Roger C, Philogene BJR, Vincent C (2005) Biopesticides of plant origin. Intercept Ltd., Wimborne, UK
Leduc R, Unny TE, McBean EA (1987) Stochastic modeling of the insecticide fenitrothion in water and sediment compartments of a stagnant pond. Water Resour Res 23(7):1105–1112. https://doi.org/10.1029/WR023i007p01105
Ellgehausen H, Guth JA, Esser HO (1980) Factors determining the bioaccumulation potential of pesticides in the individual compartments of aquatic food-chains. Ecotox Environ Safe 4(2):134–157. https://doi.org/10.1016/0147-6513(80)90015-9
Oberemok VV, Zaitsev AS, Levchenko NN, Nyadar PM (2015) A brief review of most widely used modern insecticides and prospects for the creation of DNA insecticides. SSN 0013–8738. Entomol Rev 95(7): 824–831
Vaccari A, Strom F, Alleman E (2006) Environmental biology for engineers and scientists
Thierry L, Armelle B, Karine J (2008) Performance of bioaugmentation– assisted phytoextraction applied to metal contaminated soils: a review. Environ Pollut 153:497–522
Philip JC, Atlas RM (2005) Bioremediation of contaminated soils and aquifers. In: Atlas RM, Philp JC (eds) Bioremediation: applied microbial solutions for real-world environmental cleanup. American Society for Microbiology (ASM) Press, Washington, pp 139–236
Azubuike CC, Chikere CB, Okpokwasili GC (2016) World J Microbiol Biotechnol 32:180
Mohan SV, Sirisha K, Rao NC, Sarma PN, Reddy SJ (2004) Degradation of chlorpyrifos contaminated soil by bioslurry reactor operated in sequencing batch mode: bioprocess monitoring. J Hazard Mater 10:116(1–2):39–48
Uqab B, Mudasir S, Nazir R (2016) Review on bioremediation of pesticides. J Bioremediat Biodegrad 7:343. https://doi.org/10.4172/2155-6199.1000343
Mary Kensa V (2011) Bioremediation - an overview. J Indust Pollut Control 27(2):161–168
Xi X, Yan J, Quan G, Cui L (2014) Removal of the pesticide pymetrozine from aqueous solution by biochar produced from brewer’s spent grain at different pyrolytic temperatures. BioResources 9:7696–7709
Ochman H, Lawrence JG, Groisman EA (2000) Lateral gene transfer and the nature of bacterial innovation. Nature 405:299
DiGiovanni GD, Neilson JW, Pepper IL, Sinclair NA (1996) Gene transfer of Alcaligenes eutrophus JMP134 plasmid pJP4 to indigenous soil recipients. Appl Environ Microbiol 62:2521
Top EM, Maila MP, Clerinx M, Goris J, De Vos P, Verstraete W (1999) Methane oxidation as a method to evaluate the removal of 2,4– dichlorophenoxyacetic acid (2,4–D) from soil by plasmid mediated bioaugmentation. FEMS Microb Ecol 28:203
Newby DT, Gentry TJ, Pepper IL (2000) Comparison of 2,4– dichlorophenoxyacetic acid degradation and plasmid transfer in soil resulting from bioaugmentation with two different pJP4 donors. Appl Environ Microbiol 66:3399
Dejonghe W, Goris J, El Fantroussi S, Hofte M, De Vos P, Verstraete W, Top EM (2000) Effect of dissemination of 2,4–dichlorophenoxyacetic acid (2,4–D) degradation plasmids on 2,4–D degradation and on bacterial community structure in two different soil horizons. Appl Environ Microbiol 66:3297
Perlak FJ, Oppenhuizen M, Gustafson K, Voth R, Sivasupramaniam S, Heering D, Carey B, Ihrig RA, Roberts JK (2001) Development and commercial use of Bollgard® cotton in the USA—Early promises versus today’s reality. Plant J 27:489
Kota M, Daniell H, Varma S, Garczynski SF, Gould F, Moar WJ (1999) Overexpression of the Bacillus thuringiensis (Bt) Cry2Aa2 protein in chloroplasts confers resistance to plants against susceptible and Bt–resistant insects: Proc. Natl Acad Sci USA 96:1840
Kim SII, Kim SJ, Nam MH (2002) Proteome analysis of aniline– induced proteins in Acinetobacter lwoffi K24. Curr Microbiol 44:61–66
Huang J, Qiao Ch–L, Li, X. and Xing, J.M. (2001) Cloning and fusion expression of detoxifing gene in Escherichia coli. Acta Genet Sin 28:583–588
Shaw LJ, Burns RG (2004) Enhanced mineralisation of [U–14C] 2,4– dichlorophenoxyacetic acid in soil from the rhizosphere of Trifolium pretense. Appl Environ Microbiol 70:4766–4774
Shaw LJ, Burns RG (2005) Rhizodeposition and the enhanced mineralization of 2,4–dichlorophenoxyacetic acid in soil from the Trifolium pretense rhizosphere. Environ Microbiol 7:191–202
Piutti S, Hallet S, Rousseaux S, Philippot L, Soulas G, Martin– Laurent, F. (2002) Accelerated mineralisation of atrazine in maize rhizosphere soil. Biol. Fert. Soils 36:434–441
Zhang R, Cui Z, Zhang X, Jiang J, Gu JD, Li S (2006) Cloning of the organophosphorus pesticide hydrolase gene clusters of seven degradative bacteria isolated from a methyl parathion contaminated site and evidence of their horizontal gene transfer. Biodegradation 17:465–472
Devers M, Henry S, Hartmann A, Laurent FM (2005) Horizontal gene transfer of atrazine–degrading genes (atz) from Agrobacterium tumefaciens St96–4 pADP1:Tn5 to bacteria of maize–cultivated soil. Pest Manage. Sci. 61:870–880
Boltner D, Moreno-Morillas S, Ramos JL (2005) 16S rDNA phylogeny and distribution of lin genes in novel hexachlorocyclohexane-degrading Sphingomonas strains. Environ Microbiol 7:1329–1338
Arshad M, Hussain S, Saleem M (2007) Optimization of environmental parameters for biodegradation of alpha and beta endosulfan in soil slurry by Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Appl Microbiol 104:364–370
Arshad M, Saleem M, Hussain S (2007) Perspectives of bacterial ACC deaminase in phytoremediation. Trends Biotechnol 8:356–362
Paknikar KM, Nagpal V, Pethkar AV, Rajwade JM (2005) Degradation of lindane from aqueous solutions using iron sulfide nanoparticles stabilized by biopolymers. Sci Technol Adv Mater 6:370–374
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2023 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Singapore Pte Ltd.
About this paper
Cite this paper
Sivarathnakumar, S., Praveenkumar, R., Vinotharulraj, J., Gayathiri, D., Amirthavarshini, A. (2023). Current Developments in Bioremediation of Pesticides and Insecticides. In: Siddiqui, N.A., Baxtiyarovich, A.S., Nandan, A., Mondal, P. (eds) Advances in Waste Management. AIR 2021. Lecture Notes in Civil Engineering, vol 301. Springer, Singapore. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-19-7506-6_18
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-19-7506-6_18
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Singapore
Print ISBN: 978-981-19-7505-9
Online ISBN: 978-981-19-7506-6
eBook Packages: EngineeringEngineering (R0)