Abstract
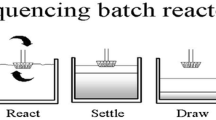
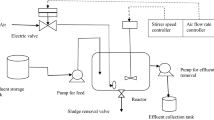
Water is an essential commodity that is getting scarce due to its overuse. The primary consumers of water resources are the industries, and due to industrialization, the generation of wastewater is increasing. When discharged into water bodies, this wastewater contaminates the water bodies greatly, and thus its treatment is of utmost importance. The treatment facility is not economical for small and medium-scale industries. Hence, for such industries, a Common Effluent Treatment facility (CETP) is provided where the wastewater from a cluster of industries is collected, treated and finally discharged. The present study treats CETP wastewater using a sequencing batch reactor (SBR) with suspended biomass and an SBR-IFAS, which uses a combined suspended and attached growth process. The study was done on homogeneous textile wastewater from a CETP. HRT for the system was 10 h, with 9 h aeration and 1 h settling. The pre-treated wastewater was used as an influent in the study with an inlet COD concentration varying between 600 and 1160 mg/L. After the treatment in the SBR reactor, the maximum COD removal was 65.7% for homogeneous textile wastewater. Chromium removal was 48%, at a maximum suspended MLSS of 2852 mg/L with an SVI of 30 mL/g. In SBR- IFAS, maximum COD removal was 74.28%, chromium removal was 53.33% with a suspended MLSS of 2600 mg/L and attached biomass of 6.72 mg/m with SVI of 96 mL/g. Thus, the study indicates that the IFAS system incorporated in SBR will enhance the treatment efficiency while reducing the effluent concentration and help treat a larger volume of industrial wastewater for the same footprint.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Popat A, Nidheesh PV, Singh TSA, Kumar MS (2019) Mixed industrial wastewater treatment by combined electrochemical advanced oxidation and biological processes. Chemosphere 237:124419
Holkar CR, Jadhav AJ, Pinjari DV, Mahamuni NM, Pandit AB (2016) A critical review on textile wastewater treatments: possible approaches. J Environ Manage 182:351–366
Waqas S, Bilad MR, Man Z, Wibisono Y, Jaafar J, Mahlia TMI, Khan AL, Aslam M (2020) Recent progress in integrated fixed-film activated sludge process for wastewater treatment: a review. Journal Environ Manage 268:110718
Hait S, Mazumder D (2008) Scope of improvement of treatment capacity of activated sludge process by hybrid modification. J Environ Eng 7:147–158
Sen D, Farren G, Sturdevant J, Copithorn RR (2006) Case study of an IFAS system—Over 10 years of experience 4309–4324
Metcalf & Eddy, Inc. (2017) Wastewater engineering: treatment and reuse. Boston :McGraw-Hill
Mirbolooki H, Amirnezhad R, Pendashteh AR (2017) Treatment of high saline textile wastewater by activated sludge microorganisms. J Appl Res Technol 15:167–172
Maddad M, Abid S, Hamdi M, Boullagui H (2018) Reduction of adsorbed dyes content in the discharged sludge coming from an industrial textile wastewater treatment plant using aerobic activated sludge process. J Environ Eng 223:936–946
Kumar K, Singh GK, Dastidar MG, Sreekrishnan TR (2014) Effect of mixed liquor volatile suspended solids (MLVSS) and hydraulic retention time (HRT) on the performance of activated sludge process during the biotreatment of real textile wastewater. Water Resour Ind 5:1–8
Pophali GR, Kaul SN, Mathur S (2003) Influence of hydraulic shock loads and TDS on the performance of large-scale CETPs treating textile effluents in India. Water Res 37:353–361
Vaiopoulou E, Gikas P (2012) Effects of chromium on activated sludge and on the performance of wastewater treatment plants: a review. Water Res 46:549–570
Mojiri A, Ohashi A, Ozaki N, Kindaichi T (2018) Pollutants removal from synthetic wastewater by the combined electrochemical, adsorption and sequencing batch reactor (SBR). Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 137–144
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2023 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Singapore Pte Ltd.
About this paper
Cite this paper
Sudhakar, S., Moondra, N., Christian, R.A. (2023). Comparison of Suspended Growth and IFAS Process for Textile Wastewater Treatment. In: Ranadive, M.S., Das, B.B., Mehta, Y.A., Gupta, R. (eds) Recent Trends in Construction Technology and Management. Lecture Notes in Civil Engineering, vol 260. Springer, Singapore. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-19-2145-2_34
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-19-2145-2_34
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Singapore
Print ISBN: 978-981-19-2144-5
Online ISBN: 978-981-19-2145-2
eBook Packages: EngineeringEngineering (R0)