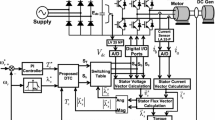
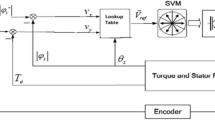
Abstract
Robustness, cost, reliability and effectiveness are the important characteristics of the induction motor (IM). IM is generally controlled by v/f-based SVPWM voltage source inverter (VSI). In industry, PI controllers are the best choice due to simple and robust performance at wide range of operation. This paper tends to show simulation of PI, FLC, ANN and ANFIS using MATLAB/Simulink and their real-time implementation using dSPACE controller. Simulation results are analyzed with the practical results, thereby confirming the performance of AI-based induction motor drive (IMD).
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Dyck Derek N, Gilbert Geoff, Lowther David A (2010) A performance model of an induction motor for transient simulation with a PWM drive. IEEE Trans Magn 46(8):3093–3096
Mishra RN, Mohanty KB (2016) Real time implementation of An ANFIS-based induction motor drive via feedback linearization for performance enhancement. Elsevier Int J Eng Sci Technol 19:1714–1730
Abdesh Khan M, Nasir Uddin M, Rahman MA (2011) Real time performance investigation of an intelligent controller based speed control of induction motor drives. In: IEEE international conference electric machines & drives, 2011, pp 164–169
Saad N, Arrofiq M (2012) A PLC-based modified-fuzzy controller for PWM-driven induction motor drive with constant V/Hz ratio control. Elsevier J Rob Comput-Int Manuf 28:95–112
Mohan N (2001) Advanced electric drives: analysis, control modeling using simulink, 1st edn. MNPERE Publication
Krause PC (2000) Analysis of electrical machinery and drives system. IEEE Willey Press
Menghal PM, Jaya Laxmi A (2013) Adaptive neuro fuzzy based dynamic simulation of induction motor drives. In: International conference on fuzzy system, (FUZZ 2013),7th–10th July 2013, pp 1–8
Abbou A, Nasser T, Mahmoudi H, Akherraz M, Essadki A (2012) Induction motor/controls and Implementation using dSPACE. WSEAS Trans on Syst An//d Control 1(7):26–35
Suetake M, da Silva IN, Goedtel A (2011) Embedded DSP-based compact fuzzy system and its application for induction-motor V/f speed control. IEEE Trans Ind Electron 58(3):750–760
Arulmozhiyal R, Baskaran K, Devarajan N, Kanagaraj J (2010) Real time MATLAB Interface for speed control of Induction motor drive using dsPIC 30F4011. Int J Comput Appl 1(5):85–90
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Appendix A
Appendix A
Parameters of induction motor:
1 HP, 3-phase, 415 V, 50 Hz, 1440 rpm, star connected induction machine
Stator resistance Rs = 10.1 Ω,
Stator reactance Xs = 15.81 Ω,
Rotor resistance Rr’ = 9.8546 Ω,
Rotor reactance Xr’ = 15.81 Ω
Mutual reactance Xm = 245.8954 Ω.
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2021 Springer Nature Singapore Pte Ltd.
About this paper
Cite this paper
Menghal, P.M., Jaya Laxmi, A. (2021). Artificial Intelligence-Based Real-Time Control of Induction Motor Using dSPACE Controller. In: Komanapalli, V.L.N., Sivakumaran, N., Hampannavar, S. (eds) Advances in Automation, Signal Processing, Instrumentation, and Control. i-CASIC 2020. Lecture Notes in Electrical Engineering, vol 700. Springer, Singapore. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-15-8221-9_75
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-15-8221-9_75
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Singapore
Print ISBN: 978-981-15-8220-2
Online ISBN: 978-981-15-8221-9
eBook Packages: EngineeringEngineering (R0)