Abstract
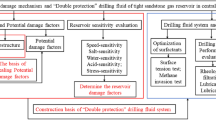
Borehole collapse has always been encountered when drilling the Shiqianfeng and Shihezi formations in Yanchang. It was found that the collapses were due to “double layers of stone” which were brittle, strong, porous, and water sensitive, with a high mineral content within their skeleton particles. Water-locking properties and stress sensitivity are potential factors known to induce wall collapse. To resolve this drilling problem in the Yanchang gas field an anti-sloughing drilling fluid system was devised for use in its “double layer of stone”. The system (complex fluid loss—dual inhibition—materialized block) incorporates a multiple cooperative mechanism of drilling fluid to prevent further drilling collapses. The drilling fluid system developed was applied to Yanchang gas field 645, part of the Shiqianfeng group, and resulted in the Shihezi hole enlargement rates reducing from an average of 22.49 and 22.04% to 15 and 12% respectively, with a filtration rate less than or equal to 5 mL, demonstrating that the drilling fluid system had an obvious anti-collapse effect.
Copyright 2017, Shaanxi Petroleum Society.
This paper was prepared for presentation at the 2017 International Petroleum and Petrochemical Technology Conference in Beijing, China, 20–22 March, 2017.
This paper was selected for presentation by the IFEDC&IPPTC Committee following review of information contained in an abstract submitted by the author(s). Contents of the paper, as presented, have not been reviewed by the IFEDC&IPPTC Committee and are subject to correction by the author(s). The material does not necessarily reflect any position of the IFEDC&IPPTC Committee, its members. Papers presented at the Conference are subject to publication review by Professional Committee of Petroleum Engineering of Shaanxi Petroleum Society. Electronic reproduction, distribution, or storage of any part of this paper for commercial purposes without the written consent of Shaanxi Petroleum Society is prohibited. Permission to reproduce in print is restricted to an abstract of not more than 300 words; illustrations may not be copied. The abstract must contain conspicuous acknowledgment of IFEDC&IPPTC. Contact email: paper@ifedc.org or paper@ipptc.org.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Zhao JZ, Fu J, Yao J, Liu X, Wang H, Cao Q, Wang X (2012) Where the Yuan Fang. ordos basin quasi continuous tight sandstone gas reservoir. Acta Pet Sin S1:37–52
Bai Y, Zhao J, Cao Q, Ear C (2016) A quasi continuous low permeability and tight sandstone reservoir in the Ordos Basin. Oil Gas Geol 06:811–827
Zhengwei J, Xu SS, Dong X, Wang H, Zhang Y, Wu B (2015) Extended field Shiqianfeng group Xiashihezi borehole instability mechanism research. Drill Completion Fluids 01:34–37 + 41 + 99–100
Wu MC, Wang H, Yang M, Qiongjie Y (2010) CB5-2 drilling fluid technology. Drill Completion Fluids 01:79–81 + 94
Alford SE (1991) North sea field application of an environmentally responsible water-base shale stabilizing system model. SPE/IADC 21936, Mar 1991
Li L, Zhu M, Blue Z, Chen Y (2011) Horizontal wells in northern shaanxi yokoyama block fluid technology. Drill Completion Fluids 04:88–90 + 98
Ning Y, Cui Y, Xue B, Mao Y (2009) Ordos basin block gas exploratory drilling technology improvement and application. Drill Completion Fluids 02:126–128 + 140
Xu J, Zhang, Mei C, Deng H, Liu C (2012) Ordos basin in deep drilling technology complex formation. Drill Completion Fluids 02:24–26 + 29 + 91
Tao C, Jin X, Dong H, Li J, Wu X (2011) Sulige gas field full of peach well area 7 horizontal wells deviated and horizontal sections suitable drilling fluid system gas industry, 03:66–69 + 113
Li B, Jia J, Zhang J, Chen En L, Zhao H (2012) Flat peach 1 well drilling technology. Drill Completion Fluids 06:79–81 + 92
Wang Q, Zhou YC, Tang Y, Zhibo J (2012) Shale wellbore stability factors. Rock Mech Eng 01:171–179
Downs JD, van Oort E, Redman DI et al (1993) A new concept in water-based drilling fluids for shales model. SPE 26699, Sept 1993
Aston MS, Elliott GP (1994) Water-based glycol drilling muds: shale inhibition mechanisms model. SPE 28818, Oct 1994
Bol GM, Wong SW, Davidson CJ et al (1994) Borehole stability in shales model. SPE 24975, June 1994
Jie Y (1999) Borehole instability mechanism and the mechanism of anti-collapse of several new anti-sloughing muds. Oilfield Chem 16(2):179–184
Acknowledgements
Thanks to the Xi’an Shi you University. I would especially like to thank my professor Litiantai for a tireless attitude toward research—your attitude moved me. Thank you for your help and support in my study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2019 Springer Nature Singapore Pte Ltd.
About this paper
Cite this paper
Yangying, Litiantai (2019). Research and Applications of Anti-Sloughing Drilling Fluid for the “Double Stone” Layers of the Yanchang Tight Sandstone Gas Field. In: Qu, Z., Lin, J. (eds) Proceedings of the International Field Exploration and Development Conference 2017. Springer Series in Geomechanics and Geoengineering. Springer, Singapore. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-10-7560-5_60
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-10-7560-5_60
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Singapore
Print ISBN: 978-981-10-7559-9
Online ISBN: 978-981-10-7560-5
eBook Packages: EngineeringEngineering (R0)