Abstract
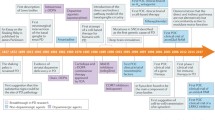
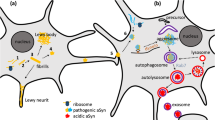
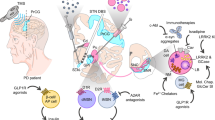
Parkinson’s disease (PD) is a multifactorial neurodegenerative disease that disturbs the dopamine neural circuit by affecting the basal nuclei. It is symptomized as motor and cognitive disturbances. Standard therapeutic regimen exhibits improvement in motor symptoms but is ineffectual in reversing the condition and delaying the progression of the disease. Thus, alternative approaches have been pursued in various areas. This perspective analyzes the various strategies studied and researched for treatment of PD along with contributions in the treatment of PD.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ellis JM, Fell MJ (2017) Current approaches to the treatment of Parkinson’s disease. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 27:4247–4255
Stopping Parkinson’s Disease before it Starts (2019). https://medicalxpress.com/news/2019-06-parkinson-disease.html. Accessed 14 Aug 2019
Dorszewska J, Kozubski W (2016) Genetic and biochemical factors in Parkinson’s disease. In: Dorszewska J, Kozubski W (eds) Challenges in Parkinson’s disease. IntechOpen, London
Dorszewska J, Prendecki M, Lianeri M, Kozubski W (2014) Molecular effects of L-dopa therapy in Parkinson’s disease. Curr Genomics 15:11–17
Parkinson’s Disease (2019). https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/parkinsons-disease/diagnosis-treatment/drc-20376062. Accessed 16 Aug 2019
Perez-Lloret S, Barrantes FJ (2016) Deficits in cholinergic neurotransmission and their clinical correlates in Parkinson’s disease. NPJ Park Dis 2:16001
What are Anticholinergics? (2019). https://parkinsonsdisease.net/medications/anticholinergics/. Accessed 16 Aug 2019
Medications Used To Treat Parkinson’s (2019). https://parkinsonsdisease.net/medications/. Accessed 16 Aug 2019
Yadav A, Agarwal S, Tiwari SK, Chaturvedi RK (2014) Mitochondria: prospective targets for neuroprotection in Parkinson’s disease. Curr Pharm Des 20:5558–5573
Freitas ME, Fox SH (2016) Nondopaminergic treatments for Parkinson’s disease: current and future prospects. Neurodegenerative Dis Manag 6:249–268
FDA (2019) FDA approves new add-on drug to treat off episodes in adults with Parkinson’s disease. https://www.fda.gov/news-events/press-announcements/fda-approves-new-add-drug-treat-episodes-adults-parkinsons-disease. Accessed 23 Aug 2019
Parkinson’s Tozadenant Trial Discontinued (2019). https://www.michaeljfox.org/news/parkinsons-tozadenant-trial-discontinued. Accessed 23 Aug 2019
Yuan G, Jankins TC, Patrick CG Jr, Philbrook P, Sears O, Hatfield S, Sitkovsky M, Vasdev N, Liang SH, Ondrechen MJ, Pollastri MP, Jones GB (2017) Fluorinated adenosine A2A receptor antagonists inspired by preladenant as potential cancer immunotherapeutics. Int J Med Chem 2017:1–8. https://www.hindawi.com/journals/ijmc/2017/4852537. Accessed 23 Aug 2019
Isaacson SH, Skettini J (2014) Neurogenic orthostatic hypotension in Parkinson’s disease: evaluation, management, and emerging role of droxidopa. Vasc Health Risk Manag 10:169–176
Sánchez-ferro Á, Benito-león J, Gómez-esteban JC (2013) The management of orthostatic hypotension in Parkinson’s disease. Front Neurol 4:1–11
Treatment of Orthostatic Intolerance in Patients With Parkinson’s Disease using Midodrine (2019). https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT02365012. Accessed 23 Aug 2019
Buddhala C, Loftin SK, Kuley BM, Cairns NJ, Campbell MC, Perlmutter JS, Kotzbauer PT (2015) Dopaminergic, serotonergic, and noradrenergic deficits in Parkinson disease. Ann Clin Transl Neurol 2:949–959
Trenkwalder C et al (2015) Prolonged-release oxycodone—naloxone for treatment of severe pain in patients with Parkinson’s disease (PANDA): a double-blind, randomised, placebo-controlled trial. Lancet Neurol 14:1161–1170
Blair HA, Dhillon S (2017) Safinamide: a review in Parkinson’s disease. CNS Drugs 31:169–176
FDA Accepts New Drug Application for Opicapone as Add-on Therapy (2019). https://parkinsonsnewstoday.com/2019/07/15/fda-accepts-new-drug-application-opicapone-add-on-therapy-parkinsons-neurocrine-biosciences/. Accessed 24 Aug 2019
Monti DA, Zabrecky G, Kremens D, Liang TW, Wintering NA, Cai J, Wei X, Bazzan AJ, Zhong L, Bowen B, Intenzo CM, Iacovitti L, Newberg AB (2016) N-acetyl cysteine may support dopamine neurons in Parkinson’s disease: preliminary clinical and cell line data. PLoS One 11:1–15
Pires AO, Teixeira FG, Sousa N (2017) Old and new challenges in Parkinson’s disease therapeutics. Prog Neurobiol 156:69–89
Pandey S (2012) Parkinson’s disease: recent advances. J Assoc Physicians India 60:30–32
Shukla AW, Okun MS (2013) Surgical treatment of Parkinson’s disease: patients, targets, devices, and approaches. Neurotherapeutics 11:47–59
A Responsive Closed-Loop Approach to Treat Freezing of Gait in Parkinson’s Disease (2019). https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT02318927. Accessed 25 Aug 2019
Combined Deep Brain Stimulation for Parkinson’s Disease (2019). https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT01485276. Accessed 25 Aug 2019
Randomised Crossover Trial of Deep Brain Stimulation of Differential Posterior Subthalamic Area Regions in Parkinson’s Disease and Tremor (2019). https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT01945567. Accessed 25 Aug 2019
Mandler M, Valera E, Rockenstein E, Mante M, Weninger H, Patrick C, Adame A, Schmidhuber S, Santic R, Schneeberger A, Schmidt W, Mattner F, Masliah E (2015) Active immunization against alpha-synuclein ameliorates the degenerative pathology and prevents demyelination in a model of multiple system atrophy. Mol Neurodegener 10:1–15
George S, Brundin P (2015) Immunotherapy in Parkinson’s disease: micromanaging alpha-synuclein aggregation. J Park Dis 5:413–424
Jankovic J, Goodman I, Safirstein B, Marmon TK, Schenk DB, Koller M, Zago W, Ness DK, Griffith SG, Grundman M, Soto J, Ostrowitzki S, Boess FG, Martin-Facklam M, Quinn JF, Isaacson SH, Omidvar O, Ellenbogen A, Kinney GG (2018) Safety and tolerability of multiple ascending doses of PRX002/RG7935, an anti-alpha-synuclein monoclonal antibody, in patients with Parkinson disease: a randomized clinical trial. JAMA Neurol 75:1206–1214
Brys M, Fanning L, Hung S, Ellenbogen A, Penner N, Yang M, Welch M, Koenig E, David E, Fox T, Makh S, Aldred J, Goodman I, Pepinsky B, Liu Y, Graham D, Weihofen A, Cedarbaum JM (2019) Randomized phase I clinical trial of anti-alpha-synuclein antibody BIIB054. Mov Disord 34:1154–1163
Single-Ascending Dose Study of BIIB054 in Healthy Participants and Early Parkinson’s Disease (2019). https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT02459886. Accessed 30 Aug 2019
Zella SMA, Metzdorf J, Ciftci E, Ostendorf F, Muhlack S, Gold R, Tönges L (2019) Emerging immunotherapies for Parkinson disease. Neurol Ther 8:29–44
AFFITOPE®PD03A (2019) Affiris announces top line results of first-in-human clinical study using AFFITOPE®PD03A, Confirming immunogenicity and safety profile In Parkinson’s disease patients. https://affiris.com/news/affiris-announces-top-line-results-of-first-in-human-clinical-study-using-affitope/. Accessed 30 Aug 2019
Axelsen TM, Woldbye DPD (2018) Gene therapy for Parkinson’s disease, an update. J Park Dis 8:195–215
Sanders TH, Jaeger D (2016) Optogenetic stimulation of cortico-subthalamic projections is sufficient to ameliorate bradykinesia in 6-OHDA lesioned mice. Neurobiol Dis 95:225–237
Uehara T, Choong CJ, Nakamori M, Hayakawa H, Nishiyama K, Kasahara Y, Baba K, Nagata T, Yokota T, Tsuda H, Obika S, Mochizuki H (2019) Amido-bridged nucleic acid (AmNA)-modified antisense oligonucleotides targeting α-synuclein as a novel therapy for Parkinson’s disease. Sci Rep 9:1–13
Nakamori M, Junn E, Mochizuki H, Mouradian MM (2019) Nucleic acid-based therapeutics for Parkinson’s disease. Neurotherapeutics 16:287–298
de Ynigo-Mojado L, Martin-Ruiz I, Sutherland JD (2011) Efficient allele-specific targeting of LRRK2 R1441 mutations mediated by RNAi. PLoS One 6:1–10
Zhu Z, Yang C, Iyaswamy A, Krishnamoorthi S, Sreenivasmurthy SG, Liu J, Wang Z, Tong BC, Song J, Lu J, Cheung KH, Li M (2019) Balancing mTOR signaling and autophagy in the treatment of Parkinson’s disease. Int J Mol Sci 20:1–15
Sardi SP, Cedarbaum JM, Brundin P (2018) Targeted therapies for Parkinson’s disease: from genetics to the clinic. Mov Disord 33:684–696
Nilotinib in Parkinson’s Disease (NILO-PD) (2019). https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT03205488. Accessed 2 Sept 2019
Phase 1 Study of NPT200-11 in Healthy Subjects (2019). https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT02606682. Accessed 2 Sept 2019
Multiple Dose Safety Study of NPT088 in Patients With Mild to Moderate Probable Alzheimer’s Disease (2019). https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT03008161. Accessed 3 Sept 2019
Gonzalez C, Bonilla S, Flores AI, Cano E, Liste I (2016) An update on human stem cell-based therapy in Parkinson’s disease. Curr Stem Cell Res Ther 11:561–568
Barker RA, Drouin-Ouellet J, Parmar M (2015) Cell-based therapies for Parkinson disease-past insights and future potential. Nat Rev Neurol 11:492–503
TRANSEURO (2019) TRANSEURO Open Label Transplant Study in Parkinson’s Disease. https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT01898390. Accessed 4 Sept 2019
Parmar M, Torper O, Drouin-Ouellet J (2019) Cell-based therapy for Parkinson’s disease: a journey through decades toward the light side of the force. Eur J Neurosci 49:463–471
Stoker TB, Blair NF, Barker RA (2017) Neural grafting for Parkinson’s disease: challenges and prospects. Neural Regen Res 12:389–392
Medicine P, Pluripotent I (2019) Treatment of Parkinson’s disease through personalized medicine and induced pluripotent stem cells. Cell 8:2–15
Hayashi T, Wakao S, Kitada M, Ose T, Watabe H, Kuroda Y, Mitsunaga K, Matsuse D, Shigemoto T, Ito A, Ikeda H, Fukuyama H, Onoe H, Tabata Y, Dezawa M (2013) Autologous mesenchymal stem cell-derived dopaminergic neurons function in parkinsonian macaques. J Clin Invest 123:272–284
Khoo MLM, Tao H, Meedeniya ACB, Mackay-Sim A, Ma DDF (2011) Transplantation of neuronal-primed human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells in hemiparkinsonian rodents. PLoS One 6:1–16
Filho DM, Ribeiro PDC, Oliveira LF, de Paula DRM, Capuano V, de Assunção TSF, da Silva VJD (2018) Therapy with mesenchymal stem cells in Parkinson disease history and perspectives. Neurologist 23:141–147
Inden M, Yanagisawa D, Hijioka M (2016) Annals of neurodegenerative disorders therapeutic effects of mesenchymal stem cells for Parkinson’s disease. Ann Neurodegener Disord 1002:1–8
AZD5904 Mechanism of action: Myeloperoxidase (MPO) inhibitor (2019). https://openinnovation.astrazeneca.com/azd5904.html. Accessed 10 Sept 2019
First Parkinson’s Patient Dosed in Early Trial of DNL151, Potential LRRK2 Inhibitor (2019). https://parkinsonsnewstoday.com/2019/09/10/1st-parkinsons-patient-dosed-in-phase-1b-trial-of-dnl151-potential-lrrk2-inhibitor/. Accessed 10 Sept 2019
Study to Evaluate DNL201 in Subjects With Parkinson’s Disease (2019). https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT03710707. Accessed 10 Sept 2019
Lemos A, Melo R, Preto AJ, Almeida JG, Moreira IS, Dias Soeiro Cordeiro MN (2018) In silico studies targeting G-protein coupled receptors for drug research against Parkinson’s disease. Curr Neuropharmacol 16:786–848
Balestrino R, Schapira AHV (2018) Glucocerebrosidase and Parkinson disease: molecular, clinical, and therapeutic implications. Neuroscientist 24:540–559
Elkouzi A, Vedam-Mai V, Eisinger RS, Okun MS (2019) Emerging therapies in Parkinson disease—repurposed drugs and new approaches. Nat Rev Neurol 15:204–233
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2020 Springer Nature Singapore Pte Ltd.
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Mohammed, M., Alenezi, S.K. (2020). Advancement and Challenges in Parkinson’s Disease: A Recent Outlook. In: Mathew, B., Thomas Parambi, D.G. (eds) Principles of Neurochemistry. Springer, Singapore. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-15-5167-3_8
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-15-5167-3_8
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Singapore
Print ISBN: 978-981-15-5166-6
Online ISBN: 978-981-15-5167-3
eBook Packages: Biomedical and Life SciencesBiomedical and Life Sciences (R0)