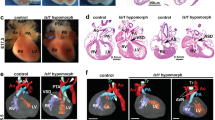
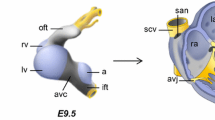
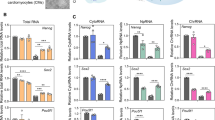
Abstract
Cell fate commitment is achieved by cell type-specific transcription, which in turn is guided by epigenetic mechanisms. Epigenetic and chromatin modifications play important roles in embryonic development, allowing cells to differentiate into particular lineages. Chromatin remodeling correlates well with gene expression, thus contributes to cell fate commitment. Chromatin remodeling enzymes exist as large complexes and possess one or more types of remodeling activities. These enzymes are divided into two categories. The first one consists of enzymes that posttranslationally modify amino termini of histone proteins, by adding or removing methyl, acetyl, sumo, phosphate, or ubiquitin moieties. The other category uses ATP hydrolysis to disrupt interactions between DNA and histone proteins, leading to changes in nucleosome positioning and higher-order chromatin structure. These enzymes increase DNA accessibility, thus allowing gene regulators or transcription factors to bind in order to modulate gene expression. Cardiac tissue development and differentiation is a complex process that relies on extensive networks of interacting transcription factors. The chromatin remodeling enzymes are closely associated with these networks, thus providing an added layer of complexity and refinement to the regulation of heart development. Brahma related gene-1 (BRG-1) and BRG-1 related factors (BAF-60c, BAF-180, and BAF250a) are some of the chromatin remodeling enzymes that have been implicated in the process of chromatin remodeling and involved in cardiac differentiation. The role of these complexes and other factors in the cardiac differentiation of stem cells will be discussed in this chapter.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- ACF:
-
ATP-dependent chromatin assembly factor
- ADAMTS1:
-
A disintegrin and metalloproteinase with thrombospondin motifs 1
- ANP:
-
Atrial natriuretic peptide
- ARID:
-
AT-rich interaction domain
- BAF:
-
Brahma-associated factor/BRG-1 related factor
- BMP:
-
Bone morphogenetic protein
- BNP:
-
Brain natriuretic peptide
- BRD-7:
-
Bromodomain 7
- BRG-1:
-
Brahma related gene-1
- BRK:
-
Brahma and Kismet
- BRM:
-
Brahma
- C/EBP β:
-
CCAAT-enhancer binding protein β
- CDKN1C:
-
Cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor 1C
- CERF:
-
CECR2-containing remodeling factor
- CHD:
-
Chromodomain helicase DNA binding
- CHRAC:
-
Chromatin remodeling and assembly complex
- CPB-300:
-
CREB-binding protein
- DNMT1:
-
DNA methyltransferase 1
- DOT1L:
-
Disruptor of telomeric silencing 1-like
- EHMT:
-
Euchromatic histone-lysine N-methyltransferase
- ESCs:
-
Embryonic stem cells
- EZH2:
-
Enhancer of zeste homolog 2
- FGFR-3:
-
Fibroblast growth factor receptor-3
- GATA-4:
-
GATA binding protein-4
- GLP:
-
G9a-like protein
- GNAT:
-
Gcn-5 related N-acetyltransferase
- HAND2:
-
Heart and neural crest derivatives expressed 2
- HAT:
-
Histone acetyltransferases
- HDAC:
-
Histone deacetylase
- HDM:
-
Histone demethylase
- HKMT:
-
Histone lysine methyltransferase
- HMT:
-
Histone methyltransferases
- HP-1:
-
Heterochromatin protein 1
- ING:
-
Inhibitor of growth
- INO-80:
-
Inositol requiring
- ISL-1:
-
Insulin gene enhancer binding protein 1
- ISWI:
-
Imitation switch
- JARID:
-
Jumonji domain ARID-containing protein
- Jmj:
-
Jumonji
- KDM-1:
-
Lysine demethylase 1
- LSD:
-
Lysine-specific demethylase
- MBT:
-
Malignant brain tumor
- MEF2c:
-
Myocyte enhancer factor 2c
- MHC:
-
Myosin heavy chain
- MSCs:
-
Mesenchymal stem cells
- MYH6:
-
Myosin heavy chain 6
- MYST:
-
MOZ, Ybf2, Sas2, and Tip60
- Nkx2.5:
-
Nk2 homoebox5
- NoRC:
-
Nucleolar remodeling complex
- NuRD:
-
Nucelosome remodeling and deacetylase
- NuRF:
-
Nucelosome remodeling factor
- Oct4:
-
Octamer-binding transcription factor 4
- PBAF:
-
Polybromide-associated BAF
- PHD:
-
Plant homeodomain
- PPAR-γ:
-
Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma-γ
- PRC2:
-
Polycomb repressive complex 2
- PRMT:
-
Protein arginine methyltransferase
- PWWP:
-
Conserved proline and tryptophan
- RSF:
-
Human remodeling and spacing factor
- RUNX-2:
-
Runt-related transcription factor-2
- SANT:
-
Switching-defective protein 3 (Swi3), adaptor 2 (Ada2), nuclear receptor corepressor (N-CoR), and transcription factor (TF)IIIB
- SIRT:
-
Sirtuin
- SMAD-1:
-
Mothers against decapentaplegic homolog 1
- SNF:
-
Sucrose nonfermenting protein
- SNF2H:
-
Sucrose nonfermenting protein 2 homolog
- Sox-9:
-
SRY-box transcription factor 2
- SP:
-
Specificity protein
- SRCAP:
-
Snf2-related CREBBP activator protein
- SUV39H1:
-
Suppression of variegation 3–9 homolog 1
- SWI/SNF:
-
Switch/Sucrose nonfermenting
- Tbx:
-
T-box protein
- TIP60:
-
Tat-interacting protein of 60 kDa
- UTX:
-
Ubiquitously transcribed tetratricopeptide repeat, X chromosome
- WHSC1:
-
Wolf-Hirschhorn syndrome candidate 1
- WICH:
-
WSTF-ISWI chromatin remodeling complex
References
Arcipowski KM, Martinez CA, Ntziachristos P (2016) Histone demethylases in physiology and cancer: a tale of two enzymes, JMJD3 and UTX. Curr Opin Genet Dev 36:59–67. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gde.2016.03.010
Banerjee T, Chakravarti D (2011) A peek into the complex realm of histone phosphorylation. Mol Cell Biol 31:4858–4873. https://doi.org/10.1128/MCB.05631-11
Bannister AJ, Kouzarides T (2011) Regulation of chromatin by histone modifications. Cell Res 21:381–395. https://doi.org/10.1038/cr.2011.22
Bao Y, Shen X (2007) INO80 subfamily of chromatin remodeling complexes. Mutat Res 618(1–2):18–29. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mrfmmm.2006.10.006
Bedford MT, Clarke SG (2009) Protein arginine methylation in mammals: who, what, and why. Mol Cell 33(1):1–13. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molcel.2008.12.013
Bevilacqua A, Willis MS, Bultman SJ (2014) SWI/SNF chromatin-remodeling complexes in cardiovascular development and disease. Cardiovasc Pathol 23(2):85–91. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carpath.2013.09.003
Champagne KS, Kutateladze TG (2009) Structural insight into histone recognition by the ING PHD fingers. Curr Drug Targets 10:432–441. https://doi.org/10.2174/138945009788185040
Chen Y, Wang M, Chen D, Wang J, Kang N (2016) Chromatin remodeling enzyme CHD7 is necessary for osteogenesis of human mesenchymal stem cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 478(4):1588–1593. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2016.08.161
Clapier CR, Cairns BR (2009) The biology of chromatin remodeling complexes. Annu Rev Biochem 78:273–304. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.biochem.77.062706.153223
Clapier CR, Iwasa J, Cairns BR, Peterson CL (2017) Mechanisms of action and regulation of ATP-dependent chromatin-remodelling complexes. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 18(7):407. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrm.2017.26
Fink M, Imholz D, Thoma F (2007) Contribution of the serine 129 of histone H2A to chromatin structure. Mol Cell Biol 27(10):3589–3600. https://doi.org/10.1128/MCB.02077-06
Flaus A, Martin DM, Barton GJ, Owen-Hughes T (2006) Identification of multiple distinct Snf2 subfamilies with conserved structural motifs. Nucleic Acids Res 34:2887–2905. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkl295
Fujita J, Tohyama S, Kishino Y, Okada M, Morita Y (2019) Concise review: genetic and epigenetic regulation of cardiac differentiation from human pluripotent stem cells. Stem Cells 37(8):992–1002. https://doi.org/10.1002/stem.3027
Gillette TG, Hill JA (2015) Readers, writers, and erasers: chromatin as the white board of heart disease. Circ Res 116:1245–1253. https://doi.org/10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.116.303630
Han P, Hang CT, Yang J, Chang CP (2011) Chromatin remodeling in cardiovascular development and physiology. Circ Res 108(3):378–396. https://doi.org/10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.110.224287
Ho L, Crabtree GR (2010) Chromatin remodelling during development. Nature 463(7280):474. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature08911
Hota SK, Bruneau BG (2016) ATP-dependent chromatin remodeling during mammalian development. Development 143:2882–2897. https://doi.org/10.1242/dev.128892
Huang Y, Fang J, Bedford MT, Zhang Y, Xu RM (2006) Recognition of histone H3 lysine-4 methylation by the double tudor domain of JMJD2A. Science 312:748–751. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1125162
Husmann D, Gozani O (2019) Histone lysine methyltransferases in biology and disease. Nat Struct Mol Biol 26:880–889. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41594-019-0298-7
Kadoch C, Crabtree GR (2015) Mammalian SWI/SNF chromatin remodeling complexes and cancer: mechanistic insights gained from human genomics. Sci Adv 1(5):e1500447. https://doi.org/10.1126/sciadv.1500447
Kiefer CM, Hou C, Little JA, Dean A (2008) Epigenetics of beta globin gene regulation. Mutat Res 647:68–76. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mrfmmm.2008.07.014
Kouzarides T (2007) Chromatin modifications and their functions. Cell 128:693–705. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2007.02.005
LeBlanc SE, Wu Q, Lamba P, Sif S, Imbalzano AN (2016) Promoter–enhancer looping at the PPARγ2 locus during adipogenic differentiation requires the Prmt5 methyltransferase. Nucleic Acids Res 44(11):5133–5147. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkw129
Lei I, Gao X, Sham MH, Wang Z (2012) SWI/SNF protein component BAF250a regulates cardiac progenitor cell differentiation by modulating chromatin accessibility during second heart field development. J Biol Chem 287(29):24255–24262. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M112.365080
Lei I, Tian S, Chen V, Zhao Y, Wang Z (2020) SWI/SNF component BAF250a coordinates Oct4 and Wnt signaling pathway to control cardiac lineage differentiation. Front Cell Dev Biol 7:358. https://doi.org/10.3389/fcell.2019.00358
Lu F, Langenbacher AD, Chen JN (2016) Transcriptional regulation of heart development in Zebrafish. J Cardiovasc Dev Dis 3(2):14. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcdd3020014
Luo RX, Dean DC (1999) Chromatin remodeling and transcriptional regulation. J Natl Cancer Inst 91(15):1288–1294. https://doi.org/10.1093/jnci/91.15.1288
Lusser A, Urwin DL, Kadonaga JT (2005) Distinct activities of CHD1 and ACF in ATP-dependent chromatin assembly. Nat Struct Mol Biol 12:160–166. https://doi.org/10.1038/nsmb884
Marfella CGA, Imbalzano AN (2007) The Chd family of chromatin remodelers. Mutat Res 618(1–2):30–40. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mrfmmm.2006.07.012
Mathiyalagan P, Keating ST, Du XJ, El-Osta A (2014) Chromatin modifications remodel cardiac gene expression. Cardiovasc Res 103(1):7–16. https://doi.org/10.1093/cvr/cvu122
Maurer-Stroh S, Dickens NJ, Hughes-Davies L, Kouzarides T, Eisenhaber F, Ponting CP (2003) The tudor domain ‘Royal Family’: tudor, plant Agenet, Chromo, PWWP and MBT domains. Trends Biochem Sci 28:69–74. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0968-0004(03)00004-5
Miller JL, Grant PA (2013) The role of DNA methylation and histone modifications in transcriptional regulation in humans. Subcell Biochem 61:289–317. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-94-007-4525-4_13
Moore IVJB, Zhao J, Kieth MCL et al (2016) The epigenetic regulator HDAC1 modulates transcription of a core cardiogenic program in human cardiac mesenchymal stromal cells (CMCs) through a p53-dependent mechanism. Stem Cells 34(12):2916–2929. https://doi.org/10.1002/stem.2471. Epub 2016 Sep 1
Narlikar GJ, Sundaramoorthy R, Owen-Hughes T (2013) Mechanisms and functions of ATP-dependent chromatin-remodeling enzymes. Cell 154(3):490–503. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2013.07.011
Ohtan K, Dimmeler S (2011) Epigenetic regulation of cardiovascular differentiation. Cardiovasc Res 90(3):404–412. https://doi.org/10.1093/cvr/cvr019
Pandey SM (2016) Chromatin remodeling complexes: the regulators of genome function. Global J Zool 1(1):007–013. https://doi.org/10.17352/gjz.000003
Pursani V, Bhartiya D, Tanavde V, Bashir M, Prabh S (2018) Transcriptional activator DOT1L putatively regulates human embryonic stem cell differentiation into the cardiac lineage. Stem Cell Res Ther 9:97. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13287-018-0810-8
Shi X, Hong T, Walter KL et al (2006) ING2 PHD domain links histone H3 lysine 4 methylation to active gene repression. Nature 442:96–99. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature04835
Shogren-Knaak M, Ishii H, Sun JM, Pazin MJ, Davie JR, Peterson CL (2006) Histone H4-K16 acetylation controls chromatin structure and protein interactions. Science 311:844–847. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1124000
Sims RJ III, Chen CF, Santos-Rosa H, Kouzarides T, Patel SS, Reinberg D (2005) Human but not yeast CHD1 binds directly and selectively to histone H3 methylated at lysine 4 via its tandem chromodomains. J Biol Chem 280:41789–41792. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.C500395200
Singh AP, Archer TK (2014) Analysis of the SWI/SNF chromatin-remodeling complex during early heart development and BAF250a repression cardiac gene transcription during P19 cell differentiation. Nucleic Acids Res 42:2958–2975. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkt1232
Sun F, Chen Q, Yang S, Pan Q, Ma J, Wan Y, Hong A (2009) Remodeling of chromatin structure within the promoter is important for bmp-2-induced fgfr3 expression. Nucleic Acids Res 37(12):3897–3911. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkp261
Sun X, Hota SK, Zhou YQ et al (2018) Cardiac-enriched BAF chromatin-remodeling complex subunit Baf60c regulates gene expression programs essential for heart development and function. Biol Open 7(1):bio02951. https://doi.org/10.1242/bio.029512
Swygert SG, Peterson CL (2014) Chromatin dynamics: interplay between remodeling enzymes and histone modifications BRG-1 and cardiomyocyte development. Biochim Biophys Acta 1839(8):728–736. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbagrm.2014.02.013
Torigoe SE, Urwin DL, Ishii H, Smith DE, Kadonaga JT (2011) Identification of a rapidly formed non nucleosomal histone-DNA intermediate that is converted into chromatin by ACF. Mol Cell 43:638–648. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molcel.2011.07.017
Tyagi M, Imam N, Verma K, Patel AK (2016) Chromatin remodelers: we are the drivers!! Nucleus 7(4):388–404. https://doi.org/10.1080/19491034.2016.1211217
Vignali A, Hassan AH, Neely KE, Workman JL (2000) ATP-dependent chromatin-remodeling complexes. Mol Cell Biol 20(6):1899–1910. https://doi.org/10.1128/MCB.20.6.1899-1910.2000
Wang Y, Li Y, Guo C et al (2016) ISL1 and JMJD3 synergistically control cardiac differentiation of embryonic stem cells. Nucleic Acids Res 44(14):6741–6755. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkw301
Wang Z, Zang C, Rosenfeld JA et al (2008) Combinatorial patterns of histone acetylations and methylations in the human genome. Nat Genet 40:897–903. https://doi.org/10.1038/ng.154
Wei Y, Mizzen CA, Cook RG, Gorovsky MA, Allis CD (1998) Phosphorylation of histone H3 at serine 10 is correlated with chromosome condensation during mitosis and meiosis in Tetrahymena. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 95:7480–7484. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.95.13.7480
Xiao H, LeBlanc SE, Wu Q (2011) Chromatin accessibility and transcription factor binding at the PPARγ2 promoter during adipogenesis is protein kinase A-dependent. J Cell Physiol 226(1):86–93. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcp.22308
Xu Y, Zhang S, Lin S et al (2017) WERAM: a database of writers, erasers and readers of histone acetylation and methylation in eukaryotes. Nucleic Acids Res 45:D264–D270. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkw1011
Yan Z, Cui K, Murray DM, Ling C, Xue Y, Gerstein A et al (2005) PBAF chromatin-remodeling complex requires a novel specificity subunit, BAF200, to regulate expression of selective interferon-responsive genes. Genes Dev 19:1662–1667. https://doi.org/10.1101/gad.1323805
Zhang P, Torres K, Liu X, Liu CG, Pollock R (2016) An overview of chromatin-regulating proteins in cells. Curr Prot Peptide Sci 17(5):401–410. https://doi.org/10.2174/1389203717666160122120310
Zhou Y, Kim J, Yuan X, Braun T (2011) Epigenetic modifications of stem cells: a paradigm for the control of cardiac progenitor cells. Circ Res 109(9):1067–1081. https://doi.org/10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.111.243709
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2021 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Singapore Pte Ltd.
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Ullah, M., Iqbal, H., Haneef, K., Khan, I., Salim, A. (2021). Chromatin Remodeling and Cardiac Differentiation of Stem Cells. In: Haider, K.H. (eds) Stem cells: From Potential to Promise. Springer, Singapore. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-16-0301-3_9
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-16-0301-3_9
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Singapore
Print ISBN: 978-981-16-0300-6
Online ISBN: 978-981-16-0301-3
eBook Packages: Biomedical and Life SciencesBiomedical and Life Sciences (R0)