Abstract
With the rise of knowledge graph (KG), question answering over knowledge base (KBQA) has attracted increasing attention in recent years. Despite much research has been conducted on this topic, it is still challenging to apply KBQA technology in industry because business knowledge and real-world questions can be rather complicated. In this paper, we present AliMe-KBQA, a bold attempt to apply KBQA in the E-commerce customer service field. To handle real knowledge and questions, we extend the classic “subject-predicate-object (SPO)” structure with property hierarchy, key-value structure and compound value type (CVT), and enhance traditional KBQA with constraints recognition and reasoning ability. We launch AliMe-KBQA in the Marketing Promotion scenario for merchants during the “Double 11” period in 2018 and other such promotional events afterwards. Online results suggest that AliMe-KBQA is not only able to gain better resolution and improve customer satisfaction, but also becomes the preferred knowledge management method by business knowledge staffs since it offers a more convenient and efficient management experience.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Notes
- 1.
We use “QA” to refer to “question answering” and “question-answer” interchangeably.
- 2.
It is worth to mention that nearly a quarter of questions are vague or incomplete in practice.
- 3.
Entity linking is not performed as disambiguation is not necessary in our current scenario.
- 4.
We use an indicator to denote whether the domain (resp. range) of a property need to be inferred (yes:1, no:0), and how it will be inferred (e.g., by following the “member_of” property).
- 5.
The resolution rate rr is calculated as follows:
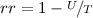 , where U denotes the number of unsolved sessions, which includes disliked sessions, no-answer sessions, and sessions that explicitly requests for staff service, and T stands for the number of total sessions.
, where U denotes the number of unsolved sessions, which includes disliked sessions, no-answer sessions, and sessions that explicitly requests for staff service, and T stands for the number of total sessions. - 6.
Note that the slot “participated goods” is defaulted as “Yes”.
References
Auer, S., Bizer, C., Kobilarov, G., Lehmann, J., Cyganiak, R., Ives, Z.: DBpedia: a nucleus for a web of open data. In: Aberer, K., et al. (eds.) ASWC/ISWC -2007. LNCS, vol. 4825, pp. 722–735. Springer, Heidelberg (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-540-76298-0_52
Bao, J., Duan, N., Yan, Z., Zhou, M., Zhao, T.: Constraint-based question answering with knowledge graph. In: Proceedings of COLING 2016, The 26th International Conference on Computational Linguistics: Technical Papers, pp. 2503–2514 (2016)
Berant, J., Chou, A., Frostig, R., Liang, P.: Semantic parsing on freebase from question-answer pairs. In: Proceedings of the 2013 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing, pp. 1533–1544 (2013)
Berant, J., Liang, P.: Semantic parsing via paraphrasing. In: Proceedings of the 52nd Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics (Volume 1: Long Papers), vol. 1, pp. 1415–1425 (2014)
Bollacker, K., Evans, C., Paritosh, P., Sturge, T., Taylor, J.: Freebase: a collaboratively created graph database for structuring human knowledge. In: Proceedings of the 2008 ACM SIGMOD International Conference on Management of Data, pp. 1247–1250. ACM (2008)
Bordes, A., Chopra, S., Weston, J.: Question answering with subgraph embeddings. arXiv preprint arXiv:1406.3676 (2014)
Bordes, A., Usunier, N., Garcia-Duran, A., Weston, J., Yakhnenko, O.: Translating embeddings for modeling multi-relational data. In: Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, pp. 2787–2795 (2013)
Burges, C.J.: From ranknet to lambdarank to lambdamart: an overview. Learning 11(23–581), 81 (2010)
Dong, L., Wei, F., Zhou, M., Xu, K.: Question answering over freebase with multi-column convolutional neural networks. In: Proceedings of the 53rd Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics and the 7th International Joint Conference on Natural Language Processing (Volume 1: Long Papers), vol. 1, pp. 260–269 (2015)
Kim, Y.: Convolutional neural networks for sentence classification. arXiv preprint arXiv:1408.5882 (2014)
Kwiatkowski, T., Choi, E., Artzi, Y., Zettlemoyer, L.: Scaling semantic parsers with on-the-fly ontology matching. In: Proceedings of the 2013 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing, pp. 1545–1556 (2013)
Lao, N., Mitchell, T., Cohen, W.W.: Random walk inference and learning in a large scale knowledge base. In: Proceedings of the Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing, pp. 529–539. Association for Computational Linguistics (2011)
Li, F.L., et al.: Alime assist: an intelligent assistant for creating an innovative e-commerce experience. In: Proceedings of the 2017 ACM on Conference on Information and Knowledge Management, pp. 2495–2498. ACM (2017)
Lin, Y., Liu, Z., Sun, M., Liu, Y., Zhu, X.: Learning entity and relation embeddings for knowledge graph completion. In: Twenty-Ninth AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence (2015)
Niklaus, C., Cetto, M., Freitas, A., Handschuh, S.: A survey on open information extraction. arXiv preprint arXiv:1806.05599 (2018)
Suchanek, F.M., Kasneci, G., Weikum, G.: Yago: a core of semantic knowledge. In: Proceedings of the 16th International Conference on World Wide Web, pp. 697–706. ACM (2007)
Sun, Y., et al.: Semantic parsing with syntax-and table-aware SQL generation. arXiv preprint arXiv:1804.08338 (2018)
Wang, Z., Zhang, J., Feng, J., Chen, Z.: Knowledge graph embedding by translating on hyperplanes. In: Twenty-Eighth AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence (2014)
Yih, S.W.T., Chang, M.W., He, X., Gao, J.: Semantic parsing via staged query graph generation: Question answering with knowledge base. In: Proceedings of the Joint Conference of the 53rd Annual Meeting of the ACL and the 7th International Joint Conference on Natural Language Processing of the AFNLP (2015)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2019 Springer Nature Singapore Pte Ltd.
About this paper
Cite this paper
Li, FL., Chen, W., Huang, Q., Guo, Y. (2019). AliMe KBQA: Question Answering over Structured Knowledge for E-Commerce Customer Service. In: Zhu, X., Qin, B., Zhu, X., Liu, M., Qian, L. (eds) Knowledge Graph and Semantic Computing: Knowledge Computing and Language Understanding. CCKS 2019. Communications in Computer and Information Science, vol 1134. Springer, Singapore. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-15-1956-7_12
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-15-1956-7_12
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Singapore
Print ISBN: 978-981-15-1955-0
Online ISBN: 978-981-15-1956-7
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)


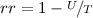 , where U denotes the number of unsolved sessions, which includes disliked sessions, no-answer sessions, and sessions that explicitly requests for staff service, and T stands for the number of total sessions.
, where U denotes the number of unsolved sessions, which includes disliked sessions, no-answer sessions, and sessions that explicitly requests for staff service, and T stands for the number of total sessions.