Abstract
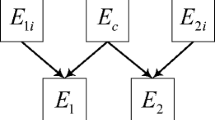
Two dependent evidences can be viewed as resulted from orthogonal sum of one dependent original evidence and two independent original evidences, respectively. The original method has so many iterations and big calculation, based on these disadvantages, a fast combination method for dependent evidences in the framework of hyper-power sets is proposed in this paper. Equipollent classic Dezert-Smarandache (DSm) rule of combination can be got through importing the commonality function, according to the results of model analysis, theorem proving and example comparison show the feasibility and effectiveness of the proposed method.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
He Y, Wang GH, Guan X (2010) Information fusion theory with application. Publish House of Electronics Industry, Beijing
Guan X, Sun GD, Guo Q (2014) Rader emitter parameter recognition based on inter number and evidence theory. Syst Eng Electron 36(7):1269–1274
Guo Q, Guan X, Pan LN, Sun GD (2015) An inference method for evidential networks of multiply connected structure based on mixed parameters and DSmT theory. J CAEIT 10(1):67–74
Fu YW, Yang W, Zhuang ZW (2013) Review on evidence modeling. Syst Eng Electron 35(6):1160–1167
Sun HJ, Yang JY (1999) A combination method for dependent evidences. Chin J Comput 22(9):1004–1007
Wang J, Sun HJ (2009) Model for dependent evidences in DSmT framework. Comput Sci 36(8):260–263
Guo Q, He Y, Li XD (2015) Fast DSmT-DS approximate reasoning method. J Electron Inf Technol 37(9):2040–2046
Liu Z, Pan Q, Dezert J (2014) Credal classification rule for uncertain data based on belief functions. Pattern Recogn 47(7):2532–2541
Abbas N, Chibani Y, Belhadi Z (2013) A DSmT based combination scheme for multi-class classification. In: Proceedings 16th international conference on information FUSION (ICIF), Istanbul, Turkey, July 9–12, pp. 1950–1957
Dezert J, Smarandache F (2015) Advances and applications of DSmT for information fusion. American Research Press, Rehohoth
Guo Q, He Y, Guan X (2015) An evidence clustering DSmT approximate reasoning method based on convex function analysis. Digit Sig Process
Tan Ji-Wen, Zhan Hong, Wen Yan, Zhan Wei-Xia (2014) New method for multiple cues fusion combined DST and DSmT. Inf Technol J 13(2):393–396
Smarandache F., Dezert J., Martin A (2014) An alternative combination rule for evidential reasoning. In: Fusion 2014 Conference, pp. 91–94
Qin D, Miao Z, Wang Y (2014) Improved method based on DSmT and its applications in C4ISR system. J Univ Electron Sci Technol China
Rodríguez RM, Bedregal B, Bustince H (2016) A position and perspective analysis of hesitant fuzzy sets on information fusion in decision making: towards high quality progress. Inf Fusion 29:89–97
Sun GD, Guan X, Yi X, Zhao J (2018) Innovative conflict measurement based on the modified weighted union kernel correlation coefficient. IEEE Access 6:30458–30472
Sun G D, Guan X, Yi X, Zhao J (2018) Belief intervals aggregation. Int J Intell Syst
Duan XS (1993) Evidence theory, decision making and artificial intelligence. China Renmin University Press, Beijing
Wen C, Xu X, Jiang H, Zhou Z (2012) A new DSmT combination rule in open frame of discernment and its application. Sci China Inf Sci 55(3):551–557
Smets P, Kennes R (1992) The concept of distinct evidence. In: Proceedings of the 4th conf on information processing and management of uncertainty in knowledge-based systems (IPMU), pp 789-794
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2019 Springer Nature Singapore Pte Ltd.
About this paper
Cite this paper
Jing, Z., Xin, G., Haiqiao, L. (2019). Fast Combination Method for Dependent Evidences in the Framework of Hyper-Power Sets. In: Zhang, X. (eds) The Proceedings of the 2018 Asia-Pacific International Symposium on Aerospace Technology (APISAT 2018). APISAT 2018. Lecture Notes in Electrical Engineering, vol 459. Springer, Singapore. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-13-3305-7_166
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-13-3305-7_166
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Singapore
Print ISBN: 978-981-13-3304-0
Online ISBN: 978-981-13-3305-7
eBook Packages: EngineeringEngineering (R0)