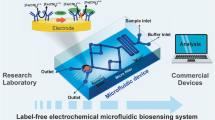
Abstract
The increasing demand of biosensing in the health care sector is meticulously associated with the need of fabricating diagnostic tools with an instant, point-of-care (POC) approach. These devices are expected to have high sensitivity, portability and selectivity. Off lately, an extensive focus on designing biosensors with an imperative technique has been accomplished to ensemble the materials, equipment and methodologies to improve their performance. Basically, biosensor is an analytical sensor which has a biological moiety, like enzymes, antibodies, live cells, etc., as an electron transfer mediator to detect analytes via a suitable detection mechanism including electro-catalytic activity. These sensors tend to produce electrical current signals whose intensity is dependent on the concentration of the selective analyte. Since, 1999, when IUPAC designated biosensor as a sovereign tool for selective qualitative and quantitative analyte detection, several chemically modified biosensors have been reported. However, most of these are bulk electrodes that are laboratory-based, use large sample volumes, lack POC approach and therefore cannot be employed for real time field sensing. To overcome this, significant research has been carried out to miniaturize and integrate microfluidic concept with these devices. The advent of microfluidics not only makes these biosensors suitable for real-time practical application but also makes them cost-effective, portable and more sensitive. During the last few years, several research groups globally have successfully developed miniaturized/microfluidic biosensor-integrated electrochemical platforms for health care applications. The present chapter briefly describes the fabrication, characterization, materials used and types of these biosensor devices and summarizes some of the recent advance applications in health management. The future prospects and present limitations are also highlighted.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Panjan, P., Virtanen, V., Sesay, A.M.: Determination of stability characteristics for electrochemical biosensors via thermally accelerated ageing. Talanta 170, 331–336 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2017.04.011
Thévenot, D.R., Toth, K., Durst, R.A., Wilson, G.S.: Electrochemical biosensors: recommended definitions and classification. Biosens. Bioelectron. 16, 121–131 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0956-5663(01)00115-4
Lowe, C.R., Lowe, C.R., Collyer, S.D., Higson, S.P.J., Newman, J.D., Turner, A.P.F., Marks, R.S., Mccourt, P., Kramer, K.: Handbook of Biosensors and Biochips Table of Contents, vol. 41, pp. 217–232 (2007), ISBN: 9780470019054
Clark, L.C., Lyons, C.: Electrode systems for continuous monitoring in cardiovascular surgery. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 102, 29–45 (1962). https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1749-6632.1962.tb13623.x
Perumal, V., Hashim, U.: Advances in biosensors: principle, architecture and applications. J. Appl. Biomed. 12, 1–15 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jab.2013.02.001
Wilson, G.S., Hu, Y.: Enzyme-based biosensors for in vivo measurements. Chem. Rev. 100, 2693–2704 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1021/cr990003y
Conroy, P.J., Hearty, S., Leonard, P., O’Kennedy, R.J.: Antibody production, design and use for biosensor-based applications. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 20, 10–26 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.semcdb.2009.01.010
Cagnin, S., Caraballo, M., Guiducci, C., Martini, P., Ross, M., Santaana, M., Danley, D., West, T., Lanfranchi, G.: Overview of electrochemical DNA biosensors: new approaches to detect the expression of life. Sensors (Switzerland) 9, 3122–3148 (2009). https://doi.org/10.3390/s90403122
Suzuki, K.: Biosensing. Anal. Sci. 23, 3 (2007). https://doi.org/10.2116/analsci.23.3
Lu, L., Hu, X., Zhu, Z.: Biomimetic sensors and biosensors for qualitative and quantitative analyses of five basic tastes. TrAC—Trends Anal. Chem. 87, 58–70 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trac.2016.12.007
Abdulhalim, I., Zourob, M., Lakhtakia, A.: Overview of Optical Biosensing Techniques (2008). https://doi.org/10.1002/9780470061565.hbb040
Yang, W., Ratinac, K.R., Ringer, S.R., Thordarson, P., Gooding, J.J., Braet, F.: Carbon nanomaterials in biosensors: should you use nanotubes or graphene. Angew. Chem.—Int. Ed. 49, 2114–2138 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.200903463
Aydemir, N., Malmström, J., Travas-Sejdic, J.: Conducting polymer based electrochemical biosensors. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 18, 8264–8277 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1039/c5cp06830d
Monošík, R., Streďanský, M., Šturdík, E.: Biosensors—Classification, characterization and new trends. Acta Chim. Slovaca 5, 109–120 (2012). https://doi.org/10.2478/v10188-012-0017-z
Alonso-Lomillo, M.A., Domínguez-Renedo, O., Arcos-Martínez, M.J.: Screen-printed biosensors in microbiology: a review. Talanta 82, 1629–1636 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2010.08.033
Dong, Y., Min, X., Kim, W.S.: A 3-D-printed integrated PCB-based electrochemical sensor system. IEEE Sens. J. 18, 2959–2966 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1109/JSEN.2018.2801459
Goral, V.N., Hsieh, Y.C., Petzold, O.N., Faris, R.A., Yuen, P.K.: Hot embossing of plastic microfluidic devices using poly(dimethylsiloxane) molds. J. Micromech. Microeng.. 21 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1088/0960-1317/21/1/017002
Gale, B.K., Jafek, A.R., Lambert, C.J., Goenner, B.L., Moghimifam, H., Nze, U.C., Kamarapu, S.K.: A review of current methods in microfluidic device fabrication and future commercialization prospects. Inventions 3 (2018). https://doi.org/10.3390/inventions3030060
Stevenson, J.T.M., Gundlach, A.M.: The application of photolithography to the fabrication of microcircuits. J. Phys. E. 19, 654–667 (1986). https://doi.org/10.1088/0022-3735/19/9/001
Campaña, A.L., Florez, S.L., Noguera, M.J., Fuentes, O.P., Puentes, P.R., Cruz, J.C., Osma, J.F.: Enzyme-based electrochemical biosensors for microfluidic platforms to detect pharmaceutical residues in wastewater. Biosensors 9 (2019). https://doi.org/10.3390/bios9010041
Nadar, S.S., Patil, P.D., Tiwari, M.S., Ahirrao, D.J.: Enzyme embedded microfluidic paper-based analytic device (μPAD): a comprehensive review. Crit. Rev. Biotechnol. 41, 1046–1080 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1080/07388551.2021.1898327
Mohammad, M., Razmjou, A., Liang, K., Asadnia, M., Chen, V.: Metal-organic-framework-based enzymatic microfluidic biosensor via surface patterning and biomineralization. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 11, 1807–1820 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.8b16837
Cao, L., Han, G.C., Xiao, H., Chen, Z., Fang, C.: A novel 3D paper-based microfluidic electrochemical glucose biosensor based on rGO-TEPA/PB sensitive film. Anal. Chim. Acta. 1096, 34–43 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aca.2019.10.049
Li, J., Li, Z., Dou, Y., Su, J., Shi, J., Zhou, Y., Wang, L., Song, S., Fan, C.: A nano-integrated microfluidic biochip for enzyme-based point-of-care detection of creatinine. Chem. Commun. 57, 4726–4729 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1039/d1cc00825k
Zhu, X., Huang, J., Liu, J., Zhang, H., Jiang, J., Yu, R.: A dual enzyme-inorganic hybrid nanoflower incorporated microfluidic paper-based analytic device (μPAD) biosensor for sensitive visualized detection of glucose. Nanoscale 9, 5658–5663 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1039/c7nr00958e
Shitanda, I., Mitsumoto, M., Loew, N., Yoshihara, Y., Watanabe, H., Mikawa, T., Tsujimura, S., Itagaki, M., Motosuke, M.: Continuous sweat lactate monitoring system with integrated screen-printed Mgo-templated carbon-lactate oxidase biosensor and microfluidic sweat collector. Electrochim. Acta. 368, 137620 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.electacta.2020.137620
Nasseri, B., Soleimani, N., Rabiee, N., Kalbasi, A., Karimi, M., Hamblin, M.R.: Point-of-care microfluidic devices for pathogen detection. Biosens. Bioelectron. 117, 112–128 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2018.05.050
Rumeysa Akçapınar.pdf (n.d.)
Funari, R., Chu, K.Y., Shen, A.Q.: Detection of antibodies against SARS-CoV-2 spike protein by gold nanospikes in an opto-microfluidic chip. Biosens. Bioelectron. 169, 112578 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2020.112578
Zhang, W., He, Z., Yi, L., Mao, S., Li, H., Lin, J.M.: A dual-functional microfluidic chip for on-line detection of interleukin-8 based on rolling circle amplification. Biosens. Bioelectron. 102, 652–660 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2017.12.017
Nunna, B.B., Mandal, D., Lee, J.U., Singh, H., Zhuang, S., Misra, D., Bhuyian, M.N.U., Lee, E.S.: Detection of cancer antigens (CA-125) using gold nano particles on interdigitated electrode-based microfluidic biosensor. Nano Converg. 6 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1186/s40580-019-0173-6
Evans, D., Papadimitriou, K.I., Vasilakis, N., Pantelidis, P., Kelleher, P., Morgan, H., Prodromakis, T.: A novel microfluidic point-of-care biosensor system on printed circuit board for cytokine detection. Sensors (Switzerland) 18, 1–14 (2018). https://doi.org/10.3390/s18114011
Liu, J., Jasim, I., Shen, Z., Zhao, L., Dweik, M., Zhang, S., Almasri, M.: A microfluidic based biosensor for rapid detection of Salmonella in food products. PLoS ONE 14, 1–18 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0216873
Adampourezare, M., Dehghan, G., Hasanzadeh, M., Hosseinpoure Feizi, M.A.: Application of lateral flow and microfluidic bio-assay and biosensing towards identification of DNA-methylation and cancer detection: recent progress and challenges in biomedicine. Biomed. Pharmacother. 141, 111845 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopha.2021.111845
Wu, Q., Zhang, Y., Yang, Q., Yuan, N., Zhang, W.: Review of electrochemical DNA biosensors for detecting food borne pathogens. Sensors (Switzerland) 19 (2019). https://doi.org/10.3390/s19224916
Bruch, R., Johnston, M., Kling, A., Mattmüller, T., Baaske, J., Partel, S., Madlener, S., Weber, W., Urban, G.A., Dincer, C.: CRISPR-powered electrochemical microfluidic multiplexed biosensor for target amplification-free miRNA diagnostics. Biosens. Bioelectron. 177 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2020.112887
Caneira, C.R.F., Soares, R.R.G., Pinto, I.F., Mueller-Landau, H.S., Azevedo, A.M., Chu, V., Conde, J.P.: Development of a rapid bead-based microfluidic platform for DNA hybridization using single- and multi-mode interactions for probe immobilization. Sens. Actuators, B Chem. 286, 328–336 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2019.01.133
Ghrera, A.S., Pandey, C.M., Malhotra, B.D.: Multiwalled carbon nanotube modified microfluidic-based biosensor chip for nucleic acid detection. Sens. Actuators, B Chem. 266, 329–336 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2018.03.118
Pursey, J.P., Chen, Y., Stulz, E., Park, M.K., Kongsuphol, P.: Microfluidic electrochemical multiplex detection of bladder cancer DNA markers. Sens. Actuators, B Chem. 251, 34–39 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2017.05.006
Alsabbagh, K., Hornung, T., Voigt, A., Sadir, S., Rajabi, T., Länge, K.: Microfluidic impedance biosensor chips using sensing layers based on DNA-based self-assembled monolayers for label-free detection of proteins. Biosensors 11, 1–12 (2021). https://doi.org/10.3390/bios11030080
Gupta, N., Renugopalakrishnan, V., Liepmann, D., Paulmurugan, R., Malhotra, B.D.: Cell-based biosensors: recent trends, challenges and future perspectives. Biosens. Bioelectron. 141, 111435 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2019.111435
Zhai, J., Yi, S., Jia, Y., Mak, P.I., Martins, R.P.: Cell-based drug screening on microfluidics. TrAC—Trends Anal. Chem. 117, 231–241 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trac.2019.05.018
Liu, Q., Wu, C., Cai, H., Hu, N., Zhou, J., Wang, P.: Cell-based biosensors and their application in biomedicine. Chem. Rev. 114, 6423–6461 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1021/cr2003129
Su, L., Jia, W., Hou, C., Lei, Y.: Microbial biosensors: a review. Biosens. Bioelectron. 26, 1788–1799 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2010.09.005
Chen, P., Guo, Y., Wang, J., Du, W., Feng, X., Liu, B.F.: A localized chemical pulse generator for the development of a microfluidic cell-based biosensor. Sens. Actuators, B Chem. 251, 112–119 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2017.05.038
Brennan, L.M., Widder, M.W., McAleer, M.K., Mayo, M.W., Greis, A.P., van der Schalie, W.H.: Preparation and testing of impedance-based fluidic biochips with RTgill-W1 cells for rapid evaluation of drinking water samples for toxicity. J. Vis. Exp. 2016, 1–8 (2016). https://doi.org/10.3791/53555
Khan, N.I., Song, E.: Lab-on-a-chip systems for aptamer-based biosensing. Micromachines 11, 1–30 (2020). https://doi.org/10.3390/mi11020220
Vandghanooni, S., Sanaat, Z., Farahzadi, R., Eskandani, M., Omidian, H., Omidi, Y.: Recent progress in the development of aptasensors for cancer diagnosis: focusing on aptamers against cancer biomarkers. Microchem. J. 170, 106640 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.microc.2021.106640
Jiang, Y., Zou, S., Cao, X.: A simple dendrimer-aptamer based microfluidic platform for E. coli O157:H7 detection and signal intensification by rolling circle amplification. Sens. Actuators, B Chem. 251, 976–984 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2017.05.146
Bhardwaj, T., Dalal, P., Rathore, A.S., Jha, S.K.: An aptamer based microfluidic chip for impedimetric detection of Ranibizumab in a bioreactor. Sens. Actuators, B Chem. 312, 127941 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2020.127941
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2023 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Singapore Pte Ltd.
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Amreen, K., Guha, K., Goel, S. (2023). An Overview of Integrated Miniaturized/Microfluidic Electrochemical Biosensor Platforms for Health Care Applications. In: Dutta, G., Biswas, A. (eds) Next Generation Smart Nano-Bio-Devices. Smart Innovation, Systems and Technologies, vol 322. Springer, Singapore. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-19-7107-5_5
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-19-7107-5_5
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Singapore
Print ISBN: 978-981-19-7106-8
Online ISBN: 978-981-19-7107-5
eBook Packages: EngineeringEngineering (R0)