Abstract
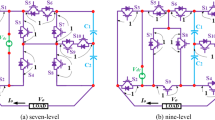
The MLI is developed by combining cross-switched MLI (main circuit) with switched-capacitor MLI (auxiliary circuit). For different combinations of input DC voltage sources, the proposed inverter is analyzed and the general equations of different quantities have been found out. As the switched-capacitor circuit is interconnected with the cross-switched MLI, it reduces the number of power supplies and switching devices and further boosted the input voltage. A detailed comparison study has been presented. Half height (HH) pulse width modulation scheme has been chosen as the switching scheme in order to reduce the switching loss of the multilevel inverter.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
K.K. Gupta, A. Ranjan, L. Bhatnagar, Multilevel inverter topologies with reduced device count: a review. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 31(1), 135–151 (2016)
L.G. Franquelo, J. Rodriguez, J.I. Leon, The age of multilevel converters arrives. IEEE Ind. Electron. Mag. 2(2), 28–39 (2008)
J. Rodriguez, J. Lai, Multilevel inverters: a survey of topologies, controls, and applications. IEEE Trans. Industr. Electron. 49(4), 724–738 (2002)
J. Lai, F. Peng, Multilevel converters-a new breed of power converters. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 32(3), 509–517 (1996)
L. Nanda, A. Dasgupta, U.K. Rout, A comparative analysis of symmetrical and asymmetrical cascaded multilevel inverter having reduced number of switches and DC sources. Int. J. Power Electron. Drive Syst. 8(4), 1595–1602 (2017)
L. Nanda, A. Dasgupta, A comparative studies of cascaded multilevel inverters havingreduced number of switches with R and RL-load. Int. J. Power Electron. Drive Syst. (IJPEDS) 8(1), 40–50 (2017)
M.F. Kangarlu, E. Babaei, Cross-switched multilevel inverter: an innovative topology. IET Power Electron. 6(4), 642–651 (2013)
S. Thamizharasan, J. Baskaran, S. Ramkumar, Cross-switched multilevel inverter using auxiliary reverse-connected voltage sources. IET Power Electron. 7(6), 1519–1526 (2014)
Y.H. Liao, C.M. Lai, Newly-constructed simplified single-phase multistring multi-level inverter topology for distributed energy resources. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 26(9), 2386–2392 (2011)
L. Nanda, A. Dasgupta, U.K. Rout, A comparative analysis of modified cascaded multilevel inverter having reduced number of switches and DC sources. Int. J. Appl. Eng. Res. 12(20), 10121–10126 (2017)
L. Nanda, A. Dasgupta, U.K. Rout, A comparative analysis of symmetrical andasymmetrical cascaded multilevel inverter having reduced number of switches and DC sources. Int. J. Power Electron. Drive Syst. (IJPEDS) 8(4), 1595–1602 (2017)
P. Palanivel, S.S. Dash, Analysis of THD and output voltage performance for cascaded multilevel inverter using carrier pulse width modulation techniques. Power Electron. IET 4(8), 951–958 (2011)
L. Nanda et al., A comparative studies of different topologies of multilevel inverterwith SIMULINK, in 2017 International Conference on Inventive Systems and Control (ICISC), pp. 1–7 (2017)
M.W. Tesfay, T. Roy, S.K. Swain, L. Nanda, A novel step-up 7L switched-capacitor multilevel inverter and its extended structure, in 2021 1st International Conference on Power Electronics and Energy (ICPEE), pp. 1–6 (2021)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2022 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Singapore Pte Ltd.
About this paper
Cite this paper
Nanda, L., Jena, C., Panda, B., Pradhan, A. (2022). A Cross-connected Switch Capacitor Multilevel Inverter: A Proposed Topology and Its Analysis. In: Pundir, A.K.S., Yadav, N., Sharma, H., Das, S. (eds) Recent Trends in Communication and Intelligent Systems. Algorithms for Intelligent Systems. Springer, Singapore. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-19-1324-2_6
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-19-1324-2_6
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Singapore
Print ISBN: 978-981-19-1323-5
Online ISBN: 978-981-19-1324-2
eBook Packages: Intelligent Technologies and RoboticsIntelligent Technologies and Robotics (R0)