Abstract
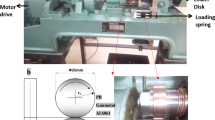
Wear of a material is one of the most undesirable processes experienced in practical applications. It results in energy loss, material degradation and life-shortening of machine components. This study aims to investigate the behavior of wear rate as a function of different operating parameters. The experiments were conducted on reciprocating tribometer, with three different tribopairs, of ball-on-disc configuration. The 52,100 chromium steel ball was allowed to slide with gun metal, mild-steel and EN-31 steel discs under different conditions. The wear rate for the specimens for each test was calculated by weight loss method. The effect of time, sliding distance and material hardness on the wear rate was examined there off. The Power Law and ANN models were developed for the estimation of wear rate. The model outputs were compared with the observed experimental results. The accuracy of the models was assessed using statistical parameters viz, coefficient of determination (R2), mean absolute percentage error (MAPE) and mean square error (MSE). It was observed that ANN model was more accurate compared to power law. Further, ANOVA analysis, with 5% p-value, was performed to enunciate the dominant factor affecting the wear rate. It was concluded that the load was the dominant factor influencing the wear rate and was succeeded by the velocity and hardness.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kumar, R., Prakash, B., Sethuramiah, B.: A systematic methodology to characterise the running-in and steady-state wear processes. Wear 252, 20445–20453 (2002)
Argatov, I.I., Fadin, Y.A.: A macroscale approximation for the running-in period. Tribol. Lett. 42, 311–317 (2011)
Wenlong, Z., Gengpei, X.L., Liping, Z., Liangzhou, C., Xiangqian, J.: Prediction of surface topography at the end of sliding running-in wear based on areal surface parameters. Tribol. Trans. 57, 553–560 (2014)
Hanief, M., Wani, M.F.: Modeling and prediction of surface roughness for running-in wear using Gauss-Newton algorithm and ANN. Appl. Surf. Sci. 357, 1573–1577 (2015)
Hanief, M., Wani, M.F. Effect of surface roughness on wear rate during running-in of En31-steel: modeling and experimental validation. Mater. Lett. (2016)
Masouros, G., Dimarogonas, A., Lefas, K.: A model for wear and surfaceroughness transients during the running-in of bearings. Wear 45, 375–382 (1997)
Mezghani, S., Demirci, I., Yousfi, M.: Running-in wear modeling of honed surface for combustion engine cylinder liners. Wear 302, 1360–1369 (2013)
Al-Samarai, R.A., Haftirman, A.K., Al-Douri, Y.: Effect of process parameters on wear rate of Al 6061-Cu reinforced SiCp metal matrix composites. Int. J. Sci. Res. Publ. 2, 3 (2012)
Ozioko, F.U.: Synthesis and study on effect of parameters on dry sliding wear characteristics of AL-SI alloys. Leonardo Electron. J. Pract. Technol. 20, 39–48 (2012)
Meng, H.C., Ludema, K.C. Wear models and predictive equations: their form and content. Wear 181, 443–457 (1995)
Singh, R., Gupta, R., Tripathi, J.: Surface roughness analysis and compare prediction and experimental value for cylindrical stainless steel pipe ss 316l in CNC lathe turning process using ANN method for re-optimization and cutting fluid. Int. J. Eng. Sci. 7, 58–71 (2014)
Hani, A., Khairia, A., Hassan, S., Ethar, M., Mubarak, M.: Effect of loads sliding speeds and times on the wear rate for different materials. Am. J. Sci. Ind. 299, 106 (2011)
Singla, D., Mediratta, S.R.: Effect of load and speed on wear properties of Al7075-Fly ash composite material. Int. J. Innov. Res. Sci. Eng. Technol. 2, 5 (2013)
Feng, C., Jack, X., Wang, X.: Development of empirical models for surface roughness prediction in finish turning. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 20, 348–356 (2002)
Choudhury, S.K. Bartarya, G.: Role of temperature and surface finish in predicting tool wear using neural network and design of experiments. Int. J. Mach. Tools Manuf. 43, 747–753 (2003)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2022 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Singapore Pte Ltd.
About this paper
Cite this paper
Hanief, M. (2022). Effect of Material Hardness and Operating Conditions on Wear Rate of Sliding Tribopair. In: Rao, V.V., Kumaraswamy, A., Kalra, S., Saxena, A. (eds) Computational and Experimental Methods in Mechanical Engineering. Smart Innovation, Systems and Technologies, vol 239. Springer, Singapore. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-16-2857-3_25
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-16-2857-3_25
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Singapore
Print ISBN: 978-981-16-2856-6
Online ISBN: 978-981-16-2857-3
eBook Packages: EngineeringEngineering (R0)