Abstract
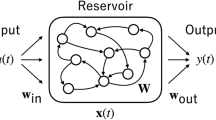
Echo state network (ESN) is a class of neuromorphic computing approach called reservoir computing consisting of a large number of randomly interconnected neurons. Only the reservoir-to-output readout mappings are variable and are modified during the process of training. ESN functions as a densely interconnected recurrent neural network and is suitable for temporal prediction tasks, but with significantly reduced training complexity. In this article, we propose an equalizer based on ESN and evaluate its performance over nonlinear dispersive channels. We also perform experiments for selection various parameters of ESN and study their effect on performance of the equalizer. Based on extensive simulations performed, proposed scheme shows notable decrease in bit-error rate (BER) compared to existing equalizer in literature.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bang SH, Sheu BJ (1996) A neural network for detection of signals in communication. IEEE Tran Circ Syst I: Fund Theory Appl 43(8):644–655
Siu S, Gibson GJ, Cowan CFN (1990) Decision feedback equalisation using neural network structures and performance comparison with standard architecture. IEE Proc I-Commun Speech Vis 137(4):221–225
Chen S, Gibson GJ, Cowan CFN, Grant PM (1990) Adaptive equalization of finite non-linear channels using multilayer perceptrons. Sig Process 20(2):107–119
Meyer M, Pfeiffer G (1993) Multilayer perceptron based decision feedback equalisers for channels with intersymbol interference. IEE Proc I (Commun Speech Vis) 140(6):420–424
Burse K, Yadav RN, Shrivastava SC (2010) Channel equalization using neural networks: a review. IEEE Trans Syst Man Cybern Part C (Appl Rev) 40(3):352–357
Pao Y (1989) Adaptive pattern recognition and neural networks. Addison-Wesley, Reading, MA
Patra JC, Poh WB, Chaudhari NS, Das A (2005) Nonlinear channel equalization with QAM signal using Chebyshev artificial neural network. In: Proceedings of international joint conference on neural networks, 2005, vol 5, pp 3214–3219 (2005)
Patra JC, Meher PK, Chakraborty G (2009) Nonlinear channel equalization for wireless communication systems using Legendre neural networks. Sig Process 89(11):2251–2262
Chen S, Mulgrew B, Grant PM (1993) A clustering technique for digital communications channel equalization using radial basis function networks. IEEE Trans Neural Networks 4(4):570–590
Jianping D, Sundararajan N, Saratchandran P (2002) Communication channel equalization using complex-valued minimal radial basis function neural networks. IEEE Trans Neural Networks 13(3):687–696
Nanda SJ, Jonwal N (2017) Robust nonlinear channel equalization using WNN trained by symbiotic organism search algorithm. Appl Soft Comput 57:197–209
Al-Awami AT, Zerguine A, Cheded L, Zidouri A, Saif W (2011) A new modified particle swarm optimization algorithm for adaptive equalization. Digit Signal Proc 21(2):195–207
Iqbal N, Zerguine A, Al-Dhahir N (2015) Decision feedback equalization using particle swarm optimization. Sig Process 108:1–12
Panda S, Mohapatra PK, Panigrahi SP (2015) A new training scheme for neural networks and application in non-linear channel equalization. Appl Soft Comput 27:47–52
Panda S, Sarangi A, Panigrahi SP (2014) A new training strategy for neural network using shuffled frog-leaping algorithm and application to channel equalization. AEU-Int J Electron Commun 68(11):1031–1036
Nanda SJ, Garg S (2019) Design of supervised and blind channel equalizer based on moth-flame optimization. J Inst Eng (India): Ser B 100(2):105–115
Kechriotis G, Zervas E, Manolakos ES (1994) Using recurrent neural networks for adaptive communication channel equalization. IEEE Trans Neural Networks 5(2):267–278
Mosleh S, Liu L, Sahin C, Zheng YR, Yi Y (2017) Brain-inspired wireless communications: where reservoir computing meets MIMO-OFDM. IEEE Trans Neural Networks Learn Syst 99:1–15
Bauduin M, Massar S, Horlin F (2016) Non-linear satellite channel equalization based on a low complexity echo state network. In: Annual conference on information science and systems (CISS). IEEE, New York, pp 99–104
Jaeger H (2001) The echo state approach to analysing and training recurrent neural networks-with an erratum note. German National Research Center for Information Technology GMD Technical Report, vol 148(34), p 13
Lukoeviius M (2012) A practical guide to applying echo state networks. In: Neural networks-tricks of the trade, Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg, pp 659–686
Ozturk MC, Xu D, Principe JC (2007) Analysis and design of echo state networks. Neural Comput 19(1):111–138
Rodan A, Tino P (2010) Minimum complexity echo state network. IEEE Trans Neural Networks 22(1):131–144
Millea A (2014) Explorations in echo state networks. Master’s Thesis, University of Groningen
Patra JC, Pal RN, Baliarsingh R, Panda G (1999) Nonlinear channel equalization for QAM signal constellation using artificial neural networks. IEEE Trans Syst Man Cybern Part B (Cybern) 29(2):262–271
Haykin S (2005) Adaptive filter theory. Pearson Education, New Delhi
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2020 Springer Nature Singapore Pte Ltd.
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Majumder, S. (2020). Echo State Network Based Nonlinear Channel Equalization in Wireless Communication System. In: Johri, P., Verma, J., Paul, S. (eds) Applications of Machine Learning. Algorithms for Intelligent Systems. Springer, Singapore. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-15-3357-0_9
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-15-3357-0_9
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Singapore
Print ISBN: 978-981-15-3356-3
Online ISBN: 978-981-15-3357-0
eBook Packages: EngineeringEngineering (R0)