Abstract
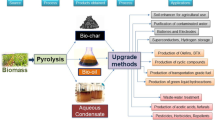
Catalytic fast pyrolysis (CFP) processes for conversion of lignocellulose biomass into liquid biofuels (bio-oil) have been extensively studying to meet increasing fuel demands and to address environmental issues. Direct use of crude bio-oil, however, is usually restricted due to its high content of oxygen. Therefore, reaction principles and mechanisms of the biomass catalytic pyrolysis need further reveal to develop improved bio-oil. This chapter presents a comprehensive review of the development of biomass CFP and bio-oil improving routes, including its catalysts, feedstocks, reaction methods and reactors.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Li R, Zhong ZP, Jin BS, Zheng AJ. Selection of temperature for bio-oil production from pyrolysis of algae from lake blooms. Energy Fuel. 2012;26:2996–3002. https://doi.org/10.1021/ef300180r.
Yanik J, Kornmayer C, Saglam M, Yüksel M. Fast pyrolysis of agricultural wastes: characterization of pyrolysis products. Fuel Process Technol. 2007;88:942–7. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuproc.2007.05.002.
Czernik S, Bridgwater AV. Overview of applications of biomass fast pyrolysis oil. Energy Fuel. 2004;18:590–8. https://doi.org/10.1021/ef034067u.
French R, Czernik S. Catalytic pyrolysis of biomass for biofuels production. Fuel Process Technol. 2010;91:25–32. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuproc.2009.08.011.
Encinar JM, González JF, González J. Fixed-bed pyrolysis of Cynara cardunculus L. product yields and compositions. Fuel Process Technol. 2000;68(3):209–22. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0378-3820(00)00125-9.
Jiang XX, Zhong ZP, Ellis N, Wang Q. Aging and thermal stability of the mixed product of the ether-soluble fraction of bio-oil and bio-diesel. Chem Eng Technol. 2011;34(5):727–36. https://doi.org/10.1002/ceat.201000441.
Zhang B, Zhong ZP, Ding K, Cao YY, Liu ZC. Catalytic upgrading of corn stalk fast pyrolysis vapors with fresh and hydrothermally treated HZSM-5 catalysts using Py-GC/MS. Ind Eng Chem Res. 2014;53(24):9979–84. https://doi.org/10.1021/ie404426x.
Shao SS, Zhang HY, Xiao R, Shen DK, Zheng J. Comparison of catalytic characteristics of biomass derivates with different structures over ZSM-5. Bioenerg Res. 2013;6:1173–82. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12155-013-9303-x.
Liu HL, Ma XQ, Li LJ, Hu ZF, Guo PS, Jiang YH. The catalytic pyrolysis of food waste by microwave heating. Bioresour Technol. 2014;106:45–50. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2014.05.020.
Dickerson T, Soria J. Catalytic fast pyrolysis: a review. Energies. 2013;6:514–38. https://doi.org/10.3390/en6010514.
Adam J, Antonakou E, Lappas A, Stocker M, Nilsen MH, Bouzga A, Hustad JE, Oye G. In situ catalytic upgrading of biomass derived fast pyrolysis vapours in a fixed bed reactor using mesoporous materials. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2006;96:93–101. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.micromeso.2006.06.021.
Imran A, Bramer EA, Seshan K, Brem G. High quality bio-oil from catalytic flash pyrolysis of lignocellulosic biomass over alumina-supported sodium carbonate. Fuel Process Technol. 2014;127:72–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuproc.2014.06.011.
Güngör A, Önenc S, Ucar S, Yanika J. Comparison between the “one-step” and “two-step” catalytic pyrolysis of pine bark. J Anal Appl Pyrolysis. 2012;97:39–48. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaap.2012.06.011.
Williams PT, Nugranad N. Comparison of products from the pyrolysis and catalytic pyrolysis of rice husks. Energy. 2000;25:493–513. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6701(02)85315-2.
Fan LL, Chen P, Zhou N, Liu SY, Zhang YN, Liu YH, Wang YP, Omar MM, Peng P, Addy M, Cheng YL, Ruan R. In-situ and ex-situ catalytic upgrading of vapors from microwave-assisted pyrolysis of lignin. Bioresour Technol. 2018;247:851–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0960-8524(99)00085-1.
Zhang B, Zhong ZP, Xie QL, Liu SY, Ruan R. Two-step fast microwave-assisted pyrolysis of biomass for bio-oil production using microwave absorbent and HZSM-5 catalyst. J Environ Sci. 2016;45:240–7. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jes.2015.12.019.
De Wild PJ, Den Uil H, Reith JH, Kiel JHA, Heeres HJ. Biomass valorisation by staged degasification A new pyrolysis-based thermochemical conversionoption to produce value-added chemicals from lignocellulosic biomass. J Anal Appl Pyrolysis. 2009;85:124–33. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaap.2008.08.008.
Radlein D, Piskorz J, Scott DS. Fast pyrolysis of natural polysaccharides as a potential industrial process. J Anal Appl Pyrolysis. 1991;19:41–63. https://doi.org/10.1016/0165-2370(91)80034-6.
Shen DK, Gu S, Bridgwater AV. Study on the pyrolytic behaviour of xylan-based hemicellulose using TG–FTIR and Py–GC–FTIR. J Anal Appl Pyrolysis. 2010;87:199–206. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaap.2009.12.001.
Bayerbach R, Meier D. Characterization of the water-insoluble fraction from fast pyrolysis liquids (pyrolytic lignin). Part IV: structure elucidation of oligomeric molecules. J Anal Appl Pyrolysis. 2009;85:98–107. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaap.2008.10.021.
Trendewicz A, Evans R, Dutta A. Evaluating the effect of potassium on cellulose pyrolysis reaction kinetics. Biomass Bioenergy. 2015;74:15–25. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biombioe.2015.01.001.
Di Blasi C, Branca C, Galgano A. Modifications in the thermicity of the pyrolysis reactions of ZnCl2-loaded wood. Ind Eng Chem Res. 2015;54(51):12741–9. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.iecr.5b03694.
Stefanidis SD, Kalogiannis KG, Iliopoulou EF. In-situ upgrading of biomass pyrolysis vapors: catalyst screening on a fixed bed reactor. Bioresour Technol. 2011;102(17):8261–7. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2011.06.032.
Lin Y, Zhang C, Zhang M. Deoxygenation of bio-oil during pyrolysis of biomass in the presence of CaO in a fluidized-bed reactor. Energ Fuels. 2011;24(10):5686–95. https://doi.org/10.1021/ef1009605.
Veses A, Aznar M, Martínez I. Catalytic pyrolysis of wood biomass in an auger reactor using calcium-based catalysts. Bioresour Technol. 2011;162:250–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2014.03.146.
Torri C, Reinikainen M, Lindfors C. Investigation on catalytic pyrolysis of pine sawdust: catalyst screening by Py-GC-MIP-AED. J Anal Appl Pyrolysis. 2010;88(1):7–13. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaap.2010.02.005.
Imran A, Bramer E, Seshan K, Brem G. Catalytic flash pyrolysis of biomass using different types of zeolite and online vapor fractionation. Energies. 2016;9(3):187. https://doi.org/10.3390/en9030187.
Wang SR, Dai GX, Yang HP, Luo ZY. Lignocellulosic biomass pyrolysis mechanism: a state-of-the-art review. Prog Energy Combust Sci. 2017;62:33–86. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pecs.2017.05.004.
Foster AJ, Jae J, Cheng YT, Huber GW, Lobo RF. Optimizing the aromatic yield and distribution from catalytic fast pyrolysis of biomass over ZSM-5. Appl Catal A Gen. 2012;423:154–61. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcata.2012.02.030.
Yang HP, Coolman R, Karanjkar P, Wang HY, Dornath P, Chen HP, Fan W, Conner WC, Mountziaris TJ, Huber G. The effects of contact time and coking on the catalytic fast pyrolysis of cellulose. Green Chem. 2017;19:286–97. https://doi.org/10.1039/c6gc02239a.
Maneffa M, Priecel P, Lopez-Sanchez JA. Biomass-derived renewable aromatics: selective routes and outlook for p-xylene commercialization. ChemSusChem. 2016;9:2736–48. https://doi.org/10.1002/cssc.201600605.
Hassan E, Elsayed I, Eseyin A. Production high yields of aromatic hydrocarbons through catalytic fast pyrolysis of torrefied wood and polystyrene. Fuel. 2016;174:317–24. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuel.2016.02.031.
Zhang HY, Xiao R, Huang H, Xiao G. Comparison of non-catalytic and catalytic fast pyrolysis of corncob in a fluidized bed reactor. Bioresour Technol. 2009;100(3):1428–34. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2008.08.031.
Zhang B, Zhong ZP, Ding K, Song ZW. Production of aromatic hydrocarbons from catalytic co-pyrolysis of biomass and high density polyethylene: analytical Py-GC/MS study. Fuel. 2015;139:622–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuel.2014.09.052.
Dahl IM, Kolboe SJ. On the reaction mechanism for hydrocarbon formation from methanol over SAPO-34: 2. Isotopic labeling studies of the co-reaction of propene and methanol. J Catal. 1996;161:304–9. https://doi.org/10.1006/jcat.1996.0188.
Tau LM, Fort AW, Bao SQ, Davis BH. Methanol to gasoline: 14C tracer studies of the conversion of methanol/higher alcohol mixtures over ZSM-5. Fuel Process Technol. 1990;26:209–19. https://doi.org/10.1016/0378-3820(90)90006-e.
Zhang B, Zhong ZP, Chen P, Ruan R. Microwave-assisted catalytic fast co-pyrolysis of Ageratina adenophora and kerogen with CaO and ZSM-5. J Anal Appl Pyrolysis. 2017;127:246–57. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaap.2017.07.027.
Carlson TR, Jae J, Lin YC, Tompsett GA, Huber GW. Catalytic fast pyrolysis of glucose with HZSM-5: the combined homogeneous and heterogeneous reactions. J Catal. 2010;270:110–24. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcat.2009.12.013.
Zhang HY, Xiao R, Jin BS, Xiao GM, Chen R. Biomass catalytic pyrolysis to produce olefins and aromatics with a physically mixed catalyst. Bioresour Technol. 2013;140:256–62. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2013.04.094.
Lu Q, Zhang ZF, Dong CQ, Zhu XF. Catalytic upgrading of biomass fast pyrolysis vapors with nano metal oxides: an analytical Py-GC/MS study. Energies. 2010;3:1805–20. https://doi.org/10.3390/en3111805.
Ding K, He AX, Zhong DX, Fan LL, Liu SY, Wang YP, Liu YH, Chen P, Lei HW, Ruan R. Improving hydrocarbon yield via catalytic fast co-pyrolysis of biomass and plastic over ceria and HZSM-5: an analytical pyrolyzer analysis. Bioresour Technol. 2018;268:1–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2018.07.108.
Casoni AI, Nievas ML, Moyano EL, Alvarez M, Diez A, Dennehy M, Volpe MA. Catalytic pyrolysis of cellulose using MCM-41 type catalysts. Appl Catal A Gen. 2016;514:235–40. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcata.2016.01.017.
Zhang B, Zhong ZP, Li T, Xue ZY, Wang XJ, Ruan R. Biofuel production from distillers dried grains with solubles (DDGS) co-fed with waste agricultural plastic mulching films via microwave-assisted catalytic fast pyrolysis using microwave absorbent and hierarchical ZSM-5/MCM-41 catalyst. J Anal Appl Pyrolysis. 2018;130:1–7. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaap.2018.02.007.
Carlson TR, Cheng YT, Jae J, Huber GW. Production of green aromatics and olefins by catalytic fast pyrolysis of wood sawdust. Energy Environ Sci. 2011;4:145–61. https://doi.org/10.1039/C0EE00341G1.
Zhang B, Zhong ZP, Song ZW, Ding K, Chen P, Ruan R. Optimizing anti-coking abilities of zeolites by ethylene diamine tetraacetie acid modification on catalytic fast pyrolysis of corn stalk. J Power Sources. 2015;300:87–94. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpowsour.2015.09.075.
Chen NY, Degnan TF, Koenig LR. Liquid fuel from carbohydrates. Chem Tech. 1986;16(8):506–11.
Valle B, Aramburu B, Santiviago C, Bilbao J, Gayubo AG. Upgrading of bio-oil in a continuous process with dolomite catalyst. Energy Fuel. 2014;28:6419–28. https://doi.org/10.1021/ef501600f.
Dorado C, Mullen CA, Boateng AA. H-ZSM5 catalyzed co-pyrolysis of biomass and plastics. ACS Sustain Chem Eng. 2014;2(2):301–11. https://doi.org/10.1021/sc400354g.
Liu SY, Xie QL, Zhang B, Cheng YL, Liu YH, Chen P, Ruan R. Fast microwave-assisted catalytic co-pyrolysis of corn stover and scum for bio-oil production with CaO and HZSM-5 as the catalyst. Bioresour Technol. 2016;204:164–70. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2015.12.085.
Wan S, Wang Y. A review on ex situ catalytic fast pyrolysis of biomass. Front Chem Sci Eng. 2014;8(3):280–94. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11705-014-1436-8.
Galadima A, Muraza O. In situ fast pyrolysis of biomass with zeolite catalysts for bioaromatics/gasoline production: a review. Energ Convers Manag. 2015;105:338–54. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enconman.2015.07.078.
Wang S, Ru B, Lin H. Pyrolysis mechanism of hemicellulose monosaccharides in different catalytic processes. Chem Res Chin Univ. 2014;30(5):848–54. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40242-014-4019-9.
Park YK, Jung JS, Jae J, Hong SB, Watanabe A, Kim Y-M. Catalytic fast pyrolysis of wood plastic composite over microporous zeolites. Chem Eng J. 2019;377:119742. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2018.08.128.
Nguyen TS, Zabeti M, Lefferts L, Brem G, Seshan K. Catalytic upgrading of biomass pyrolysis vapours using faujasite zeolite catalysts. Biomass Bioenergy. 2012;48:100–10. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biombioe.2012.10.024.
Duan D, Wang Y, Dai L, Ruan R, Zhao Y, Fan L, Tayier M, Liu Y. Ex-situ catalytic co-pyrolysis of lignin and polypropylene to upgrade bio-oil quality by microwave heating. Bioresour Technol. 2017;241:207–13. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2017.04.104.
Zhang HY, Zheng J, Xiao R, Shen DK, Jin BS, Xiao GM, Chen R. Co-catalytic pyrolysis of biomass and waste triglyceride seed oil in a novel fluidized bed reactor to produce olefins and aromatics integrated with self-heating and catalyst regeneration processes. RSC Adv. 2013;3:5769–74. https://doi.org/10.1039/c3ra40694f.
Zhang HY, Xiao R, Wang DH, Cho J, He GY, Shao SS, Zhang JB. Hydrodynamics of a novel biomass autothermal fast pyrolysis reactor: solid circulation rate and gas bypassing. Chem Eng J. 2012;181-182:685–93. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2011.12.057.
Bridgwater AV. Fast pyrolysis reactors worldwide. PyNe. 2010;27(1):8–20.
Wu CZ, Yin XL, Yuan ZH. The development of bioenergy technology in China. Energy. 2010;35(11):4445–50. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.energy.2009.04.006.
Epsterin N, Grace JR. Spouted and spout-flmd beds: fundamentals and applications. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press; 2011. https://doi.org/10.1017/CBO9780511777936.011.
Bridgwater AV. Biomass for energy. J Sci Food Agric. 2006;86(12):1755–68. https://doi.org/10.1002/jsfa.2605.
Hayes RD. Biomass pyrolysis technology and products: a Canadian viewpoint. In: Pyrolysis oils from biomass. Washington: American Chemical Society; 1988. https://doi.org/10.1021/bk-1988-0376.ch002.
Galadima A, Muraza O. In situ fast pyrolysis of biomass with zeolite catalysts for bioaromatics/gasoline production: a review. Energy Convers Manag. 2015;105:338–54. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enconman.2015.07.078.
Li F, Choudhari MM, Paredes P. GÃķrtler instability and its control via surface suction over an axisymmetric cone fluid dynamics conference 3069; 2018.
Diebold JP, Czernik S. Additives to lower and stabilize the viscosity of pyrolysis oils during storage. Energy Fuel. 1997;11(5):1081–91. https://doi.org/10.1021/ef9700339.
Zhang W, Yuan C, Xu J. Beneficial synergetic effect on gas production during co-pyrolysis of sewage sludge and biomass in a vacuum reactor. Bioresour Technol. 2015;183:255–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2015.01.113.
Yu F, Deng SB, Chen P, Liu YH, Wan YQ, Olson A, Kittelson D, Ruan R. Physical and chemical properties of bio-oils from microwave pyrolysis of corn stover. Appl Biochem Biotechnol. 2007;136-140:957–70. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-007-9111-x.
Lam SS, Liew RK, Cheng CK, Chase HA. Catalytic microwave pyrolysis of waste engine oil using metallic pyrolysis char. Appl Catal B Environ. 2015;176-177:601–17. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2015.04.014.
Zhang B, Tan GW, Zhong ZP, Ruan R. Microwave-assisted catalytic fast pyrolysis of spent edible mushroom substrate for bio-oil production using surface modified zeolite catalyst. J Anal Appl Pyrolysis. 2017;123:92–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaap.2016.12.022.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2020 Springer Nature Singapore Pte Ltd.
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Zhang, B., Wu, K., Zhang, J., Zhong, S., Zhang, H. (2020). Catalytic Pyrolysis of Lignocellulosic Biomass for Production of Liquid Biofuels. In: Fang, Z., Smith Jr, R.L., Xu, L. (eds) Production of Biofuels and Chemicals with Pyrolysis. Biofuels and Biorefineries, vol 10. Springer, Singapore. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-15-2732-6_6
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-15-2732-6_6
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Singapore
Print ISBN: 978-981-15-2731-9
Online ISBN: 978-981-15-2732-6
eBook Packages: Biomedical and Life SciencesBiomedical and Life Sciences (R0)