Abstract
Artificial intelligence (AI) is already part of our everyday life. Nowadays, facial recognition and autonomous driving are common applications of AI. It has now gone on to invade the field of medicine, and many studies showed promising applications of AI in radiology, pathology, endoscopy, and so on. Artificial intelligence (AI) has been a disruptive innovation in all areas of medicine including surgery. Not only has it been applied for research purpose but also AI can already provide significant solutions in clinical settings. Attention is now turning to the potential of AI in the field of endoscopic surgery. It is essential to understand how machine learning (ML) and deep learning (DL) work, understand current applications in surgery, and prepare for the future of surgery in the era of AI.
In the fields of medicine that rely mainly on pattern recognition, such as endoscopy and radiology, have evolved artificial intelligence models that have become more accurate than human decisions. To date, usefulness of artificial intelligence in the endoscopic diagnosis of gastrointestinal lesions is reported from many institutions. Progress in computing technology including the use of graphical processing units (GPUs) for parallel processing, the accessibility of types of movie data, and the resurgence of interest in neural networks, and other ML approaches has led to recent advances in AI application in endoscopic surgery.
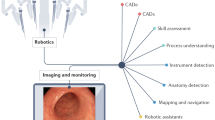
In this chapter, we present the current and future applications of AI in the field of endoscopic surgery by highlighting following topics in order: (1) diagnosis, (2) navigation, (3) decision support, (4) preoperative prediction, (5) education, (6) video recognition, and (7) autonomous surgery.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- FESS:
-
Flexible endoscopic surgery system
References
Hirasawa T, Aoyama K, Tanimoto T, Ishihara S, Shichijo S, Ozawa T, Ohnishi T, Fujishiro M, Matsuo K, Fujisaki J, Tada T. Application of artificial intelligence using a convolutional neural network for detecting gastric cancer in endoscopic images. Gastric Cancer. 2018;21(4):653–60. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10120-018-0793-2.
Reismann J, Romualdi A, Kiss N, Minderjahn MI, Kallarackal J, Schad M, Reismann M. Diagnosis and classification of pediatric acute appendicitis by artificial intelligence methods: an investigator-independent approach. PLoS One. 2019;14(9):e0222030. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0222030.
Luo X, Mori K, Peters TM. Advanced endoscopic navigation: surgical big data, methodology, and applications. Annu Rev Biomed Eng. 2018;20:221–51. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-bioeng-062117-120917.
Auloge P, Cazzato RL, Ramamurthy N, de Marini P, Rousseau C, Garnon J, Charles YP, Steib JP, Gangi A. Augmented reality and artificial intelligence-based navigation during percutaneous vertebroplasty: a pilot randomised clinical trial. Eur Spine J. 2019;29(7):1580–9. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00586-019-06054-6.
Lin B, Sun Y, Qian X, Goldgof D, Gitlin R, You Y. Video-based 3D reconstruction, laparoscope localization and deformation recovery for abdominal minimally invasive surgery: a survey. Int J Med Robot. 2016;12(2):158–78. https://doi.org/10.1002/rcs.1661.
Maubert A, Birtwisle L, Bernard JL, Benizri E, Bereder JM. Can machine learning predict resecability of a peritoneal carcinomatosis? Surg Oncol. 2019;29:120–5. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.suronc.2019.04.008.
Ramkumar PN, Karnuta JM, Navarro SM, Haeberle HS, Scuderi GR, Mont MA, Krebs VE, Patterson BM. Deep learning preoperatively predicts value metrics for primary total knee arthroplasty: development and validation of an artificial neural network model. J Arthroplast. 2019;34(10):2220–2227 e2221. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arth.2019.05.034.
Lundberg SM, Nair B, Vavilala MS, Horibe M, Eisses MJ, Adams T, Liston DE, Low DK, Newman SF, Kim J, Lee SI. Explainable machine-learning predictions for the prevention of hypoxaemia during surgery. Nat Biomed Eng. 2018;2(10):749–60. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41551-018-0304-0.
Reznick RK, MacRae H. Teaching surgical skills--changes in the wind. N Engl J Med. 2006;355(25):2664–9. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMra054785.
Bissonnette V, Mirchi N, Ledwos N, Alsidieri G, Winkler-Schwartz A, Del Maestro RF. Artificial intelligence distinguishes surgical training levels in a virtual reality spinal task. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2019;101(23):e127. https://doi.org/10.2106/JBJS.18.01197.
Winkler-Schwartz A, Yilmaz R, Mirchi N, Bissonnette V, Ledwos N, Siyar S, Azarnoush H, Karlik B, Del Maestro R. Machine learning identification of surgical and operative factors associated with surgical expertise in virtual reality simulation. JAMA Netw Open. 2019;2(8):e198363. https://doi.org/10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2019.8363.
Hashimoto DA, Rosman G, Witkowski ER, Stafford C, Navarette-Welton AJ, Rattner DW, Lillemoe KD, Rus DL, Meireles OR. Computer vision analysis of intraoperative video: automated recognition of operative steps in laparoscopic sleeve gastrectomy. Ann Surg. 2019;270(3):414–21. https://doi.org/10.1097/SLA.0000000000003460.
Mascagni P, Fiorillo C, Urade T, Emre T, Yu T, Wakabayashi T, Felli E, Perretta S, Swanstrom L, Mutter D, Marescaux J, Pessaux P, Costamagna G, Padoy N, Dallemagne B. Formalizing video documentation of the critical view of safety in laparoscopic cholecystectomy: a step towards artificial intelligence assistance to improve surgical safety. Surg Endosc. 2019;34(6):2709–14. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00464-019-07149-3.
Shademan A, Decker RS, Opfermann JD, Leonard S, Krieger A, Kim PC. Supervised autonomous robotic soft tissue surgery. Sci Transl Med. 2016;8(337):337ra364. https://doi.org/10.1126/scitranslmed.aad9398.
Moustris GP, Hiridis SC, Deliparaschos KM, Konstantinidis KM. Evolution of autonomous and semi-autonomous robotic surgical systems: a review of the literature. Int J Med Robot. 2011;7(4):375–92. https://doi.org/10.1002/rcs.408.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2021 Springer Nature Singapore Pte Ltd.
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Wada, N., Kitagawa, Y. (2021). Application of AI in Endoscopic Surgical Operations. In: Takenoshita, S., Yasuhara, H. (eds) Surgery and Operating Room Innovation. Springer, Singapore. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-15-8979-9_8
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-15-8979-9_8
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Singapore
Print ISBN: 978-981-15-8978-2
Online ISBN: 978-981-15-8979-9
eBook Packages: MedicineMedicine (R0)