Abstract
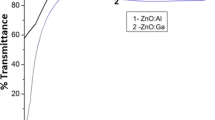
Structural, optical and electrical properties of ZnO thin films doped with different elements (Al, Al + H, V, Nb), deposited by r.f. magnetron sputtering on glass substrates at different temperature Ts between 50 and 500 °C are studied. XRD spectra demonstrate a preferential (002) crystallographic orientation with the c-axis perpendicular to the substrate surface and grains sizes of about 19–29 nm. The value of band gap energy Eg is in the range of 3.49–3.58 eV for ZnO:Al, 3.51–3.58 eV for ZnO:Al:H, 3.44–3.47 eV for ZnO:V, and 3.28–3.44 eV for ZnO:Nb. The deposited ZnO films doped with Al, H, V and Nb have low resistivities of 1.6–2.2⋅10−3 Ωcm. The transparency of the studied films is about 85–90 % in the visible region. The obtained transparent conductive ZnO thin films can be applied in solar cells and other optoelectronic devices as TCO.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Li Y, Gong J, McCune M, He G, Deng Y (2010) Synth Met 160:499
Seshadri R (2005) Curr Opinion Solid State Mater Sci 9:1
Minami T (2005) Semicond Sci Technol 20:S35
Koshizaki N, Oyama T (2000) Sensors Actuators B 66:119
Saeki H, Tabata H, Kawai T (2001) Solid State Commun 120:439
Fukumura T, Jin Z, Ohtomo A, Koinuma H, Kawasaki M (2000) Appl Phys Lett 75:3366
Yin Z, Chen N, Yang F, Song S, Chai C, Zhong J, Qian H, Ibrahim K (2005) Solid State Commun 135:430
Dimova-Malinovska D, Angelov O, Nichev H, Kamenova M, Pivin JC (2007) J Optoelectron Adv Mater 9:2512
Pankove J (1971) Optical processes in semiconductors. Prentice-Hall, Inc., Englewood Cliffs
Dragoman D, Dragoman M (2002) Optical characterization of solids. Springer, Heidelberg
Girtan M, Folsher G (2003) Surf Coat Technol 172:242
Swanepoel R (1983) J Phys E Sci Instrum 16:1214
Van der Walle GC (2000) Phys Rev Lett 85:1012
Mollwo E (1954) Z Phys 138:478
Seraphin BO (1979) Solar energy conversion. Springer, Berlin/Heidelberg
Roth A, Williams D (1981) J Appl Phys 52:6685
Lovchinov K, Nichev H, Angelov O, Sendova-Vassileva M, Dimova-Malinovska D, Mikli V (2010) J Phys Conf Ser 253:012030
Dimova-Malinovska D, Nichev H, Angelov O (2009) Phys Status Solidi 5:3353
Burstein E (1954) Phys Rev 93:632
Mott N, Davis E (1979) Electronic processes in noncrystalline materials. Oxford, Clarendon, p 289
Saito N (1985) J Appl Phys 58:3504
Miyata T, Suzuki S, Ishii M, Minami T (2002) Thin Solid Films 411:76
Hickenell FS (1975) J Vac Sci Technol 12:879
Dimova-Malinovska D, Nichev H, Angelov O, Grigorov V, Kamenova M (2007) Superlattice Microst 42:123
Tzolov M, Tzenov N, Dimova-Malinovska D, Kalitzova M, Pizzuto C, Vitali G, Zollo G, Ivanov I (2000) Thin Solid Films 379:28
Ke X, Zou C, Li M, Liu C, Guo L, Fu D (2010) Jpn J Appl Phys 49:033001
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2015 Springer Science+Business Media Dordrecht
About this paper
Cite this paper
Lovchinov, K., Petrov, M., Angelov, O., Nichev, H., Mikli, V., Dimova-Malinovska, D. (2015). Structural, Optical and Electrical Properties of ZnO Thin Films Doped with Al, V and Nb, Deposited by r.f. Magnetron Sputtering. In: Petkov, P., Tsiulyanu, D., Kulisch, W., Popov, C. (eds) Nanoscience Advances in CBRN Agents Detection, Information and Energy Security. NATO Science for Peace and Security Series A: Chemistry and Biology. Springer, Dordrecht. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-94-017-9697-2_29
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-94-017-9697-2_29
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Dordrecht
Print ISBN: 978-94-017-9696-5
Online ISBN: 978-94-017-9697-2
eBook Packages: Biomedical and Life SciencesBiomedical and Life Sciences (R0)