Abstract
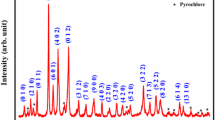
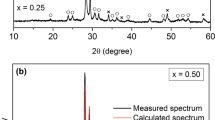
(Bi1-xFex)NbO4 powders with 0.00 ≤ x ≤ 0.75 were prepared by a wet-chemical route. Pellets from these powders were made and sintered at temperatures between 500 and 1100 °C. The dielectric properties were analyzed as a function of the thermally activated structural and morphologic evolution. The structure was studied by X-ray diffraction (XPD) and the morphology by scanning electron microscopy (SEM). The XRD results revealed that the substitution of bismuth by iron was successful for x = 0.25 and 0.50, with the formation of the non-stoichiometric phases Bi1.34Fe0.66Nb1.34O6.35 and Bi1.721Fe1.056Nb1.134O7. The dielectric properties were measured by impedance spectroscopy method in the frequency range of 102–106 Hz as a function of temperature (200–330 K). For the samples with x ≥ 0.25 treated at 800 and 1100 °C, the dielectric constant and the dielectric losses remain practically constant with the frequency and temperature. The dielectric relaxation mechanisms were studied using the complex modulus formalism.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Filho RC, Araújo JH, Ginani MF, D’Assunção AG Jr, Martins RA, D’Assunção AG, Mendonça LM (2010) Simulation and measurement of inset‐fed microstrip patch antennas on BiNbO4 substrates. Microw Opt Technol Lett 52:1034
Freire FNA, Santos MRP, Pereira FMM, Sohn RSTM, Almeida JS, Medeiros AML, Sancho EO, Costa MM, Sombra ASB (2009) Studies of the temperature coefficient of capacitance (TCC) of a new electroceramic composite: Pb(Fe0.5Nb0.5)O3 (PFN)–Cr0.75Fe1.25O3(CRFO). J Mater Sci Mater Electron 20:149
Butee S, Kulkarni AR, Prakash O, Aiyar RPRC, Sudheendran K, Raju KCJ (2010) Effect of lanthanide ion substitution on RF and microwave dielectric properties of BiNbO4 ceramics. J Alloys Compd 492:351
Savina AA, Atuchin VV, Solodovnikov SF, Solodovnikova ZA, Krylov AS, Maximovskiy EA, Molokeev MS, Oreshonkov AS, Pugachev AM, Khaikina EG (2015) Synthesis, structural and spectroscopic properties of acentric triple molybdate Cs2NaBi(MoO4)3. J Solid State Chem 225:53
Rao KS, Buddhudu S (2010) Structural, Thermal and Dielectric Properties of BiNbO4 Ceramic Powder. Ferroelectr Lett 37:101
Mohan R, Leonard N, Wieland L (2002) Applications of bismuth (III) compounds in organic synthesis. Tetrahedron 58:8373
Yang N, Sun H (2007) Biocoordination chemistry of bismuth: Recent advances. Coord Chem Rev 251:2354
Shihua D, Xi Y, Yu M, Puling L (2006) Microwave dielectric properties of (Bi1−xRx)NbO4 ceramics (R=Ce, Nd, Dy, Er). J Eur Ceram Soc 26:2003
Litimein F, Khenata R, Gupta SK, Murtaza G, Reshak AH, Bouhemadou A, Omran SB, Yousaf M, Jha PK (2014) Structural, electronic, and optical properties of orthorhombic and triclinic BiNbO4 determined via DFT calculations. J Mater Sci 49:7809
Radha R, Muthurajan H, Koteswara Rao N, Sivaram, Pradhan, Gupta UN, Jha RK, Mirji SA, Ravi V (2008) Low temperature synthesis and characterization of BiNbO4 powders. Mater Charact 59:1083
Xu C, He D, Liu C, Wang H, Zhang L, Wang P, Yin S (2013) High pressure and high temperature study the phase transitions of BiNbO4. Solid State Commun 156:21
Zhou D, Wang H, Yao X, Wei X, Xiang F, Pang L (2007) Phase transformation in BiNbO4 ceramics. Appl Phys Lett 90:172910
Kagata H, Inoue T, Kato J, Kameyama I (1992) Low-fire bismuth-based dielectric ceramics for microwave use. Jpn J Appl Phys 31:3152
Devesa S, Graça MP, Costa LC (2018) Dielectric Properties of Bismuth Niobate Ceramics. In: Zhou Y, Dong F, Jin S (eds) Bismuth: advanced applications and defects characterization. IntechOpen, London, p 93
Alquier C, Vandenborre MT, Henry M (1986) Synthesis of niobium pentoxide gels. J Non-Cryst Solids 79:383
Almeida JS, Fernandes TS, Sales AJ, Silva MA, Júnior GF, Rodrigues HO, Sombra AS (2011) Study of the structural and dielectric properties of Bi2O3 and PbO addition on BiNbO4 ceramic matrix for RF applications. J Mater Sci Mater Electron 22:978
Devesa S, Graça MP, Henry F, Costa LC (2016) Dielectric properties of FeNbO4 ceramics prepared by the sol-gel method. Solid State Sci 61:44
Lee BW, Abothu IR, Raj PM, Yoon CK, Tummala RR (2006) Tailoring of temperature coefficient of capacitance (TCC) in nanocomposite capacitors. Scr Mater 54:1231
Czekaj D, Czekaj AL, Adamczyk M (2014) Influence of bismuth content on complex Immittance characteristics of Pressureless sintered BiNbO4 ceramics. Arch Metall Mater 59:225
Belattar CBJ, Graça MPF, Costa LC, Achour ME (2010) Electric modulus-based analysis of the dielectric relaxation in carbon black loaded polymer composites. J Appl Phys 107:124111
Tsangaris NKGM, Psarras GC (1998) Electric modulus and interfacial polarization in composite polymeric systems. J Mater Sci 33:2027
Saltas V, Triantis D, Manios T, Vallianatos F (2007) Biomonitoring of environmental pollution using dielectric properties of tree leaves. Environ Monit Assess 133:69
Wojnarowska Z, Knapik J, Díaz M, Ortiz A, Ortiz I, Paluch M (2014) Conductivity Mechanism in Polymerized Imidazolium-Based Protic Ionic Liquid [HSO3–BVIm][OTf]: Dielectric Relaxation Studies. Macromolecules 47:4056
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2020 Springer Nature B.V.
About this paper
Cite this paper
Devesa, S., Graça, M.P., Costa, L.C. (2020). Dielectric Characterization of (Bi1-xFex)NbO4 Ceramics Prepared by Wet-Chemical Route. In: Petkov, P., Achour, M., Popov, C. (eds) Nanoscience and Nanotechnology in Security and Protection against CBRN Threats. NATO Science for Peace and Security Series B: Physics and Biophysics. Springer, Dordrecht. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-94-024-2018-0_9
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-94-024-2018-0_9
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Dordrecht
Print ISBN: 978-94-024-2044-9
Online ISBN: 978-94-024-2018-0
eBook Packages: Physics and AstronomyPhysics and Astronomy (R0)