Abstract
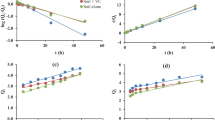
Pesticides are used in the agricultural field in order to destroy harmful pests and weeds. Nowadays, the excessive use of pesticides also produces a detrimental effect on the ecosystem. Though many European countries have banned its use, some countries like India still allow it. In this study, laboratory-scale batch experiments were conducted with the help of response surface methodology to determine the sorption behavior of a commonly used fungicide Carbendazim on a locally available silty sandy soil of the Durgapur region, West Bengal, having a saturated hydraulic conductivity of 1.66 × 10–5 cm/s. The soil proved to be moderately efficient in removing Carbendazim at the rate of 63.93% for a selective dose of Carbendazim as 12 mg/L within a contact time of 2 h. The Langmuir isotherm model and pseudo-second-order kinetic model proved to be the best fit with R2 values of 0.99 and 0.98, respectively.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Webster JPG, Bowles RG, Williams NT (1999) Estimating the economic benefits of alternative pesticide usage scenarios: wheat production in the United Kingdom. Crop Prot 18:83–89
Goodson WH et al (2015) Assessing the carcinogenic potential of low-dose exposures to chemical mixtures in the environment: the challenge ahead. Carcinogenesis 36:S254–S296. https://doi.org/10.1093/carcin/bgv039
Huan Z, Luo J, Xu Z, Xie D (2016) Acute toxicity and genotoxicity of Carbendazim, main impurities and metabolite to earthworms (Eisenia foetida). Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 96:62–69. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00128-015-1653-y
Ahmad KS, Rashid N, Nazar MF, Tazaiyen S (2013) Adsorption and desorption characteristic of benzimidazole based fungicide carbendazim in Pakistani soils. J Chem Soc Pak 34(3):1017–1024
Nemeth-Konda L, Füleky Gy, Morovjan Gy, Csokan P (2002) Sorption behaviour of acetochlor, atrazine, Carbendazim, diazinon, imidacloprid and isoproturon on Hungarian agricultural soil. Chemosphere 48(5):545–552
Adhikary A, Konar P, Chakraborty T, Pal S, Ghosh S (2021) Efficacy assessment of silty-sandy soil as bed material in constructed wetland to treat naphthalene-laden wastewater: physical and numerical modeling. J Hazard Toxic Radioact Waste 26(2):04021064. https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)HZ.2153-5515.0000670
Li X, Zhou Q, Wei S, Ren W, Sun X (2011) Adsorption and desorption of Carbendazim and cadmium in typical soils in northeastern China as affected by temperature. Geoderma 160(3–4):347–354. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geoderma.2010.10.003
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2023 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Singapore Pte Ltd.
About this paper
Cite this paper
Datta, D., Waris, A., Adhikary, A., Pal, S., Adhikari, K. (2023). Assessment of Efficacy of Silty-Sandy Soil to Treat Carbendazim-Laden Wastewater. In: Reddy, K.R., Kalia, S., Tangellapalli, S., Prakash, D. (eds) Recent Advances in Sustainable Environment . Lecture Notes in Civil Engineering, vol 285. Springer, Singapore. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-19-5077-3_31
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-19-5077-3_31
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Singapore
Print ISBN: 978-981-19-5076-6
Online ISBN: 978-981-19-5077-3
eBook Packages: EngineeringEngineering (R0)