Abstract
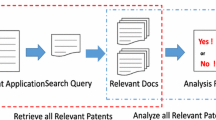
A patent is a legal right given to novel, non-obvious and useful inventions. The prior-art search involves retrieving prior works related to it to avoid duplication of the invention and granting of the patent. Moreover, it analyzes a variety of documents like newspaper articles, proceedings, and journals. The amount of patent document and the volume of filings keep on increasing at an unprecedented rate every year. Processing on this enormous volume of data sequentially is time-consuming. Hence, the proposed Prior-Art Retrieval System (PARS) retrieves only the patent documents through Google patent API, and K-Means clustering was employed in a parallel mode to cluster the documents. Through Relevance Mapping prominent document clusters were identified. The documents within the relevant clusters are ranked based on the citations. The top ranked documents were displayed to the patent analyst.The results show that the processing time with map reduce has reduced significantly and accuracy of clusters was around 50%.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Gaff, Brian M., and Bruce Rubinger.: The significance of prior art. Computer. 8, pp. 9–11 (2014)
Wanagiri, M. Z., Adriani, M.: Prior Art Retrieval Using Various Patent Document Fields Contents. CLEF (Notebook Papers/LABs/Workshops), pp. 1–6, UK (2010)
Xue, X., Croft, W. B.: Automatic query generation for patent search. In: 18th ACM conference on Information and knowledge management, pp. 2037–2040, Germany (2009)
Jun, S., Park, S. S., Jang, D. S. : Document clustering method using dimension reduction and support vector clustering to overcome sparseness. Expert Systems with Applications. 41, 7, 3204–3212 (2014)
Andrews, N. O., and Fox, E. A.: Recent developments in document clustering. Technical Report TR-07-35 (2007)
Huang, S. H., Ke, H. R., Yang, W. P.: Structure clustering for Chinese patent documents. Expert Systems with Applications. 34, 4, 2290–2297 (2008)
Balabantaray, R. C., Sarma, C., Jha, M.: Document Clustering using K-Means and K-Medoids. International Journal of Knowledge Based Computer Systems. 1, 1 (2015)
Bradley, P. S., Fayyad, U. M., Reina, C.: Scaling Clustering algorithms to large databases. In: 4th International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining (KDD-98), pp. 9–15. (1998)
Kriegel, H. P., Kroger, P., Renz, M., Wurst, S.: A generic framework for efficient subspace clustering of high-dimensional data. In: Proceedings of the 5th IEEE International conference on data mining (ICDM), pp 250–257 (2005)
Han, J. and Kamber M.: Data Mining: Concepts and Techniques. Morgan Kaufmann, Elsevier (2011)
Ngazimbi, M.: Data Clustering Using MapReduce. In Masters Thesis, Boise State University (2009)
Sun, T., Shu, C., Li, F., Yu, H., Ma, L., Fang, Y.: An Efficient Hierarchical Clustering Method for Large Datasets with Map-Reduce. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Parallel and Distributed Computing, Applications and Technologies, 12, 2, pp. 494–499 (2009)
Wang, S., Dutta, H.: PARABLE: A PArallel RAndom-partition Based HierarchicaL ClustEring Algorithm for the MapReduce Framework. In: 6th Annual Machine Learning Symposium at the New York Academy of Science. (2011)
Zhao, W., Ma, H.,He, Q.: Parallel K-means Clustering Based on MapReduce. In: IEEE International Conference on Cloud Computing, pp. 674–679 (2009)
Kang, I. S., Na, S. H., Kim, J., Lee, J. H.: Cluster-based patent retrieval. Information processing & management, 43, 5, 1173–1182 (2007)
Aleman-Meza, B., Arpinar, I. B., Nural, M. V., Sheth, A. P.: Ranking documents semantically using ontological relationships. In: 4th International Conference on semantic computing, pp. 299–304, US (2010)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2018 Springer Nature Singapore Pte Ltd.
About this paper
Cite this paper
Girthana, K., Swamynathan, S. (2018). Efficient Prior-Art Retrieval of Patent Documents Using MapReduce Paradigm. In: Mandal, J., Saha, G., Kandar, D., Maji, A. (eds) Proceedings of the International Conference on Computing and Communication Systems. Lecture Notes in Networks and Systems, vol 24. Springer, Singapore. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-10-6890-4_70
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-10-6890-4_70
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Singapore
Print ISBN: 978-981-10-6889-8
Online ISBN: 978-981-10-6890-4
eBook Packages: EngineeringEngineering (R0)