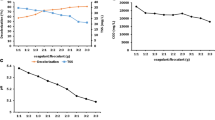
Abstract
Black liquor is one of the main by-products of the pretreatment process in bioethanol production from empty oil palm fruit bunches, with a high chemical oxygen demand (COD) and low dissolved oxygen (DO). The effect of FeSO4 as a coagulant and FeSO4–H2O2 for Fenton on the degradation of black liquor was examined. This study also identified the ability of a fungus to decolorize black liquor wastewater after the Fenton process and on original black liquor. One percent ferrous sulfate decolorized 84% of black liquor with a concentration of 30,000 ppm under the coagulation method. By adding H2O2 and FeSO4 through the Fenton process, decolorization of the original black liquor was approximately 52%. Combining Fenton and polyaluminum chloride decolorized black liquor up to 90% in 33 min, whereas Coriolus versicolor decolorized 54% and 75% Fenton-treated black liquor and original black liquor after 15 days, respectively.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alvira P, Tomás-Pejó E, Ballesteros M, Negro MJ (2010) Pretreatment technologies for an efficient bioethanol production process based on enzymatic hydrolysis: a review. Bioresour Technol 101:4851–4861
APHA-AWWA-WEF (2005) Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater, 21st edn. American Publishing Health Association, American Water Works Association and Water Environment Federation, New York
Araujo E, Rodrigues-Malaver AJ, Gonzalez AM, Rojas OJ, Penaloza N, Bullon J, Lara MA, Dmitrieva N (2002) Fenton’s reagent-mediated degradation of residual kraft black liquor. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 97:91–103
Bryant CW, Barkley WA, Garett RM, Gardner FD (1997) Biological nitrification of kraft wastewater. Water Sci Technol 35(2–3):147–153
Choudhury S, Sahoo N, Manthan M, Rohela RS (1998) Fungal treatment of pulp and paper mill effluents for pollution control. J Ind Pollut Control 14(1):1–13
Ciputra S, Antony A, Phillips R, Richardson D, Leslie G (2010) Comparison of treatment options for removal of recalcitrant dissolved organic matter from paper mill effluent. Chemosphere 81:86–91
Cundy AB, Hopkinson L, Whitby RLD (2008) Use of iron-based technologies in contaminated land and groundwater remediation: a review. Sci Total Environ 400:42–51
Da Re V, Papinutti L (2011) Black liquor decolorization by selected white-rot fungi. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 165(2):406–415
De Pinho MN, Minhalma M, Rosa MJ, Taborda F (2000) Integration of flotation/ultrafiltration for treatment of bleached pulp effluent. Pulp Pap Can 104(4):50–54
Dube M, McLean R, MacLatchy D, Savage P (2000) Reverse osmosis treatment: effects on effluent quality. Pulp Pap Can 101(8):42–45
El-Dein M, Libra A, Wiesmann JA (2001) Kinetics of decolorization and mineralization of the azo dye reactive black 5 by hydrogen peroxide and UV light. Water Sci Technol 44(5):295–301
Fernandes L, Lucas MS, Maldonado MI, Oller I, Sampaio A (2014) Treatment of pulp mill wastewater by Cryptococcus podzolicus and solar photo-Fenton: a case study. Chem Eng J 245:158–165
Freitas AC, Ferreira F, Costa AM, Pereira R, Antunes SC, Goncalves F, Rochasantos TAP, Diniz MS, Castro L, Peres I, Duarte AC (2009) Biological treatment of the effluent from a bleached kraft pulp mill using basidiomycete and zygomycete fungi. Sci Total Environ 407:3282–3289
Ghaly MY, Jamil TS, El-seesy IE, Souaya ER, Nasr RA (2011) Treatment of highly polluted paper mill wastewater by solar photocatalytic oxidation with synthesized nanoTiO2. Chem Eng J 168:446–454
Hadibarata T, Yusoff ARM, Kristanti RA (2012) Decolorization and metabolism of anthraquinone-type dye by laccase of white rot fungi Polyporus sp. S133. Water Air Soil Pollut 223:933–941
Irfan M, Butt T, Imtiaz N, Abbas N, Khan RA, Shafique A (2013) The removal of COD, TSS and colour of black liquor by coagulation–flocculation process at optimized pH, settling and dosing rate. Arab J Chem. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.arabjc.2013.08.007
Jackson-Moss CA, Maree JP, Wotton SC (1992) Treatment of bleach plant effluent with the biological granular activated carbon process. Water Sci Technol 26(1–2):427–434
Kamali M, Khodaparast Z (2015) Review on recent developments on pulp and paper mill wastewater treatment. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 114:326–342
Kang SF, Chang HM (1997) Coagulation of textile secondary effluents with Fenton’s reagent. Water Sci Technol 36(12):215–222
Kiiskinen LL, Ratto M, Kruus K (2004) Screening for novel laccase-producing microbes. J Appl Microbiol 97(3):640–646
Kristiani A, Effendi N, Styarini D, Aulia F, Sudiyani Y (2016) The effect of pretreatment by using electron beam irradiation on oil palm empty fruit bunch. Atom Indonesia 42(1):9–12
Lucas MS, Peres JA, Amor C, Prieto-rodriguez L, Maldonado MI (2012) Tertiary treatment of pulp mill wastewater by solar photo-Fenton. J Hazard Mater 225–226:173–181
Mehna A, Bajpai P, Bajpai PK (1995) Studies on decolorization of eluent from a small pulp mill utilizing agriresidues with Trametes versicolor. Enzym Microb Technol 17:18–22
Mosier N, Wyman C, Dale B, Elander R, Lee YY, Holtzapple M, Ladisch M (2005) Features of promising technologies for pretreatment of lignocellulosic biomass. Bioresour Technol 96:673–686
Pari G, Sofyan K, Syafii W (2003) Buchari. The properties of charcoal from the black liquor of the soda pulping of rice straw. Jurnal Teknologi Hasil Hutan 16(2):70–79
Poggi-Varaldo HM, Estrada-Vazquez C, Fernandez-Villagomez G, Esparza-Garcia F (1996) Pretreatment of black liquors spills effluent. In: Proceedings of the industrial waste conference, West Lafayette, vol 51, pp 651–661
Reid TK, Simon A (2000) Feasibility study of sequencing batch reactor technology treating high strength foul condensate for methanol reduction. In: Tappi international environmental conference and exhibit, vol 1, pp 185–191
Sahu OP, Chaudhari PK (2013) Review on chemical treatment of industrial waste water. J Appl Sci Environ Manag 17(2):241–257
Sanghi R, Bhattacharya B, Dixit A, Singh V (2006) Ipomoea dasysperma seed gum: an effective natural coagulant for the decolorization of textile dye solutions. J Environ Manag 81:36–41
Sari AA, Tachibana S (2012) Muryanto. Correlation of ligninolytic enzymes from the newly-found species Trametes versicolor U97 with RBBR decolorization and DDT degradation. Water Air Soil Pollut 223(9):5781–5792
Sari AA, Kristiani A, Tachibana S, Sudiyani Y, Abimanyu H (2014) Mechanisms and optimization of oil palm empty fruit bunch as a pre-grown source for white-rot fungus to degrade DDT. J Environ Chem Eng 2:1410–1415
Sari AA, Kurniawan HH, Nurdin M, Abimanyu H (2015) Decolorization of black liquor wastewater generated from bioethanol process by using oil palm empty fruit bunches. Energy Procedia 68:254–262
Sari AA, Muryanto M, Waluyo J, Wiloso EI (2017) Life cycle assessment comparison of Fenton and Fenton-like for wastewater treatment in second generation bioethanol production. In: Proceedings of the 2nd ILCAN conference series on Life cycle assessment, vol 2, pp 27–31
Shankar R, Singh L, Mondal P, Chand S (2013) Removal of lignin from wastewater through electro-coagulation. World J Environ Eng 1:16–20
Sudiyani Y, Triwahyuni E, Muryanto M, Burhani D, Waluyo J, Sulaswaty A, Abimanyu H (2016) Alkaline pretreatment of sweet sorghum bagasse for bioethanol production. J Renew Energy Dev 5(2):113–118
Taherzadeh MJ, Karimi K (2008) Pretreatment of lignocellulosic wastes to improve ethanol and biogas production: a review. Int J Mol Sci 5:337–353
Taseli B, Gokcay CF (1999) Biological treatment of paper pulping effluents by using a fungal reactor. Water Sci Technol 40(11–12):93–99
Wang J, Chen Y, Wang Y, Yuan S, Yu H (2011) Optimization of the coagulation-flocculation process for pulp mill wastewater treatment using a combination of uniform design and response surface methodology. Water Res 45:5633–5640
Acknowledgments
This research was partly supported by the Program Insentif Riset Sistem Inovasi Nasional (Insinas) – Ministry of Research, Technology and Higher Education Fiscal Year 2015–2017. We thank Mr. Nick V for language editing and proofreading this manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2018 Springer Nature Singapore Pte Ltd.
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Sari, A.A., Kristiani, A., Kurniawan, H.H., Anggraini, R.I.F. (2018). The Potency of Fenton-Polyaluminum Chloride for Black Liquor Treatment. In: McLellan, B. (eds) Sustainable Future for Human Security . Springer, Singapore. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-10-5430-3_7
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-10-5430-3_7
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Singapore
Print ISBN: 978-981-10-5429-7
Online ISBN: 978-981-10-5430-3
eBook Packages: Earth and Environmental ScienceEarth and Environmental Science (R0)