Abstract
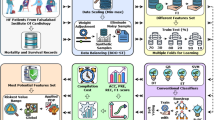
Healthcare is the cardinal component on which the foundation of human welfare can be laid. Healthcare research mainly focuses on the healthy living standards of individuals. Relationship between pulmonary embolism and cardiac arrest is presented in this paper. The proposed research is divided into two phases. The first phase includes the establishment of connectivity between the two medical fields which is done by finding out the relationship between the pulse pressure and stroke volume. The second phase includes the application and comparison of machine learning algorithms on the above-formed connectivity. Univariate technique of feature selection is performed initially in order to get the most relevant attributes. Overfitting problem has been addressed by formulating an ensemble model. Also the comparison between the boosting and bagging classifier has been done.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
ChayakritKrittanawong (2017) Artificial Intelligence in Precision Cardiovascular Medicine. J Am CollE Cardiol 30 May
Shrestha S, Sengupta PP (2018) Machine learning for nuclear cardiology: The way forward
Shashikant R, Chetankumar P (2019) Predictive model of cardiac arrest in smokers using machine learning technique based on Heart Rate Variability parameter. J Appl Comput Inform 22 June
Alizadehsani R, Habib J, Javad Hosseini M, Hoda Mashayekhi R, Boghrati (2013) A data mining approach for diagnosis of coronary artery disease
G. Hinton (2018) Deep learning—a technology with the potential to transform health care. JAMA
Cowger Matthews J, McLaughlin V (2018) Acute Right Ventricular Failure in the Setting of Acute Pulmonary Embolism or Chronic Pulmonary Hypertension. Bentham Science Publication, February
Ebrahim Laher E (2018) Cardiac arrest due to pulmnory embolism–Science Direct. Indian Hear J, October
Bizopoulos P, Koutsouris D (2019) Deep Learning in Cardiology. IEEE Review
Kim J, Kang U, Lee Y (2017) Statistics and deep belief network based cardiovascular risk prediction. Healthc Inform Res 23(3):169–175
Cano-Espinosa C, Cazorla M, Gonzalez G (2020) Computed Aided Detection of Pulmonary Embolism Using Multi-Slice Multi-Axial Segmentation, MDPI
Singh S, Pandey S, Pawar U, Ram Janghel R (2018) Classification of ECG arrhythmia using recurrent neural networks. Science Direct
Yao Z, Zhu Z, Chen Y (2017) Atrial fibrillation detection by multiscale convolution neural networks. In: Information Fusion (Fusion), 2017, 20th International Conference IEEE
Rucco M, Sousa-Rodrigues D, Merelli E, Johnson JH (2015) A Neural hypernetwork approach for Pulmonary Embolism diagnosis. BMC Res Notes 8(1):617
Agharezaei L, Agharezaei Z, Nemati A, Bahaadinbeigy K, Keynia F, Baneshi MR (2016) The Prediction of the risk level of Pulmonary Embolism & Deep Venus Thrombosis through Artificial Neural Network. Acta Information Med 24(5):354–359
Chen MC, Ball RL, Yang L, Moradzadeh N, Chapman BE, Larson DB, Langlotz CP, Amrhein TJ, Lungren MP (2017) Deep learning to classify Radiology free-text reports. Radiology 286(3):845–852
Liu W, Liu M (2020) Evaluation of acute Pulmonary Embolism & Clot burden on CTPA with deep learning. In Imaging Informatics & Artificial Intelligence, Springer
Remy-Jardin M, Faivre JB (2020) Machine Leraning & Deep Neural Network Application in Thorax. J Thorac Imaging
Kannan R, Vasanthi V (2018) Machine Learning Algorithms with ROC Curve for Predicting &Diagnosing the heart disease. In Springer Briefs in Applied Science and Technology
Atallah R, Al-Mousa A (2019) Heart Disease Detection using Machine Learning Majority Voting Ensemble Method. In 2019 IEEE
Krishnani D, Kumari A, Dewangan A (2019) Prediction of Coronary Heart Disease Using Supervised Machine Learning Algorithm 2019 IEEE
Ali L, Ullah Khan S (2019) Early detection of Heart Failure by Reducing the time complexity of Machine Learning based predictive Model. In: 1st International Conference on Electronics & Computer Engineering
Ashier SZ, Yongjian L (2019) An Intelligent learning System based on Random Search Algorithm & Optimized Random Forest Model for Improving heart Disease detection. In: IEEE Explore
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2021 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Singapore Pte Ltd.
About this paper
Cite this paper
Firdous, N., Bhardwaj, S., Bhat, A.H. (2021). Exploring Feature Selection Using Supervised Machine Learning Algorithms for Establishing a Link Between Pulmonary Embolism and Cardiac Arrest. In: Singh Pundir, A.K., Yadav, A., Das, S. (eds) Recent Trends in Communication and Intelligent Systems. Algorithms for Intelligent Systems. Springer, Singapore. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-16-0167-5_1
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-16-0167-5_1
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Singapore
Print ISBN: 978-981-16-0166-8
Online ISBN: 978-981-16-0167-5
eBook Packages: Intelligent Technologies and RoboticsIntelligent Technologies and Robotics (R0)