Abstract
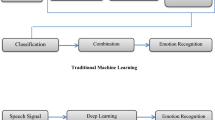
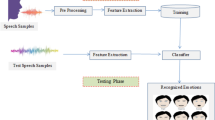
Research-oriented work in speech recognition has garnered a lot of interest since last two decades. Emotions derived from speech have drawn considerable interest of researchers especially for analysis of human behavior. Emotions from a speech are extracted and identified by classifiers and systems being developed and improved over a period of time. This paper attempts to discuss the process of speech emotion recognition, different methods of pre-processing techniques, feature extraction methods, and classifiers used for speech emotion recognition.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ayadi ME, Kamel MS, Karray F (2011) Survey on speech emotion recognition: features, classification schemes, and databases. Pattern Recogn 44:572–587
Koolagudi SG, Rao KS (2012) Emotion recognition from speech: a review. Int J Speech Technol 15(2):99–117
Huahu X, Jue G, Jian Y (2010) Application of speech emotion recognition in intelligent household robot. In: Proceedings of international conference on artificial intelligence and computational intelligence, vol 1, pp 537–541
Schuller B, Rigoll G, Lang M (2004) Speech emotion recognition combining acoustic features and linguistic information in a hybrid support vector machine-belief network architecture. In: Proceedings of IEEE international conference acoustics, speech, and signal processing, pp 577–580
Bao H, Xu M, Zheng TF (2007) Emotion attribute projection for speaker recognition on emotional speech. In: INTERSPEECH, pp 758–761
Al Machot F, Mosa AH, Dabbour K, Fasih A, Schwarzlmüller C, Ali M et al (2011) A novel real-time emotion detection system from audio streams based on Bayesian Quadratic Discriminate Classifier for ADAS. In: Proceedings of joint 3rd international work nonlinear dynamic synchronization. INDS ’11 16th international symposium theoretical electrical engineering ISTET ’11, pp 47–51
Tacconi D, Mayora O, Lukowicz P, Arnrich B, Setz C, Tröster G, Haring C (2008) Activity and emotion recognition to support early diagnosis of psychiatric diseases. In: Proceedings of 2nd international conference on pervasive computing technologies for healthcare ’08, Tampere, Finland, pp 100–102
Cowie R, Douglas-Cowie E, Savvidou S, McMahon E, Sawey M, Schroder M (2000) FEELTRACE: an instrument for recording perceived emotion in real time. In Proceedings of ISCA speech and emotion workshop, pp 19–24
Gupta P, Rajput N (2007) Two-stream emotion recognition for call center monitoring. In: INTERSPEECH, pp 2241–2244
Lee C, Narayanan S (2005) Toward detecting emotions in spoken dialogs. IEEE Trans Speech Audio Process 13(2):293–303
Sanaullah M, Gopalan K (2013) Distinguishing deceptive speech from truthful speech using MFCC. In: Proceedings of the 7th international conference on circuits, systems and signals. WSEAS, pp 167–171
Ang J, Dhillon R, Krupski A, Shriberg E, Stolcke A (2002) Prosody-based automatic detection of annoyance and frustration in human–computer dialog. In: Proceedings of international conference on spoken language processing (ICSLP ’02), vol 3, pp 2037–2040
Batliner A, Schuller B, Seppi D, Steidl S, Devillers L, Vidrascu L, Vogt T, Aharonson V, Amir N (2011) The automatic recognition of emotions in speech. Emot Oriented Syst 2:71–99
Schuller B, Zhang Z, Weninger F, Rigoll G (2011) Using multiple databases for training emotion recognition: to unite or to vote? In: International Science Congress Association, pp 1553–1556
Pan Y, Shen P, Shen L (2012) Speech emotion recognition using support vector machine. Int J Smart Home 6(2):101–108
Seehapoch T, Wongthanavasu S (2013) Speech emotion recognition using support vector machines. In: 2013 5th international conference on knowledge and smart technology, Piscataway. IEEE, pp 86–91
Burkhardt F, Paeschke A, Rolfes M, Sendlmeier W, Weiss B (2005) A database of German emotional speech. In: Proceedings of INTERSPEECH, pp 1517–1520
Schuller B, Steidl S, Batliner A (2009) The INTERSPEECH 2009 emotion challenge. In: Proceedings of INTERSPEECH, pp 312–315
Neiberg D, Elenius K, Karlsson I, Laskowski K (2006) Emotion recognition in spontaneous speech. In: Proceedings of FONETIK, pp 101–104
Lee CM, Narayanan S, Pieraccini R (2001) Recognition of negative emotion in the human speech signals. In: IEEE workshop on automatic speech and understanding, pp 240–243
Rao KS, Koolagudi SG (2011) Identification of Hindi dialects and emotions using spectral and prosodic features of speech. Syst Cybern Inform 9(4):24–33. ISSN: 1690-4524
Kandali AB, Routray A, Basu TK (2009) Vocal emotion recognition in five native languages of assam using new wavelet features. Int J Speech Technol 12:1–13
Swain M, Routray A, Kabisatpathy P (2018) Databases, features and classifiers for speech emotion recognition: a review. Int J Speech Technol 21(1):93–120
Li J, Deng L, Gong Y, Haeb-Umbach R (2014) An overview of noise-robust automatic speech recognition. IEEE/ACM Trans Audio Speech Lang Process 22(4):745–777
Boll SF (1979) Suppression of acoustic noise in speech using spectral subtraction. IEEE Trans Acoust Speech Sig Process 27(2):113–120
El-Fattah MAA, Dessouky MI, Abbas AM, Diab SM, El-Sayed M, El-Rabaie WA-N, Alshebeili SA, El-samie FEA (2013) Speech enhancement with an adaptive Wiener filter. Int J Speech Technol 1–12
Hermus K, Wambacq P, Van Hamme H (2007) A review of signal subspace speech enhancement and its application to noise robust speech recognition. EURASIP J Appl Sig Process 1:195–209
Sayed A, Hadei M (2010) A family of adaptive filter algorithms in noise cancellation for speech enhancement. Int J Comput Electr Eng 2(2):1793–1816
Chen C, You M, Song M, Bu J, Liu J (2006) An enhanced speech emotion recognition system based on discourse information. In: Computational Science–ICCS. Springer, New York, pp 449–456
Ortony A, Clore GL, Collins A (1990) The cognitive structure of emotions. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Rao KS, Yegnanarayana B (2006) Prosody modification using instants of significant excitation. IEEE Trans Audio Speech Lang Process 14:972–980
Rao KS, Koolagudi SG (2012) Emotion recognition using speech features. Springer Science & Business Media, New York
Bitouk D, Verma R, Nenkova A (2010) Class-level spectral features for emotion recognition. Speech Commun 52:613–625
Rao KS, Koolagudi SG, Vempada RR (2013) Emotion recognition from speech using global and local prosodic features. Int J Speech Technol 16(2):143–160
Nwe TL, Foo SW, Silva LCD (2003) Speech emotion recognition using hidden Markov models. Speech Commun 41:603–623
Chapaneri SV (2012) Spoken digits recognition using weighted MFCC and improved features for dynamic time warping. Int J Comput Appl 40(3):6–12
Vogt T, André E (2005) Comparing feature sets for acted and spontaneous speech in view of automatic emotion recognition. In: Proceedings IEEE international conference on multimedia and expo, pp 474–477
Xu M, Maddage NC, Xu C, Kankanhalli M, Tian Q (2003) Creating audio keywords for event detection in soccer video. In: Proceedings IEEE international conference on multimedia and expo, vol 2, pp 281–284
Drioli C, Tisato G, Cosi P, Tesser F (2003) Emotions and voice quality: experiments with sinusoidal modeling, pp 127–132
Patel S, Scherer KR, Bjorkner E, Sundberg J (2011) Mapping emotions into acoustic space: the role of voice production. Biol Psychol 93–98
Chandrasekar P, Chapaneri S, Jayaswal D (2014) Automatic speech emotion recognition: a survey. In: International conference on circuits, systems, communication and information technology applications, pp 341–346
Wu S, Falk TH, Chan WY (2011) Automatic speech emotion recognition using modulation spectral features. Speech Commun 53(5):768–785
Razak A, Komiya R, Abidin M (2005) Comparison between fuzzy and nn method for speech emotion recognition. In: Proceedings of 3rd international conference on information technology and applications ICITA, vol 1, pp 297–302
Nicholson J, Takahashi K, Nakatsu R (2000) Emotion recognition in speech using neural networks. Neural Comput Appl 11:290–296
Zhou Y, Sun Y, Zhang J, Yan Y (2009) Speech emotion recognition using both spectral and prosodic features. In: International conference on information engineering and computer science, ICIECS, Wuhan. IEEE Press, New York, pp 1–4
Cover TM, Hart PE (1967) Nearest neighbor pattern classification. Inst Electr Electron Eng Trans Inf Theory 13:21–27
Kotsiantis SB (2007) Supervised machine learning: a review of classification techniques. Informatica 31:249–268
Bhavsar H, Ganatra A (2012) A comparative study of training algorithms for supervised machine learning. Int J Soft Comput Eng (IJSCE) 2(4):2231–2307
Tarunika K, Pradeeba RB, Aruna P (2018) Applying machine learning techniques for speech emotion recognition. In: 9th ICCCNT
Duda R, Hart P (1973) Pattern classification and scene analysis. Wiley, New York
Friedman N, Geiger D, Goldszmidt M (1997) Bayesian network classifiers. Mach Learn 29:131–163
Anyanwu M, Shiva S (2009) Comparative analysis of serial decision tree classification algorithms. Int J Comput Sci Secur 3(3):230–240
Jadhav SD, Channe HP (2013) Comparative study of K-NN, naive Bayes and decision tree classification techniques. Int J Sci Res (IJSR) 5(1):1842–1845
Yang N, Yuan J, Zhou Y, Demirkol I, Duan Z, Heinzelman W, Sturge-Apple M (2017) Enhanced multiclass SVM with thresholding fusion for speech-based emotion classification. Int J Speech Technol 20(1):27–41
Londhe ND, Ahirwal MK, Lodha P (2016) Machine learning paradigms for speech recognition of an Indian dialect. In: International conference on communication and signal processing, pp 780–786
Mohanty S, Swain BK (2010) Emotion recognition using fuzzy K-means from Oriya speech, vol 1, pp 188–192
Motamed S, Setayeshi S, Rabiee A (2017) Speech emotion recognition based on a modified brain emotional learning model. Biol Inspired Cogn Archit 19:32–38
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2021 Springer Nature Singapore Pte Ltd.
About this paper
Cite this paper
Thakur, A., Dhull, S. (2021). Speech Emotion Recognition: A Review. In: Hura, G.S., Singh, A.K., Siong Hoe, L. (eds) Advances in Communication and Computational Technology. ICACCT 2019. Lecture Notes in Electrical Engineering, vol 668. Springer, Singapore. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-15-5341-7_61
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-15-5341-7_61
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Singapore
Print ISBN: 978-981-15-5340-0
Online ISBN: 978-981-15-5341-7
eBook Packages: EngineeringEngineering (R0)