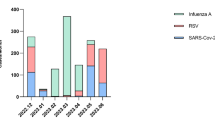
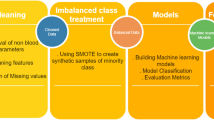
Abstract
At present, the world is suffering from coronavirus disease, or you can say COVID-19. This disease is spread worldwide because of the severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus-2 (SARS-CoV-2). The world’s first case of COVID-19 came to Wuhan city in China (late December 2019). All over the world, 9,586,769 people have been affected by it, and 488,824 people passed away due to COVID-19 now. WHO already announced an emergency due to COVID-19. The study aims to determine the effects of the SARS-CoV-2 virus on the blood; then we will describe the blood classification. After that, we will determine the effects of the SARS-CoV-2 virus on the blood cells (RBCs and WBCs) and the blood plasma. With the help of a linear classification algorithm, we will determine the speed of increasing antibody-secreting cells (ASCs) in the human body.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Soo YOY, Cheng Y, Wong R, Hui DS, Lee CK, Tsang KKS, Sung JJY (2004) Retrospective comparison of convalescent plasma with continuing high-dose methylprednisolone treatment in SARS patients. Clin Microbiol Infect 10(7):676–678
Ksiazek TG, Erdman D, Goldsmith CS, Zaki SR, Peret T, Emery S, Rollin PE (2003) A novel coronavirus associated with severe acute respiratory syndrome. N Engl J Med 348(20):1953–1966
Darnell ME, Taylor DR (2006) Evaluation of inactivation methods for severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus in noncellular blood products. Transfusion 46(10):1770–1777
Ding Y, Wang H, Shen H, Li Z, Geng J, Han H, Lu Y (2003) The clinical pathology of severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS): a report from China. J Pathol: J Pathol Soc Great Britain Ireland 200(3):282–289
Romanelli F, Smith KM, Hoven AD (2004) Chloroquine and hydroxychloroquine as inhibitors of human immunod eficiency virus (HIV-1) activity. Curr Pharm Des 10(21):2643–2648
Ludvigsson JF (2020) Systematic review of COVID-19 in children shows milder cases and a better prognosis than adults. Acta Paediatr 109(6):1088–1095
Yao X, Ye F, Zhang M, Cui C, Huang B, Niu P, Zhan S (2020) In vitro antiviral activity and projection of optimized dosing design of hydroxychloroquine for the treatment of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2). Clinical Infectious Diseases
Chen L, Xiong J, Bao L, Shi Y (2020) Convalescent plasma as a potentialtherapy for COVID-19. Lancet Infect Dis 20(4):398–400
McCreary EK, Pogue JM (2020) Coronavirus disease 2019 treatment: a review of early and emerging options. In Open Forum infectious diseases (Vol 7, No 4, p. of a a105). US: Oxford University Press
Zhang B, Liu S, Tan T, Huang W, DongY. Chen L, Zou Y (2020) Treatment with convalescent plasma for critically ill patients with SARS-CoV-2 infection. Chest
Imai Y, Kuba K, Penninger JM (2008) The discovery of angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 and its role in acute lung injury in mice. Exp Physiol 93(5):543–548
Corman VM, MuthD, Niemeyer D, Drosten C (2018) Hosts and sources of endemic human coronaviruses. In: Advances in virus research (Vol 100, pp 163–188). Academic Press
Zaigham M, Andersson O (2020) Maternal and perinatal outcomes with COVID‐19: a systematic review of 108 pregnancies. Acta Obstetrician Etgynecologica Scandinavica
McIntosh K, Hirsch MS, Bloom A (2020) Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19). Up To Date Hirsch MS Bloom 5
Program NHBPE (2000) Report of the national high blood pressure education program working group on high blood pressure in pregnancy. Am J Obstet Gynecol 183(1):s1–s22
Gu J, Korteweg C (2007) Pathology and pathogenesis of severe acute respiratory syndrome. Am J Pathol 170(4):1136–1147
Zhang JJ, Dong X, Cao YY, Yuan YD, Yang YB, Yan YQ, Gao YD (2020) Clinical characteristics of 140 patients infected with SARS‐CoV‐2 in Wuhan, China. Allergy
LaVignera S, Cannarella R, Condorelli RA, Torre F, Aversa A, Calogero A
Sex-specific SARS-CoV-2 mortality: among hormone-modulated ACE2 expression, risk of venous thromboembolism and hypovitaminosisd. Int J Molec sciences, 21(8):2948
Zhou Y, Hou Y, Shen J, Huang Y, Martin W, Cheng F (2020) Network-based drug repurposing for novel coronavirus 2019-nCoV/SARS-CoV-2. Cell Discovery 6(1):1–18
Ziegler CG, Allon SJ, Nyquist SK, Mbano IM, Miao VN, Tzouanas CN, Feldman J (2020) SARS-CoV-2 receptor ACE2 is an interferon-stimulated gene in human airway epithelial cells and is detected in specific cell subsets across tissues. Cell
Huang K, Yang T, Xu J, Yang L, Zhao J, Zhang X, Wen F (2019) Prevalence, risk factors, and management of asthma in China: a national cross-sectional study. Lancet 394(10196):407–418. Huang K, Yang T, Xu J, Yang L, Zhao J, Zhang X, Wen F (2019) Prevalence, risk factors, and management of asthma in China: a national cross-sectional study. Lancet 394(10196):407–418
Bhardwaj A, Aruna T (2013) A novel genetic programming based classifier design using a new constructive crossover operator with a local search technique. International conference on intelligent computing. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg (2013)
Tiwari S, Goel S, Bhardwaj A (2020) Machine Learning approach for the classification of EEG signals of multiple imagery tasks. 2020 11th International conference on computing, communication and networking technologies (ICCCNT). IEEE
Roberts JM, Pearson G, Cutler J, Lindheimer M (2003) Summary of the NHLBI working group on research on hypertension during pregnancy. Hypertension 41(3):437–445
Monteil V, Kwon H, Prado P, Hagelkrüys A, Wimmer RA, Stahl M, Romero JP (2020) Inhibition of SARS-CoV-2 infections in engineered human tissues using clinical-grade soluble human ACE2. Cell
Kumar A, Sinha N, Bhardwaj A (2020) A novel fitness function in genetic programming for medical data classification. J Biomed Inform, 103623
Acharya D et al (2020) A long short term memory deep learning network for the classification of negative emotions using EEG signals. 2020 International joint conference on neural networks (IJCNN). IEEE
Bhardwaj H, et al (2018) Breast cancer diagnosis using simultaneous feature selection and classification: A genetic programming approach. 2018 IEEE symposium series on computational intelligence (SSCI). IEEE
Acharya D et al (2020) A novel fitness function in genetic programming to handle unbalanced emotion recognition data. Pattern Recogn Lett
Acharya D et al (2020) Emotion recognition using fourier transform and genetic programming. Appl Acoust 164:107260
Bhardwaj H et al (2019) Classification of electroencephalogram signal for the detection of epilepsy using Innovative Genetic Programming. Expert Syst 36.1:e12338
Bhardwaj A, Tiwari A (2013) A novel genetic programming based classifier design using a new constructive crossover operator with a local search technique. In: International conference on intelligent computing (pp 86–95). Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg
Oudit GY, Kassiri Z, Jiang C, Liu PP, Poutanen SM, Penninger JM, Butany J (2009) SARS-coronavirus modulation of myocardial ACE2 expression and inflammation in patients with SARS. Eur J Clin Invest 39(7):618–625
Li Z, Yi Y, Luo X, Xiong N, Liu Y, Li S, Zhang Y (2020) Development and clinical application of a rapid IgM‐IgG combined antibody test for SARS‐CoV‐2 infection diagnosis. J Medicalvirology
Eickmann M, Gravemann U, Handke W, Tolksdorf F, Reichenberg S, Müller TH, Seltsam A (2020) Inactivation of three emerging viruses–severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus, Crimean-Congo haemorrhagic fever virus and Nipah virus–in platelet concentrates by ultraviolet C light and in plasma by methylene blue plus visible light. Vox Sang 115(3):146–151
Paniz-Mondolfi A, Bryce C, Grimes Z, Gordon RE, Reidy J, Lednicky J, Fowkes M (2020) Central nervous system involvement by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus-2 (SARS-CoV-2). J Med Virol 92(7):699–702
Acharya et al (2020) An enhanced fitness function to recognize unbalanced human emotions data. Expert Syst Appl 166:114011
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2021 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Singapore Pte Ltd.
About this paper
Cite this paper
Malik, I., Navadia, N.R., Jamshed, A., Verma, L., Singh, T., Bhardwaj, H. (2021). Effects of SARS-COV-2 on Blood. In: Tiwari, A., Ahuja, K., Yadav, A., Bansal, J.C., Deep, K., Nagar, A.K. (eds) Soft Computing for Problem Solving. Advances in Intelligent Systems and Computing, vol 1393. Springer, Singapore. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-16-2712-5_8
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-16-2712-5_8
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Singapore
Print ISBN: 978-981-16-2711-8
Online ISBN: 978-981-16-2712-5
eBook Packages: Intelligent Technologies and RoboticsIntelligent Technologies and Robotics (R0)