Abstract
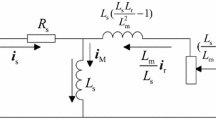
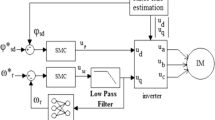
This chapter proposes full-order terminal sliding-mode (FOTSM) based observation and control approaches for the sensorless speed control system of the induction motor (IM) with the full consideration of the unmatched uncertainties. The sensorless field orientation control (FOC) system for the IM is based on the accurately observing of the speed and the flux of the motor using the full-order terminal sliding-mode observer (FOTSMO). With the feedback of the precise estimated speed/flux, the FOTSM based controllers for the speed-, flux- and current-loops are designed to strengthen the robustness, accuracy and rapidness of the FOC system for the IM. By means of the virtual control technique in the outer-loop, the unmatched uncertainties including the parameter perturbation and the external disturbance can be thoroughly compensated. The proposed adaptive gain avoids overestimating the upper bound of the uncertainties in the FOC system for the IM. Due to the integral-type control law, the current references are smoothed and the chattering in the conventional SMC is eliminated. In the inner-loop controllers, the actual voltage control signals can force the tracking errors of the currents to converge to their equilibrium points in a finite time. Finally, the simulation and experimental results have demonstrated the effectiveness and feasibility of the proposed FOTSM based controllers and observers for the sensorless speed control of the IM.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- u, u:
-
The voltage and voltage vector
- i, i:
-
The current and current vector
- ϕ, ϕ:
-
The flux and flux vector
- θ :
-
The rotor electrical angle
- ω :
-
The rotor electric angular velocity
- ω m :
-
The rotor mechanical angular velocity
- ω s :
-
The slip angle velocity
- ω 1 :
-
The synchronous angle velocity with ω1 = ω + ωs
- J :
-
The moment of inertia
- R s :
-
The stator resistance
- R r :
-
The rotor resistance
- L s :
-
The stator inductance
- L r :
-
The rotor inductance
- L m :
-
The mutual inductance between the stator and rotor windings
- T e :
-
The electrical torque
- T L :
-
The load torque
- n :
-
The rotation speed
- ^ :
-
The estimated value
- — :
-
The error value
- []0:
-
The nominal value
- []ref:
-
The reference value
- []s, []r:
-
Stator and rotor parameters
- []ABC, []abc:
-
States in abc-axis
- []α, []β:
-
States in α- and β-axis
- []q, []d:
-
States in q- and d-axis
- n p :
-
The number of pole pairs of the stator
- Lsl, Lrl:
-
The stator and rotor leakage inductance
- Lsm, Lrm:
-
The mutual inductance between the stator and rotor windings
- T r :
-
The rotor time constant Tr = Lr/Rr
- σ :
-
The leakage coefficient \(\sigma = 1 - L_m^2 /(L_s L_r )\)
- K :
-
K = 1/(σLs)
- ξ :
-
ξ = K(Lm/Ls)
- λ :
-
\(\lambda = K(R_s + R_r L_m^2 /L_r^2 )\)
- ADRC:
-
Active disturbance reject control
- AFO:
-
Adaptive full-order observer
- DTC:
-
Direct torque control
- EKF:
-
Extended kalman filter
- FOC:
-
Field-oriented control
- FOTSM:
-
Full-order terminal sliding-mode
- FOTSMO:
-
Full-order terminal sliding-mode observer
- IM:
-
Induction motor
- LSM:
-
Linear sliding-mode
- LSMO:
-
Linear sliding-mode observer
- MIMO:
-
Multiply inputs multiply outputs
- MPC:
-
Model predictive control
- MRAC:
-
Model reference adaptive control
- PI:
-
Proportion-integral
- SMC:
-
Sliding-mode control
- SMO:
-
Sliding-mode observer
- SVPWM:
-
Space vector pulse width modulation
References
C. Luo, B. Wang, Y. Yu, C. Chen, Z. Huo, D. Xu, Decoupled stator resistance estimation for speed-sensorless induction motor drives considering speed and load torque variations. IEEE J. Emerg. Sel. Top. Power Electron. 8(2), 1193–1207 (2020)
A. Datta, G. Poddar, Improved low-frequency operation of hybrid inverter for medium-voltage induction motor drive under V/F and vector control mode of operation. IEEE J. Emerg. Sel. Top. Power Electron. 8(2), 1248–1257 (2020)
F. Zhang, A new high power factor AC-AC inverter. IEEE Power Electron Lett. 1(5), 10–13 (2000)
Y. Feng, J. Zheng, X. Yu, N.V. Truong, Hybrid terminal sliding-mode observer design method for a permanent-magnet synchronous motor control system. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 56(9), 3424–3431 (2009)
A. Ammar, A. Bourek, A. Benakcha, Sensorless SVM-direct torque control for induction motor drive using sliding-mode observers. J. Control Autom. Electr. Syst. 28(2), 189–202 (2017)
M.S. Zaky, M.K. Metwaly, H.Z. Azazi, S.A. Deraz, A new adaptive SMO for speed estimation of sensorless induction motor drives at zero and very low frequencies. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 65(9), 6901–6911 (2018)
O. Barambones, P. Alkorta, Position control of the induction motor using an adaptive sliding-mode controller and observers. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 61(12), 6556–6565 (2014)
M. Morawiec, A. Lewicki, Speed observer structure of induction machine based on sliding super-twisting and backstepping techniques. IEEE Trans. Ind. Info. 17(2), 1122–1131 (2021)
L. Shen, L. Emil, J. Martin, FCS-MPC-based current control of a five-phase induction motor and its comparison with PI-PWM control. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 61(1), 149–163 (2014)
T. Jakub, L.V. Quoc, S. Vaclav, P. Zdenek, Adaptive speed control of induction motor drive with inaccurate model. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 65(11), 8532–8542 (2018)
A. Abdelkarim, B. Abdelhamid, B. Amor, Adaptive MRAC-based direct torque control with SVM for sensorless induction motor using adaptive observer. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 91(5–8), 1631–1641 (2017)
T. Murata, T. Tsuchiya, I. Takeda, Vector control for induction machine on the application of optimal control theory. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 37(4), 283–290 (1990)
A. Matsushita, T. Tsuchiya, Decoupled preview control system and its application to induction motor drive. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 42(1), 50–57 (1995)
R. Gerasimos, B. Krishna, S. Dimitrios, Nonlinear optimal control for ship propulsion with the use of an induction motor and a drivetrain. MATEC Web Conf, vol. 188, no. 1, (2018)
H. Yang, Y. Zhang, P.D. Walker, A method to start rotating induction motor based on speed sensorless model-predictive control. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 32(1), 359–368 (2017)
H. Gao, B. Wu, D. Xu, M. Pande, R.P. Aguilera, Common-mode-voltage-reduced model-predictive control scheme for current-source-converter-fed induction motor drives. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 32(6), 4891–4904 (2017)
F. Mehazzem, A. Reama, Comparative study of integral and classical backstepping controllers in IFOC of induction motor fed by voltage source inverter. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 42(28), 17953–17964 (2017)
B.R. Chiheb, F. Fethi, Z. Abderrahmen, C. Abdelkader, A novel adaptive control method for induction motor based on backstepping approach using dSpace DS 1104 control board. Mech. Syst. Signal Process 100, 466–481 (2018)
R. Christian, R. Jose, K. Samir, V. Felipe, Multiobjective fuzzy-decision-making predictive torque control for an induction motor drive, in IEEE Transaction on Power Electron, vol. 32, no. 8 (2017), pp. 6245–6260
D. Xu, J. Huang, X. Su, P. Shi, Adaptive command-filtered fuzzy backstepping control for linear induction motor with unknown end effect. Inf. Sci. 477, 118–131 (2019)
Z. Mohamed, K. Mohamed, A performance investigation of a four-switch three-phase inverter-fed IM drives at low speeds using fuzzy logic and PI controllers, in IEEE Transaction on Power Electron, vol. 32, no. 5 (2017), pp. 3741–3753
H. Sathishkumar, S. S. Parthasarathy, A novel neural network intelligent controller for vector controlled induction motor drive, Energy Procedia, vol. 138, no. 1.1 (2017), pp. 692–697
Z. Yin, C. Du, J. Liu, Research on autodisturbance-rejection control of induction motors based on an ant colony optimization algorithm. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron 65(4), 3077–3094 (2018)
A. Abdelkarim, B. Amor, B. Abdelhamid, Nonlinear SVM-DTC for induction motor drive using input-output feedback linearization and high order sliding-mode control. ISA Trans. 67, 428–442 (2017)
M. Saleh, Y. Hamid, A.K.Mojtaba, Adaptive sliding-mode type-2 neuro-fuzzy control of an induction motor, Expert Sys. Appl. 42(19), 6635–6647 (2015)
T.A.V. Ravi, C. Chandan, P. Bikash, Disturbance rejection analysis and FPGA-based implementation of a second-order sliding-mode controller fed induction motor drive, IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 33(3), 1453–1462 (2018)
A. Francesco, C. Maurizio, D. Filippo, Robust active disturbance rejection control of induction motor systems based on additional sliding-mode component. IEEE Trans. Ind Electron. 64(7), 5608–5621 (2017)
D.G. Stefano, R.D. Jorge, M.M. Antonio, Sensorless high order sliding-mode control of induction motors with core loss. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 61(6), 2678–2689 (2014)
B. Oscar, A. Patxi, Position control of the induction motor using an adaptive sliding-mode controller and observers. IEEE Trans. Ind Electron. 61(12), 6556–6565 (2014)
C. Edwards, S. Spurgeon, Sliding-Mode Control: Theory and Applications (Crc Press, 1998)
Y. Shtessel, C. Edwards, L. Fridman, Sliding-Mode Control and Observation (Springer, New York, 2014), pp. 213–249
B. Zheng, J.H. Park, Sliding-mode control design for linear systems subject to quantization parameter mismatch. J. Franklin Inst. 353(1), 37–53 (2016)
A. Ahmadreza, L. Li, S. Su, N. Hung, On LMI-based sliding-mode control for uncertain discrete-time systems. J. Franklin Inst. 353(15), 3857–3875 (2016)
H.M. Hosein, O. Mansour, T. Asghar, Modified DTC of a six-phase induction motor with a second-order sliding-mode MRAS-based speed estimator. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 34(1), 600–611 (2019)
S. Ouchen, M. Benbouzid, F. Blaabjerg, A. Betka, H. Steinhart, Direct power control of shunt active power filter using space vector modulation based on super twisting sliding-mode control, IEEE J. Emerg. Sel. Top. Power. Electron. (2020)
Y. Feng, M. Zhou, Q. Han, F. Han, Z. Cao, S. Ding, Integral-type sliding-mode control for a class of mechatronic systems with gain adaptation. IEEE Trans. Ind. Info. 16(8), 5357–5368 (2020)
Y. Feng, M. Zhou, X. Zheng, F. Han, X. Yu, Full-order terminal sliding-mode control of MIMO systems with unmatched uncertainties. J. Franklin Inst. 355(2), 653–674 (2018)
M. Zhou, Y. Feng, C. Xue, F. Han, Deep convolutional neural network based fractional-order terminal sliding-mode control for robotic manipulators. Neurocomputing (2019)
B.K. Bose, Power Electronics and AC Drives (Englewood Cliffs, 1986)
H.-J. Shieh, K.-K. Shyu, Nonlinear sliding-mode torque control with adaptive backstepping approach for induction motor drive. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 46(2), 380–389 (1999)
J. Xu, R. Yi, B. Chen, Stator-flux-orientated slip frequency control for induction motor, IPEMC, vol. 1 (2004), pp. 401–404
S. Bhat, D. Bernstein, Finite-time stability of continuous autonomous systems. SIAM J. Control Optim. 38(3), 751–766 (2000)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2022 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Singapore Pte Ltd.
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Zhou, M., Cheng, S., Xu, W., Feng, Y., Su, H. (2022). Control and Observation of Induction Motors Based on Full-Order Terminal Sliding-Mode Technique. In: Das, S.K., Islam, M.R., Xu, W. (eds) Advances in Control Techniques for Smart Grid Applications. Springer, Singapore. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-16-9856-9_11
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-16-9856-9_11
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Singapore
Print ISBN: 978-981-16-9855-2
Online ISBN: 978-981-16-9856-9
eBook Packages: EnergyEnergy (R0)