Abstract
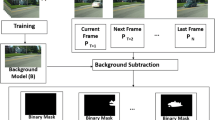
Dynamic Background Modeling (DBM) is a crucial task in many computer vision based applications such as human activity analysis, traffic monitoring, surveillance, and security. DBM is extremely challenging in scenarios like illumination changes, camouflage, intermittent object motion or shadows. In this study, we proposed an end-to-end framework based on Generative Adversarial Network, which can generate dynamic background information for the task of DBM in an unsupervised manner. Our proposed model can handle the problem of DBM in the presence of the challenges mentioned above by generating data similar to the desired information. The primary aim of our proposed model during training is to learn all the dynamic changes in a scene-specific background information. While, during testing, inverse mapping of data to latent space representation in our model generates dynamic backgrounds similar to test data. The comparative analysis of our proposed model upon experimental evaluations on SBM.net and SBI benchmark datasets has outperformed eight existing methods for DBM in many challenging scenarios.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Babaee, M., Dinh, D.T., Rigoll, G.: A deep convolutional neural network for video sequence background subtraction. Pattern Recogn. 76, 635–649 (2018)
Baber, C., Morar, N.S., McCabe, F.: Ecological interface design, the proximity compatibility principle, and automation reliability in road traffic management. IEEE Trans. Hum.-Mach. Syst. 49, 241–249 (2019)
Bakkay, M., Rashwan, H., Salmane, H., Khoudour, L., Puigtt, D., Ruichek, Y.: BSCGAN: deep background subtraction with conditional generative adversarial networks. In: 2018 25th IEEE International Conference on Image Processing (ICIP), pp. 4018–4022. IEEE (2018)
Bouwmans, T., Garcia-Garcia, B.: Background subtraction in real applications: challenges, current models and future directions. arXiv preprint arXiv:1901.03577 (2019)
Bouwmans, T., Javed, S., Sultana, M., Jung, S.K.: Deep neural network concepts for background subtraction: a systematic review and comparative evaluation. arXiv preprint arXiv:1811.05255 (2018)
Bouwmans, T., Maddalena, L., Petrosino, A.: Scene background initialization: a taxonomy. Pattern Recogn. Lett. 96, 3–11 (2017)
Bouwmans, T., Zahzah, E.H.: Robust PCA via principal component pursuit: a review for a comparative evaluation in video surveillance. Comput. Vis. Image Underst. 122, 22–34 (2014)
Candès, E.J., Li, X., Ma, Y., Wright, J.: Robust principal component analysis? J. ACM (JACM) 58(3), 11 (2011)
Cao, X., Yang, L., Guo, X.: Total variation regularized RPCA for irregularly moving object detection under dynamic background. IEEE Trans. Cybern. 46(4), 1014–1027 (2016)
Fedus, W., Rosca, M., Lakshminarayanan, B., Dai, A.M., Mohamed, S., Goodfellow, I.J.: Many paths to equilibrium: GANs do not need to decrease a divergence at every step. CoRR abs/1710.08446 (2018)
Goodfellow, I., et al.: Generative adversarial nets. In: Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, pp. 2672–2680 (2014)
Guo, X., Wang, X., Yang, L., Cao, X., Ma, Y.: Robust foreground detection using smoothness and arbitrariness constraints. In: Fleet, D., Pajdla, T., Schiele, B., Tuytelaars, T. (eds.) ECCV 2014. LNCS, vol. 8695, pp. 535–550. Springer, Cham (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-10584-0_35
He, J., Balzano, L., Szlam, A.: Incremental gradient on the Grassmannian for online foreground and background separation in subsampled video. In: 2012 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), pp. 1568–1575. IEEE (2012)
Javed, S., Bouwmans, T., Sultana, M., Jung, S.K.: Moving object detection on RGB-D videos using graph regularized spatiotemporal RPCA. In: Battiato, S., Farinella, G.M., Leo, M., Gallo, G. (eds.) ICIAP 2017. LNCS, vol. 10590, pp. 230–241. Springer, Cham (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-70742-6_22
Javed, S., Mahmood, A., Bouwmans, T., Jung, S.K.: Background–foreground modeling based on spatiotemporal sparse subspace clustering. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 26(12), 5840–5854 (2017)
Javed, S., Mahmood, A., Bouwmans, T., Jung, S.K.: Spatiotemporal low-rank modeling for complex scene background initialization. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Video Technol. 28(6), 1315–1329 (2018)
Kingma, D.P., Ba, J.: Adam: a method for stochastic optimization. arXiv preprint arXiv:1412.6980 (2014)
Laugraud, B., Piérard, S., Droogenbroeck, M.V.: LaBGen-P-semantic: a first step for leveraging semantic segmentation in background generation. J. Imaging 4, 86 (2018)
Mabrouk, A.B., Zagrouba, E.: Abnormal behavior recognition for intelligent video surveillance systems: a review. Expert Syst. Appl. 91, 480–491 (2018)
Maddalena, L., Petrosino, A.: Towards benchmarking scene background initialization. In: Murino, V., Puppo, E., Sona, D., Cristani, M., Sansone, C. (eds.) ICIAP 2015. LNCS, vol. 9281, pp. 469–476. Springer, Cham (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-23222-5_57
Patil, P., Murala, S.: FgGAN: a cascaded unpaired learning for background estimation and foreground segmentation. In: 2019 IEEE Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision (WACV), pp. 1770–1778 (2019)
Radford, A., Metz, L., Chintala, S.: Unsupervised representation learning with deep convolutional generative adversarial networks. arXiv preprint arXiv:1511.06434 (2015)
Ramirez-Alonso, G., Ramirez-Quintana, J.A., Chacon-Murguia, M.I.: Temporal weighted learning model for background estimation with an automatic re-initialization stage and adaptive parameters update. Pattern Recogn. Lett. 96, 34–44 (2017)
Sakkos, D., Ho, E.S.L., Shum, H.P.H.: Illumination-aware multi-task gans for foreground segmentation. IEEE Access 7, 10976–10986 (2019)
Sharma, L., Lohan, N.: Performance analysis of moving object detection using BGS techniques in visual surveillance. Int. J. Spatio-Temporal Data Sci. 1(1), 22–53 (2019)
Sultana, M., Mahmood, A., Javed, S., Jung, S.K.: Unsupervised deep context prediction for background estimation and foreground segmentation. Mach. Vis. Appl. 30, 375–395 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00138-018-0993-0
Sultani, W., Chen, C., Shah, M.: Real-world anomaly detection in surveillance videos. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 6479–6488 (2018)
Vaswani, N., Bouwmans, T., Javed, S., Narayanamurthy, P.: Robust subspace learning: robust PCA, robust subspace tracking, and robust subspace recovery. IEEE Signal Process. Mag. 35(4), 32–55 (2018)
Wright, J., Ganesh, A., Rao, S., Peng, Y., Ma, Y.: Robust principal component analysis: exact recovery of corrupted low-rank matrices via convex optimization. In: Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, pp. 2080–2088 (2009)
Xu, J., Ithapu, V., Mukherjee, L., Rehg, J., Singh, V.: GOSUS: Grassmannian online subspace updates with structured-sparsity. In: ICCV (2013)
Yeh, R.A., Chen, C., Lim, T.Y., Schwing, A.G., Hasegawa-Johnson, M., Do, M.N.: Semantic image inpainting with deep generative models. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 5485–5493 (2017)
Yeung, S., Russakovsky, O., Jin, N., Andriluka, M., Mori, G., Fei-Fei, L.: Every moment counts: dense detailed labeling of actions in complex videos. Int. J. Comput. Vision 126(2–4), 375–389 (2018)
Zhao, C., Cham, T.L., Ren, X., Cai, J., Zhu, H.: Background subtraction based on deep pixel distribution learning. In: 2018 IEEE International Conference on Multimedia and Expo (ICME), pp. 1–6. IEEE (2018)
Zhao, Q., Zhou, G., Zhang, L., Cichocki, A., Amari, S.I.: Bayesian robust tensor factorization for incomplete multiway data. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 27(4), 736–748 (2016)
Zheng, W., Wang, K., Wang, F.: Background subtraction algorithm based on Bayesian generative adversarial networks. Acta Automatica Sinica 44, 878–890 (2018)
Zhou, J.T., Du, J., Zhu, H., Peng, X., Liu, Y., Goh, R.S.M.: AnomalyNet: an anomaly detection network for video surveillance. IEEE Trans. Inf. Forensics Secur. 14, 2537–2550 (2019)
Zhou, X., Yang, C., Yu, W.: Moving object detection by detecting contiguous outliers in the low-rank representation. IEEE T-PAMI 35(3), 597–610 (2013)
Zivkovic, Z.: Improved adaptive Gaussian mixture model for background subtraction. In: Proceedings of the 17th International Conference on Pattern Recognition, ICPR 2004, vol. 2, pp. 28–31. IEEE (2004)
Zivkovic, Z., Van Der Heijden, F.: Efficient adaptive density estimation per image pixel for the task of background subtraction. Pattern Recogn. Lett. 27(7), 773–780 (2006)
Acknowledgements
This research was supported by Development project of leading technology for future vehicle of the business of Daegu metropolitan city (No. 20171105).
Also this study was supported by the BK21 Plus project (SW Human Resource Development Program for Supporting Smart Life) funded by the Ministry of Education, School of Computer Science and Engineering, Kyungpook National University, Korea (21A20131600005).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2020 Springer Nature Singapore Pte Ltd.
About this paper
Cite this paper
Sultana, M., Mahmood, A., Bouwmans, T., Jung, S.K. (2020). Unsupervised Adversarial Learning for Dynamic Background Modeling. In: Ohyama, W., Jung, S. (eds) Frontiers of Computer Vision. IW-FCV 2020. Communications in Computer and Information Science, vol 1212. Springer, Singapore. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-15-4818-5_19
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-15-4818-5_19
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Singapore
Print ISBN: 978-981-15-4817-8
Online ISBN: 978-981-15-4818-5
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)