Abstract
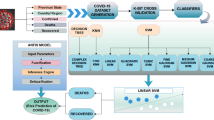
World is facing impact of COVID pandemic; every industry is facing corollaries to a great extent. With increase in number of COVID cases, it is necessary to control the spread of virus and wipe it out in the best possible manner. COVID-19, which have its rapid spread across the world, is a dangerous episode which entire community is cladding on. Proper treatment and efficient vaccine distribution are the major glitches of medical industry during this untoward outbreak. Priority in distribution of vaccine is extremely vital, to handle availability of vaccines. Our main objective is to develop methodologies with competing process which implements unsupervised k-means clustering and supervised naïve Bayes, decision tree and gradient boost classification algorithms to find the priority of individuals for distributing vaccines. Efficient pathway of distribution is implemented in layered manner based on individual’s priority, assessed in par with impact level of disease on individuals in the community. Priority for vaccine distribution is finalized with classification algorithm with the highest accuracy. It helps to distribute the available vaccines optimally among the population, and it plays major role in reducing the impact of coronavirus on individuals and society.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Deo S, Manurkar S, Krishnan S, Franz C (2020) COVID-19 vaccine: development, access and distribution in the Indian context. ORF Issue Brief No. 378, July 2020, Observer Research Foundation
Foy BH, Wahl B, Mehta K, Shet A, Menon GI, Britto C (2021) Comparing COVID-19 vaccine allocation strategies in India: a mathematical modelling study. Int J Infect Dis 103
Abebe H, Shitu S, Mose A (2021) Understanding of Covid-19 vaccine knowledge, attitude, acceptance, and determinates of COVID-19 vaccine acceptance among adult population in Ethiopia, vol 14, June 2021
Duijzer LE et al (2018) Dose-optimal vaccine allocation over multiple populations. Prod Oper Manage 27(1):143–159. https://doi.org/10.1111/poms.12788
Vani K, Gupta D (2014) Using K-means cluster based techniques in external plagiarism detection. In: 2014 International conference on contemporary computing and informatics (IC3I), pp 1268–1273
Siva Raja PM, Ramanan K (2020) Lesion localization and extreme gradient boosting characterization with brain tumor MRI images. In: Part of the Lecture notes on data engineering and communications technologies book series (LNDECT), vol 37
Pandey S, Muthuraman S, Shrivastava A (2018) Data classification using machine learning approach. In: Thampi S, Mitra S, Mukhopadhyay J, Li KC, James A, Berretti S (eds) Intelligent systems technologies and applications. ISTA 2017. Advances in intelligent systems and computing, vol 683. Springer, Cham
Grauer J et al (2020) Strategic spatiotemporal vaccine distribution increases the survival rate in an infectious disease like Covid-19. Sci Rep 10(1):21594. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-020-78447-3
Nawi NM, Atomi WH, Rehman MZ (2013) The effect of data pre-processing on optimized training of artificial neural networks. In: 4th International conference on electrical engineering and informatics, ICEEI 2013, vol 11
Li Y, Wu H (2012) A clustering method based on K-means algorithm. In: International conference on solid state devices and materials science, vol 25
Subbulakshmi S et al (2016) “Web services QoS prediction basedon dynamic non-functional quality factors and WS-security policy specification of web service”. Second International Conference on Computer paradigms(ICCP 2016), International Journal of Control Theory and Applications, vol. 9. International Science Press., pp 4591–4601
Na S, Xumin L, Yong G (2010) Research on k-means clustering algorithm: an improved k-means clustering algorithm. In: 2010 Third international symposium on intelligent information technology and security informatics, pp 63–67. https://doi.org/10.1109/IITSI.2010.74
Mishan, MT et al (2017) An analysis on business intelligence predicting business profitability model using Naïve Bayes neural network algorithm. In: 2017th IEEE International conference on system engineering and technology (ICSET). IEEE
Harahap F, Harahap AYN, Ekadiansyah E, Sari RN (2018) Implementation of Naïve Bayes classification method for predicting purchase. In: 6th International conference on cyber and IT service management (CITSM)
Pandiangan N, Buono MLC, Loppies SHD (2019) Implementation of decision tree and Naïve Bayes classification method for predicting study period. J Phys Conf Ser 1569 (International conference on science and technology)
Bansal A, Kaur S (2018) Extreme gradient boosting based tuning for classification in intrusion detection systems. In: International conference on advances in computing and data sciences
Sathyadevan S, Sarath PR, Athira U, Anjana V (2014) Improved document classification through enhanced Naive Bayes algorithm. In 2014 International Conference on Data Science & Engineering (ICDSE), pp 100–104
Sungheetha A (2021) COVID-19 Risk minimization decision making strategy using data-driven model. J Inf Technol 3(01):57–66
Chen JI-Z (2021) Design of accurate classification of COVID-19 disease in X-ray images using deep learning approach. J ISMAC 3(02):132–148
Qin F, Tang X, Cheng Z (2012) Application and research of multi-label Naïve Bayes classifier. In: Proceedings of the 10th World congress on intelligent control and automation, pp 764–768. https://doi.org/10.1109/WCICA.2012.6357980
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2022 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Singapore Pte Ltd.
About this paper
Cite this paper
Subbulakshmi, S., Nambiar, A.R., Arun, A.K., Al Faizi, F., Harish, V.N. (2022). Prediction of Priority to Individual for COVID Vaccine Distribution Using Soft Computing Techniques. In: Shakya, S., Du, KL., Haoxiang, W. (eds) Proceedings of Second International Conference on Sustainable Expert Systems . Lecture Notes in Networks and Systems, vol 351. Springer, Singapore. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-16-7657-4_15
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-16-7657-4_15
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Singapore
Print ISBN: 978-981-16-7656-7
Online ISBN: 978-981-16-7657-4
eBook Packages: Intelligent Technologies and RoboticsIntelligent Technologies and Robotics (R0)