Abstract
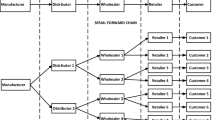
In the present world, most of the firms are facing uncertain demand due to different market conditions. This type of demand can be modelled as non-stationary demand. In this paper, different multi-echelon divergent supply chain scenarios with non-stationary demand process are considered. Stock out plays an important role in supply chains; it reduces the service level of each member in a supply chain and causes high supply chain inventory cost. In order to avoid stock out in a supply chain, safety stock is to be maintained by each member. Developed simulation models for studying the operation of divergent supply chains under non-stationary demand processes. It is found that the stock out which leads to lost sales depends on two factors, i.e. the inertia of the non-stationary demand process and the structure of the divergent supply chain. In detail, the structure of the divergent supply chain is, basically, described in terms of the divergence factor. In this situation, we propose a mathematical relation to estimate safety stock by incorporating the divergence factor of the supply chain with non-stationary demand process. The performance of the supply chain against the divergence is analysed and the analysis shows that estimation of safety stock based on divergence factor can give a good estimate of the safety stock for divergent supply chain.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
John JN, Sean PW (2009) Managing inventory in supply chains with non-stationary demand. Ins Operat Res Manag Sci 39(5):388–399
Stephen CG (1999) A single-item inventory model for a non-stationary demand process. Manufact Serv Operat Manag 1:50–61
Stephen CG, Sean PW (2008) Strategic inventory placement in supply chains: non-stationary demand. Manufact Serv Operat Manag 10(2):278–287
Morton TE, Pentico DW (1995) The finite horizon non-stationary stochastic inventory problem: Near-myopic bounds, heuristics, testing. Manage Sci 41:334–343
Ettl M, Feigin GE, Lin GY, Yao DD (2000) A supply network model with base-stock control and service requirements. Operat Res 48:216–232
Chen F, Song JS (2001) Optimal policies for multi-echelon inventory problems with Markov- modulated demand. Operat Res 49:226–234
Abhyankar HS, Stephen CG (2001) Creating an inventory hedge for Markov-modulated poisson demand: an application and a model. Manufact Serv Operat Manag 3:306–320
Treharne JT, Sox CR (2002) Adaptive inventory control for non-stationary demand and partial information. Manage Sci 48(5):196–202
Janssen L, Sauer J, Claus T, Nehls U (2018) Development and simulation analysis of a new perishable inventory model with a closing days constraint under non-stationary stochastic demand. Comput Ind Eng 118:9–22
Tunc H, Kilic OA, Tarim SA, Eksioglu B (2011) The cost of using stationary inventory policies when demand is non-stationary. Int J Manag Sci 39(4):410–415
Pauls-Worm KG, Hendrix EM, Alcoba AG, Haijema R (2016) Order quantities for perishable inventory control with non-stationary demand and a fill rate constraint. Int J Prod Econ 181:238–246
Srinivasan R (2001) Information sharing in a supply chain: a note on its value when demand is non-stationary. Manag Sci 47(4):605–610
Qiu R, Sun M, Lim YF (2017) Optimizing (s, S) policies for multi-period inventory models with demand distribution uncertainty: robust dynamic programing approaches. Eur J Oper Res 261(3):880–892
Dominguez R, Framinan JM, Cannella S (2013) Serial vs. divergent supply chain networks: a comparative analysis of the bullwhip effect. Int J Prod Res 52(7):2194–2210
Lovejoy WS (1990) Myopic policies for some inventory models with uncertain demand distributions. Manage Sci 36(6):724–738
Chopra S, Meindl P, Kalra DV (2010) Supply chain management: strategy, planning, and operation. Third edition, Pearson Education
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2021 Springer Nature Singapore Pte Ltd.
About this paper
Cite this paper
Ranjith, A.M., Pillai, V.M. (2021). Determination of Safety Stock in Divergent Supply Chains with Non-stationary Demand Process. In: Pandey, P.M., Kumar, P., Sharma, V. (eds) Advances in Production and Industrial Engineering. Lecture Notes in Mechanical Engineering. Springer, Singapore. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-15-5519-0_6
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-15-5519-0_6
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Singapore
Print ISBN: 978-981-15-5518-3
Online ISBN: 978-981-15-5519-0
eBook Packages: EngineeringEngineering (R0)