Abstract
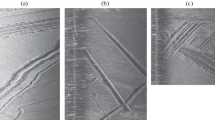
Distinctive surficial morphology (Fig. 1) and stratification are generated when sea-ice keels are driven along the seabed in the Beaufort Sea (Fig. 2). The morphology consists of linear ice-gouge furrows that criss-cross extensive shallow shelves in overlapping patterns (Fig. 3). Intense ice gouging in the Arctic is associated with the stamukhi zone [Reimnitz and Barnes, 1974], where sea-ice ridges form and are grounded on the shelf between 15–50 m water depth. Ice gouges in the Beaufort Sea typically are incised 1 m into the sea floor with maximum incisions over 4 m deep, relief of over 7 m and densities greater than 200 km-2 [Barnes et al., 1984]. The orientations and terminations of ice gouges indicate oblique uphill scouring as well as strong shore-parallel movement. Sea-floor morphology linked to studies of ice motion at Barrow, Alaska (Fig. 4) support the idea that gouging occurred during ice break-up [Shapiro and Barnes, 1991]. In contrast, investigations of ice-gouge terminations off Canada indicate ice-push events resulted from ice motion in response to storms during freeze-up [Héquette et al.,1995].
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barnes, P., D. Rearic, and E. Reimnitz, Ice gouging characteristics and processes: In, The Alaskan Beaufort Sea - Ecosystems and Environments, edited by P. Barnes, D. Schell and E. Reimnitz, Academic Press, Orlando, FL, 185–213, 1984.
Héquette, A., M. Desrosiers, and P. Barnes, Ice scouring and onshore sediment transport on the inner shelf of the Canadian Beaufort Sea: Marine Geology, 1995.
Rearic, D., E. Reimnitz, and P. Barnes, Bulldozing and resuspension of shallow-shelf sediment by ice keels: Implications for Arctic sediment transport: Marine Geology, 91, 133–1, 1990.
Reimnitz, E. and P. Barnes, Sea ice as a geologic agent on the Beaufort Sea shelf of Alaska: In, The Coast and Shelf of the Beaufort Sea, edited by J. Reed, and J. Sater, Arctic Inst. of No. Amer., Arlington, VA, 301–351, 1974.
Shapiro, L. and P. Barnes, Correlation of nearshore ice movement with seabed ice gouges near Barrow, Alaska: Journal of Geophysical Research, 96, 16,979–16, 989, 1991.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 1997 Chapman & Hall
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Barnes, P.W., Reimnitz, E. (1997). Arctic Ice Gouging and Ice Keel Turbates. In: Davies, T.A., et al. Glaciated Continental Margins. Springer, Dordrecht. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-94-011-5820-6_60
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-94-011-5820-6_60
Publisher Name: Springer, Dordrecht
Print ISBN: 978-0-412-79340-0
Online ISBN: 978-94-011-5820-6
eBook Packages: Springer Book Archive